The jakoLista() metoda Java.util.Arrays class służy do zwracania listy o stałym rozmiarze, opartej na określonej tablicy. Metoda ta działa jak pomost pomiędzy interfejsami API opartymi na tablicach i kolekcjach , w połączeniu z Collection.toArray(). Zwróconą listę można serializować i implementuje RandomAccess.
Wskazówka: Działa to w czasie O(1).
Składnia:
public static List asList(T... a)>
Parametry: Ta metoda wymaga tablica a który należy przekształcić w listę. Tutaj… jest znany jako vararg która jest tablicą parametrów i działa podobnie do parametru tablicy obiektów.
algorytm Kruskala
Specjalna notatka: Typ tablicy musi być klasą opakowującą (Integer, Float itp.) w przypadku pierwotnych typów danych (int, float itp.), tj. nie możesz przekazać int a[], ale możesz przekazać Integer a[]. Jeśli przekażesz int a[], ta funkcja zwróci List, a nie List, ponieważ w tym przypadku autoboxing nie ma miejsca, a int a[] sam jest identyfikowany jako obiekt i zwracana jest Lista tablicy int zamiast listy liczb całkowitych, co spowoduje błąd w różnych funkcjach zbierających.
Wartość zwracana: Ta metoda zwraca a widok listy określonej tablicy.
Przykład 1:
Jawa
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class for a string value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of String type> >String a[]> >=>new> String[] {>'A'>,>'B'>,>'C'>,>'D'> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements in list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statement> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Wyjście
usługi sieciowe Java
The list is: [A, B, C, D]>
Przykład 2:
Jawa
// Java program to Demonstrate asList() method> // of Arrays class For an integer value> // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Printing all the elements inside list object> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (NullPointerException e) {> >// Print statements> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Wyjście
The list is: [10, 20, 30, 40]>
Przykład 3:
Jawa
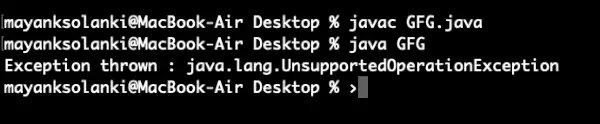
// Java Program to demonstrate asList() method> // Which returns fixed size list and> // throws UnsupportedOperationException> // if any element is added using add() method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] argv)>throws> Exception> >{> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Creating Arrays of Integer type> >Integer a[] =>new> Integer[] {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40> };> >// Getting the list view of Array> >List list = Arrays.asList(a);> >// Adding another int to the list> >// As Arrays.asList() returns fixed size> >// list, we'll get> >// java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException> >list.add(>50>);> >// Printing all the elements of list> >System.out.println(>'The list is: '> + list);> >}> >// Catch block to handle exceptions> >catch> (UnsupportedOperationException e) {> >// Display message when exception occurs> >System.out.println(>'Exception thrown : '> + e);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>
Wyjście:
drzewo avl