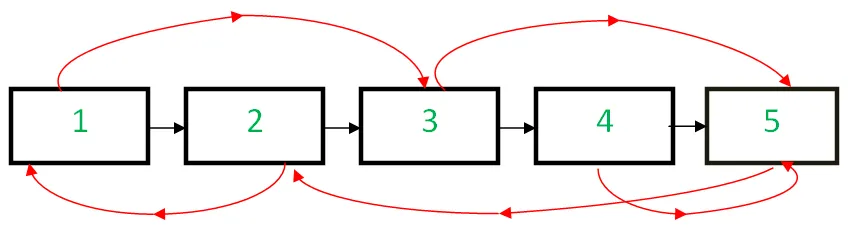
Biorąc pod uwagę A połączona lista wielkościowy N gdzie każdy węzeł ma dwa łącza: następny wskaźnik wskazując na następny węzeł i losowy wskaźnik do dowolnego losowego węzła na liście. Zadanie polega na utworzeniu klonu tej połączonej listy w przestrzeni O(1), tj. bez dodatkowej przestrzeni.
Przykłady:
Wejście: Szef poniższej połączonej listy
sznurek do niego
Wyjście: Nowa lista połączona, identyczna z listą oryginalną.
znaczenie xdxd
[Podejście oczekiwane] Poprzez wstawienie węzłów na miejscu – czas O(3n) i przestrzeń O(1)
Pomysł polega na utworzeniu duplikatu węzła i zamiast przechowywać go w osobnej tabeli mieszającej, możemy wstawić go pomiędzy pierwotnym węzłem a następnym węzłem. Teraz będziemy mieli nowe węzły w alternatywnych pozycjach. Teraz dla węzeł X będzie jego duplikat X->dalej i losowy wskaźnik duplikatu powinien wskazywać X->losowe->dalej (ponieważ jest to duplikat X->losowe ). Zatem wykonaj iterację po całej połączonej liście, aby zaktualizować losowy wskaźnik wszystkich sklonowanych węzłów, a następnie wykonaj iterację ponownie, aby oddzielić oryginalną połączoną listę od sklonowanej połączonej listy.
Aby wdrożyć pomysł, wykonaj kroki wymienione poniżej:
- Utwórz kopię węzeł 1 i włóż go pomiędzy węzeł 1 I węzeł 2 na oryginalnej liście połączonej utwórz kopię węzeł 2 i włóż go pomiędzy 2 II I 3 rd węzeł i tak dalej. Dodaj kopię N po Ntwęzeł
- Połącz węzeł klonowania, aktualizując losowe wskaźniki.
- Oddziel sklonowaną listę połączoną od oryginalnej listy, aktualizując kolejne wskaźniki.
indeks_podciągu w sql
Poniżej znajduje się implementacja powyższego podejścia:
C++// C++ code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place #include
// Java code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node { int data; Node next random; Node(int x) { data = x; next = random = null; } } class GfG { // Function to clone the linked list static Node cloneLinkedList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } // Create new nodes and insert them next to the original nodes Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Node newNode = new Node(curr.data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr != null) { if (curr.random != null) { curr.next.random = curr.random.next; } curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; Node clonedHead = head.next; Node clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next != null) { // Update the next nodes of original node // and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original and cloned // linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list public static void printList(Node head) { while (head != null) { System.out.print(head.data + '('); if (head.random != null) { System.out.print(head.random.data); } else { System.out.print('null'); } System.out.print(')'); if (head.next != null) { System.out.print(' -> '); } head = head.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; // Print the original list System.out.println('Original linked list:'); printList(head); // Function call Node clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); System.out.println('Cloned linked list:'); printList(clonedList); } }
# Python code to Clone a linked list with next and random # pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.random = None # Function to clone the linked list def clone_linked_list(head): if head is None: return None # Create new nodes and insert them next to # the original nodes curr = head while curr is not None: new_node = Node(curr.data) new_node.next = curr.next curr.next = new_node curr = new_node.next # Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head while curr is not None: if curr.random is not None: curr.next.random = curr.random.next curr = curr.next.next # Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head cloned_head = head.next clone = cloned_head while clone.next is not None: # Update the next nodes of original node # and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next clone.next = clone.next.next # Move pointers of original as well as # cloned linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next clone = clone.next curr.next = None clone.next = None return cloned_head # Function to print the linked list def print_list(head): while head is not None: print(f'{head.data}(' end='') if head.random: print(f'{head.random.data})' end='') else: print('null)' end='') if head.next is not None: print(' -> ' end='') head = head.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Creating a linked list with random pointer head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) head.random = head.next.next head.next.random = head head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next # Print the original list print('Original linked list:') print_list(head) # Function call cloned_list = clone_linked_list(head) print('Cloned linked list:') print_list(cloned_list)
// C# code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Node { public int Data; public Node next Random; public Node(int x) { Data = x; next = Random = null; } } class GfG { static Node CloneLinkedList(Node head) { if (head == null) return null; // Create new nodes and insert them next to // the original nodes Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Node newNode = new Node(curr.Data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr != null) { if (curr.Random != null) curr.next.Random = curr.Random.next; curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; Node clonedHead = head.next; Node clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next != null) { // Update the next nodes of original node // and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original as well as // cloned linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list static void PrintList(Node head) { while (head != null) { Console.Write(head.Data + '('); if (head.Random != null) Console.Write(head.Random.Data + ')'); else Console.Write('null)'); if (head.next != null) Console.Write(' -> '); head = head.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } public static void Main() { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.Random = head.next.next; head.next.Random = head; head.next.next.Random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.Random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.Random = head.next; // Print the original list Console.WriteLine('Original linked list:'); PrintList(head); Node clonedList = CloneLinkedList(head); Console.WriteLine('Cloned linked list:'); PrintList(clonedList); } }
// JavaScript code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } function cloneLinkedList(head) { if (head === null) { return null; } // Create new nodes and insert them next to the // original nodes let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { let newNode = new Node(curr.data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr !== null) { if (curr.random !== null) { curr.next.random = curr.random.next; } curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; let clonedHead = head.next; let clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next !== null) { // Update the next nodes of original node and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original as well as cloned // linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list function printList(head) { let result = ''; while (head !== null) { result += head.data + '('; result += head.random ? head.random.data : 'null'; result += ')'; if (head.next !== null) { result += ' -> '; } head = head.next; } console.log(result); } // Creating a linked list with random pointer let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; // Print the original list console.log('Original linked list:'); printList(head); let clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); console.log('Cloned linked list:'); printList(clonedList);
Wyjście
Original linked list: 1(3) -> 2(1) -> 3(5) -> 4(3) -> 5(2) Cloned linked list: 1(3) -> 2(1) -> 3(5) -> 4(3) -> 5(2)
Złożoność czasowa: O(3n) ponieważ trzykrotnie przeglądamy połączoną listę.
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(1) ponieważ przechowujemy wszystkie sklonowane węzły na oryginalnej liście połączonej, nie jest wymagana dodatkowa przestrzeń.