 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
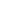
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }Biorąc pod uwagę A Drzewo binarne przekonwertuj go na Okrągła lista podwójnie połączona (Na miejscu).
- Lewe i prawe wskaźniki w węzłach mają być używane odpowiednio jako wskaźniki poprzedniego i następnego w przekonwertowanej cyklicznej liście połączonej.
- Kolejność węzłów na Liście musi być taka sama jak w Inorder dla danego Drzewa Binarnego.
- Pierwszy węzeł przejścia Inorder musi być węzłem głównym listy kołowej.
Przykłady:
Zalecana praktyka Drzewo binarne do CDLL Spróbuj!
Konwertuj drzewo binarne na listę cyklicznych podwójnych łączy za pomocą rekurencji:
Pomysł polega na stworzeniu funkcji ogólnego przeznaczenia, która połączy dwie podane cykliczne listy typu double
Aby rozwiązać problem, wykonaj poniższe czynności:
- Rekursywnie przekonwertuj lewe poddrzewo na cykliczną bibliotekę DLL. Niech przekonwertowana lista będzie lewa lista .
- Rekursywnie przekonwertuj prawe poddrzewo na cykliczną bibliotekę DLL. Niech przekonwertowana lista będzie prawa lista .
- Utwórz okrągłą połączoną listę korzeni drzewa i połącz lewy i prawy punkt główny ze sobą.
- Powiązać lewa lista z listą pojedynczego węzła głównego.
- Połącz listę utworzoną w powyższym kroku z prawa lista .
Notatka: Powyższe podejście przebiega przez drzewo w sposób postorder. Możemy przemierzać również w sposób nieuporządkowany. Możemy najpierw połączyć lewe poddrzewo i korzeń, a następnie powtórzyć to dla prawego poddrzewa i połączyć wynik za pomocą konkatenacji lewego korzenia.
Jak połączyć dwie okrągłe biblioteki DLL?
- Pobierz ostatni węzeł lewej listy. Pobranie ostatniego węzła jest operacją O(1), ponieważ poprzedni wskaźnik nagłówka wskazuje na ostatni węzeł listy.
- Połącz go z pierwszym węzłem prawej listy
- Pobierz ostatni węzeł drugiej listy
Poniżej realizacje powyższego pomysłu:
C++// C++ Program to convert a Binary Tree // to a Circular Doubly Linked List #include
// C Program to convert a Binary Tree // to a Circular Doubly Linked List #include
// Java Program to convert a Binary Tree to a // Circular Doubly Linked List // Node class represents a Node of a Tree class Node { int val; Node left right; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; left = right = null; } } // A class to represent a tree class Tree { Node root; public Tree() { root = null; } // concatenate both the lists and returns the head // of the List public Node concatenate(Node leftList Node rightList) { // If either of the list is empty then // return the other list if (leftList == null) return rightList; if (rightList == null) return leftList; // Store the last Node of left List Node leftLast = leftList.left; // Store the last Node of right List Node rightLast = rightList.left; // Connect the last node of Left List // with the first Node of the right List leftLast.right = rightList; rightList.left = leftLast; // left of first node refers to // the last node in the list leftList.left = rightLast; // Right of last node refers to the first // node of the List rightLast.right = leftList; // Return the Head of the List return leftList; } // Method converts a tree to a circular // Link List and then returns the head // of the Link List public Node bTreeToCList(Node root) { if (root == null) return null; // Recursively convert left and right subtrees Node left = bTreeToCList(root.left); Node right = bTreeToCList(root.right); // Make a circular linked list of single node // (or root). To do so make the right and // left pointers of this node point to itself root.left = root.right = root; // Step 1 (concatenate the left list with the list // with single node i.e. current node) // Step 2 (concatenate the returned list with the // right List) return concatenate(concatenate(left root) right); } // Display Circular Link List public void display(Node head) { System.out.println('Circular Linked List is :'); Node itr = head; do { System.out.print(itr.val + ' '); itr = itr.right; } while (itr != head); System.out.println(); } } // Driver Code class Main { public static void main(String args[]) { // Build the tree Tree tree = new Tree(); tree.root = new Node(10); tree.root.left = new Node(12); tree.root.right = new Node(15); tree.root.left.left = new Node(25); tree.root.left.right = new Node(30); tree.root.right.left = new Node(36); // head refers to the head of the Link List Node head = tree.bTreeToCList(tree.root); // Display the Circular LinkedList tree.display(head); } }
# Python3 Program to convert a Binary # Tree to a Circular Doubly Linked List class newNode: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.left = self.right = None # A function that appends rightList # at the end of leftList. def concatenate(leftList rightList): # If either of the list is empty # then return the other list if (leftList == None): return rightList if (rightList == None): return leftList # Store the last Node of left List leftLast = leftList.left # Store the last Node of right List rightLast = rightList.left # Connect the last node of Left List # with the first Node of the right List leftLast.right = rightList rightList.left = leftLast # Left of first node points to # the last node in the list leftList.left = rightLast # Right of last node refers to # the first node of the List rightLast.right = leftList return leftList # Function converts a tree to a circular # Linked List and then returns the head # of the Linked List def bTreeToCList(root): if (root == None): return None # Recursively convert left and # right subtrees left = bTreeToCList(root.left) right = bTreeToCList(root.right) # Make a circular linked list of single # node (or root). To do so make the # right and left pointers of this node # point to itself root.left = root.right = root # Step 1 (concatenate the left list # with the list with single # node i.e. current node) # Step 2 (concatenate the returned list # with the right List) return concatenate(concatenate(left root) right) # Display Circular Link List def displayCList(head): print('Circular Linked List is :') itr = head first = 1 while (head != itr or first): print(itr.data end=' ') itr = itr.right first = 0 print() # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': root = newNode(10) root.left = newNode(12) root.right = newNode(15) root.left.left = newNode(25) root.left.right = newNode(30) root.right.left = newNode(36) head = bTreeToCList(root) displayCList(head) # This code is contributed by PranchalK
// C# Program to convert a Binary Tree // to a Circular Doubly Linked List using System; // Node class represents a Node of a Tree public class Node { public int val; public Node left right; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; left = right = null; } } // A class to represent a tree public class Tree { internal Node root; public Tree() { root = null; } // concatenate both the lists // and returns the head of the List public virtual Node concatenate(Node leftList Node rightList) { // If either of the list is empty // then return the other list if (leftList == null) { return rightList; } if (rightList == null) { return leftList; } // Store the last Node of left List Node leftLast = leftList.left; // Store the last Node of right List Node rightLast = rightList.left; // Connect the last node of Left List // with the first Node of the right List leftLast.right = rightList; rightList.left = leftLast; // left of first node refers to // the last node in the list leftList.left = rightLast; // Right of last node refers to // the first node of the List rightLast.right = leftList; // Return the Head of the List return leftList; } // Method converts a tree to a circular // Link List and then returns the head // of the Link List public virtual Node bTreeToCList(Node root) { if (root == null) { return null; } // Recursively convert left // and right subtrees Node left = bTreeToCList(root.left); Node right = bTreeToCList(root.right); // Make a circular linked list of single // node (or root). To do so make the // right and left pointers of this node // point to itself root.left = root.right = root; // Step 1 (concatenate the left list with // the list with single node // i.e. current node) // Step 2 (concatenate the returned list // with the right List) return concatenate(concatenate(left root) right); } // Display Circular Link List public virtual void display(Node head) { Console.WriteLine('Circular Linked List is :'); Node itr = head; do { Console.Write(itr.val + ' '); itr = itr.right; } while (itr != head); Console.WriteLine(); } } // Driver Code public class GFG { public static void Main(string[] args) { // Build the tree Tree tree = new Tree(); tree.root = new Node(10); tree.root.left = new Node(12); tree.root.right = new Node(15); tree.root.left.left = new Node(25); tree.root.left.right = new Node(30); tree.root.right.left = new Node(36); // head refers to the head of the Link List Node head = tree.bTreeToCList(tree.root); // Display the Circular LinkedList tree.display(head); } } // This code is contributed by Shrikant13
<script> // javascript Program to convert a Binary Tree to a // Circular Doubly Linked List // Node class represents a Node of a Tree class Node { constructor(val) { this.val = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // A class to represent a var root = null; // concatenate both the lists and returns the head // of the List function concatenate(leftList rightList) { // If either of the list is empty then // return the other list if (leftList == null) return rightList; if (rightList == null) return leftList; // Store the last Node of left List var leftLast = leftList.left; // Store the last Node of right List var rightLast = rightList.left; // Connect the last node of Left List // with the first Node of the right List leftLast.right = rightList; rightList.left = leftLast; // left of first node refers to // the last node in the list leftList.left = rightLast; // Right of last node refers to the first // node of the List rightLast.right = leftList; // Return the Head of the List return leftList; } // Method converts a to a circular // Link List and then returns the head // of the Link List function bTreeToCList(root) { if (root == null) return null; // Recursively convert left and right subtrees var left = bTreeToCList(root.left); var right = bTreeToCList(root.right); // Make a circular linked list of single node // (or root). To do so make the right and // left pointers of this node point to itself root.left = root.right = root; // Step 1 (concatenate the left list with the list // with single node i.e. current node) // Step 2 (concatenate the returned list with the // right List) return concatenate(concatenate(left root) right); } // Display Circular Link List function display(head) { document.write('Circular Linked List is :
'); var itr = head; do { document.write(itr.val + ' '); itr = itr.right; } while (itr != head); document.write(); } // Driver Code // Build the root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(12); root.right = new Node(15); root.left.left = new Node(25); root.left.right = new Node(30); root.right.left = new Node(36); // head refers to the head of the Link List var head = bTreeToCList(root); // Display the Circular LinkedList display(head); // This code contributed by umadevi9616 </script>
Wyjście
Circular Linked List is : 25 12 30 10 36 15
Złożoność czasowa: NA) Ponieważ każdy węzeł jest odwiedzany co najwyżej raz.
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(log N) Dodatkowa przestrzeń jest używana w stosie wywołań rekurencji, który może urosnąć do maksymalnego rozmiaru logN, ponieważ jest to drzewo binarne.
Konwertuj drzewo binarne na cykliczną listę podwójnych łączy za pomocą Inorder Traversal:
Pomysł polega na tym, aby przeglądać drzewo binarne w określonej kolejności. Wykonując przechodzenie w kolejności, śledź poprzednio odwiedzony węzeł w zmiennej powiedz poprzednie . Dla każdego odwiedzonego węzła ustaw go jako następny z poprzednie i ustaw poprzedni tego węzła jako poprzednie .
Aby rozwiązać problem, wykonaj poniższe czynności:
- Najpierw przekonwertuj drzewo binarne na listę podwójnie połączoną, patrz ten post Konwertuj dane drzewo binarne na listę podwójnie połączoną .
- Teraz przekonwertuj tę listę podwójnie połączoną na cykliczną listę podwójnie połączoną, łącząc pierwszy i ostatni węzeł.
Poniżej implementacja powyższego podejścia.
C++// A C++ program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to // CDLL #include
// A Java program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to // CDLL // A binary tree node has - data left pointer and right // pointer class Node { int data; Node left right; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; left = right = null; } } class BinaryTree { Node root; // head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly // linked list Node head; // Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is // static so that the same value is accessible in all // recursive calls static Node prev = null; // A simple utility recursive function to convert a // given Binary tree to Doubly Linked List root --> Root // of Binary Tree void BTree2DoublyLinkedList(Node root) { // Base case if (root == null) return; // Recursively convert left subtree BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root.left); // Now convert this node if (prev == null) head = root; else { root.left = prev; prev.right = root; } prev = root; // Finally convert right subtree BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root.right); } // A simple function to convert a given binary tree to // Circular doubly linked list // using a utility function void BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(Node root) { BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root); // make the changes to convert a DLL to CDLL prev.right = head; head.left = prev; } /* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */ void printList(Node node) { if (node == null) return; Node curr = node; do { System.out.print(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.right; } while (curr != node); } // Driver program to test above functions public static void main(String[] args) { // Let us create the tree as shown in above diagram BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); tree.root = new Node(10); tree.root.left = new Node(12); tree.root.right = new Node(15); tree.root.left.left = new Node(25); tree.root.left.right = new Node(30); tree.root.right.left = new Node(36); // convert to DLL tree.BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(tree.root); // Print the converted List tree.printList(tree.head); } } // This code has been contributed by Abhijeet // Kumar(abhijeet19403)
# A python program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to DLL # A binary tree node has data left pointers and right pointers class Node: def __init__(self val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None # head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly linked list head = None # Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is # so that the same value is accessible in all recursive # calls prev = None # A simple recursive function to convert a given Binary tree # to Doubly Linked List # root --> Root of Binary Tree def BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root): # Base case if (root == None): return # Recursively convert left subtree BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.left) # Now convert this node global prev head if (prev == None): head = root else: root.left = prev prev.right = root prev = root # Finally convert right subtree BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.right) # Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list def printList(node): while (node != None): print(node.data) node = node.right # Driver program to test above functions # Let us create the tree as shown in above diagram root = Node(10) root.left = Node(12) root.right = Node(15) root.left.left = Node(25) root.left.right = Node(30) root.right.left = Node(36) # convert to DLL BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root) # Print the converted List printList(head) # This code is contributed by adityamaharshi21.
// A C# program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to // CDLL using System; public class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; left = right = null; } } public class BinaryTree { Node root; // head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly // linked list Node head; // Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is // static so that the same value is accessible in all // recursive calls static Node prev = null; // A simple utility recursive function to convert a // given Binary tree to Doubly Linked List root --> Root // of Binary Tree void BTree2DoublyLinkedList(Node root) { // Base case if (root == null) return; // Recursively convert left subtree BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root.left); // Now convert this node if (prev == null) head = root; else { root.left = prev; prev.right = root; } prev = root; // Finally convert right subtree BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root.right); } // A simple function to convert a given binary tree to // Circular doubly linked list // using a utility function void BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(Node root) { BTree2DoublyLinkedList(root); // make the changes to convert a DLL to CDLL prev.right = head; head.left = prev; } /* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */ void printList(Node node) { if (node == null) return; Node curr = node; do { Console.Write(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.right; } while (curr != node); } static public void Main() { // Let us create the tree as shown in above diagram BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); tree.root = new Node(10); tree.root.left = new Node(12); tree.root.right = new Node(15); tree.root.left.left = new Node(25); tree.root.left.right = new Node(30); tree.root.right.left = new Node(36); // convert to DLL tree.BTree2CircularDoublyLinkedList(tree.root); // Print the converted List tree.printList(tree.head); } } // This code is contributed by lokesh(lokeshmvs21).
// A javascript program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to DLL // A binary tree node has data left pointers and right pointers class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } var root; // head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly linked list var head; // Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is // so that the same value is accessible in all recursive // calls var prev = null; // A simple recursive function to convert a given Binary tree // to Doubly Linked List // root --> Root of Binary Tree function BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root) { // Base case if (root == null) return; // Recursively convert left subtree BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.left); // Now convert this node if (prev == null) head = root; else { root.left = prev; prev.right = root; } prev = root; // Finally convert right subtree BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.right); } /* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */ function printList(node) { while (node != null) { console.log(node.data + ' '); node = node.right; } } // Driver program to test above functions // Let us create the tree as shown in above diagram root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(12); root.right = new Node(15); root.left.left = new Node(25); root.left.right = new Node(30); root.right.left = new Node(36); // convert to DLL BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root); // Print the converted List printList(head); // This code is contributed by ishankhandelwals.
Wyjście
25 12 30 10 36 15
Złożoność czasowa: O(N) Ponieważ każdy węzeł jest odwiedzany najwyżej raz.
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(log N) Dodatkowa przestrzeń jest wykorzystywana w stosie wywołań funkcji rekurencyjnych, który może urosnąć do maksymalnego rozmiaru logN.
Do takiego podejścia przyczynił się m.in Abhijeeta Kumara
