Biorąc pod uwagę proste drzewo wyrażeń składające się z podstawowych operatorów binarnych tj. + - * i / oraz niektórych liczb całkowitych oceniają drzewo wyrażeń.
Przykłady:
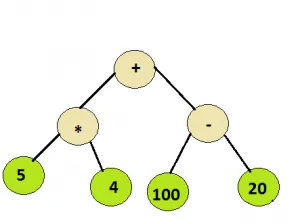
Zalecana praktyka Drzewo wyrażeń Spróbuj!Wejście: Węzeł główny poniższego drzewa
Wyjście: 100
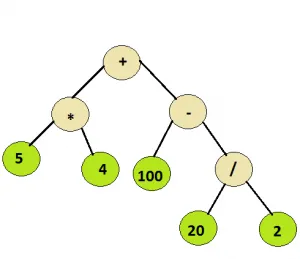
Wejście: Węzeł główny poniższego drzewa
zwracanie tablicy Java
Wyjście: 110
Zbliżać się: Podejście do rozwiązania tego problemu opiera się na następujących obserwacjach:
Ponieważ wszystkie operatory w drzewie są binarne, każdy węzeł będzie miał 0 lub 2 dzieci. Jak można wywnioskować z powyższych przykładów, wszystkie wartości całkowite pojawią się w węzłach liści, podczas gdy węzły wewnętrzne reprezentują operatory.
Dlatego możemy to zrobić wewnętrzne przechodzenie przez drzewo binarne i oceń wyrażenie w miarę dalszych postępów.
Aby ocenić drzewo składni, można zastosować podejście rekurencyjne.
Algorytm:
- Niech t będzie drzewem składni
- Jeśli t nie ma wartości null, to
- Jeśli t.info jest operandem, to
- Wróć do t.info
- W przeciwnym razie
- A = rozwiązanie (t.lewo)
- B = rozwiązanie (t.po prawej)
- return A operator B, gdzie operator jest informacją zawartą w t
Poniżej implementacja powyższego podejścia:
C++// C++ program to evaluate an expression tree #include
// Java program to evaluate expression tree import java.lang.*; class GFG{ Node root; // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree public static class Node { String data; Node left right; Node(String d) { data = d; left = null; right = null; } } private static int toInt(String s) { int num = 0; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if (s.charAt(0) != '-') for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) num = num * 10 + ((int)s.charAt(i) - 48); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for(int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) num = num * 10 + ((int)(s.charAt(i)) - 48); num = num * -1; } return num; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it public static int evalTree(Node root) { // Empty tree if (root == null) return 0; // Leaf node i.e an integer if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return toInt(root.data); // Evaluate left subtree int leftEval = evalTree(root.left); // Evaluate right subtree int rightEval = evalTree(root.right); // Check which operator to apply if (root.data.equals('+')) return leftEval + rightEval; if (root.data.equals('-')) return leftEval - rightEval; if (root.data.equals('*')) return leftEval * rightEval; return leftEval / rightEval; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a sample tree Node root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('-4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('20'); System.out.println(evalTree(root)); root = null; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('/'); root.right.right.left = new Node('20'); root.right.right.right = new Node('2'); System.out.println(evalTree(root)); } } // This code is contributed by Ankit Gupta
# Python program to evaluate expression tree # Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree class node: def __init__(self value): self.left = None self.data = value self.right = None # This function receives a node of the syntax tree # and recursively evaluate it def evaluateExpressionTree(root): # empty tree if root is None: return 0 # leaf node if root.left is None and root.right is None: return int(root.data) # evaluate left tree left_sum = evaluateExpressionTree(root.left) # evaluate right tree right_sum = evaluateExpressionTree(root.right) # check which operation to apply if root.data == '+': return left_sum + right_sum elif root.data == '-': return left_sum - right_sum elif root.data == '*': return left_sum * right_sum else: return left_sum // right_sum # Driver function to test above problem if __name__ == '__main__': # creating a sample tree root = node('+') root.left = node('*') root.left.left = node('5') root.left.right = node('-4') root.right = node('-') root.right.left = node('100') root.right.right = node('20') print (evaluateExpressionTree(root)) root = None # creating a sample tree root = node('+') root.left = node('*') root.left.left = node('5') root.left.right = node('4') root.right = node('-') root.right.left = node('100') root.right.right = node('/') root.right.right.left = node('20') root.right.right.right = node('2') print (evaluateExpressionTree(root)) # This code is contributed by Harshit Sidhwa
// C# program to evaluate expression tree using System; public class GFG { // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree public class Node { public String data; public Node left right; public Node(String d) { data = d; left = null; right = null; } } private static int toInt(String s) { int num = 0; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if (s[0] != '-') for (int i = 0; i < s.Length; i++) num = num * 10 + ((int) s[i] - 48); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for (int i = 1; i < s.Length; i++) num = num * 10 + ((int) (s[i]) - 48); num = num * -1; } return num; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it public static int evalTree(Node root) { // Empty tree if (root == null) return 0; // Leaf node i.e an integer if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return toInt(root.data); // Evaluate left subtree int leftEval = evalTree(root.left); // Evaluate right subtree int rightEval = evalTree(root.right); // Check which operator to apply if (root.data.Equals('+')) return leftEval + rightEval; if (root.data.Equals('-')) return leftEval - rightEval; if (root.data.Equals('*')) return leftEval * rightEval; return leftEval / rightEval; } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { // Creating a sample tree Node root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('-4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('20'); Console.WriteLine(evalTree(root)); root = null; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('/'); root.right.right.left = new Node('20'); root.right.right.right = new Node('2'); Console.WriteLine(evalTree(root)); } } // This code is contributed by umadevi9616
<script> // javascript program to evaluate expression tree var root; // Class to represent the nodes of syntax tree class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function toInt( s) { var num = 0; // Check if the integral value is // negative or not // If it is not negative generate // the number normally if (s.charAt(0) != '-') for (i = 0; i < s.length; i++) num = num * 10 + ( s.charCodeAt(i) - 48); // If it is negative calculate the +ve number // first ignoring the sign and invert the // sign at the end else { for (i = 1; i < s.length; i++) num = num * 10 + (s.charCodeAt(i) - 48); num = num * -1; } return num; } // This function receives a node of the syntax // tree and recursively evaluate it function evalTree(root) { // Empty tree if (root == null) return 0; // Leaf node i.e an integer if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return toInt(root.data); // Evaluate left subtree var leftEval = evalTree(root.left); // Evaluate right subtree var rightEval = evalTree(root.right); // Check which operator to apply if (root.data === ('+')) return leftEval + rightEval; if (root.data === ('-')) return leftEval - rightEval; if (root.data === ('*')) return leftEval * rightEval; return leftEval / rightEval; } // Driver code // Creating a sample tree var root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('-4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('20'); document.write(evalTree(root)); root = null; // Creating a sample tree root = new Node('+'); root.left = new Node('*'); root.left.left = new Node('5'); root.left.right = new Node('4'); root.right = new Node('-'); root.right.left = new Node('100'); root.right.right = new Node('/'); root.right.right.left = new Node('20'); root.right.right.right = new Node('2'); document.write('
'+evalTree(root)); // This code is contributed by gauravrajput1 </script>
Wyjście
60 110
Złożoność czasowa: O(n), ponieważ każdy węzeł jest odwiedzany raz.
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: NA)