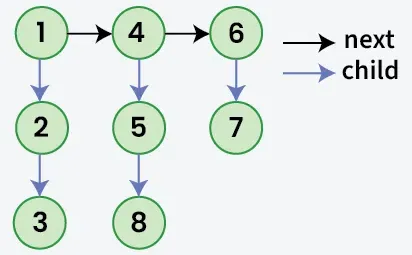
Biorąc pod uwagę połączoną listę, gdzie oprócz Następny wskaźnik, każdy węzeł ma dziecko wskaźnik, który może, ale nie musi, wskazywać na oddzielną listę. Te listy podrzędne mogą mieć jeden lub więcej własne dzieci, aby wyprodukować a wielopoziomowy połączona lista. Biorąc pod uwagę głowa z pierwszy poziom z listy. Zadanie polega na spłaszczyć listę, tak aby wszystkie węzły pojawiły się w a jednopoziomowy połączona lista. Spłaszcz listę w taki sposób, aby wszystkie węzły w pierwszy poziom powinien przyjść Pierwszy następnie węzły drugi poziom i tak dalej.
Przykłady:
Wejście:
Wyjście: 1->4->6->2->5->7->3->8
Wyjaśnienie: Wielopoziomowa lista połączona jest spłaszczona, ponieważ nie zawiera wskaźników podrzędnych.
Omówiliśmy spłaszczenie wielopoziomowej listy połączonej gdzie węzły mają dwa wskaźniki w dół i dalej. W poprzednim poście my spłaszczony połączona lista na poziomie. Jak spłaszczyć połączoną listę, gdy zawsze musimy przetworzyć plik wskaźnik w dół przed następnym w każdym węźle.
Spis treści
- [Podejście oczekiwane] Korzystanie z rekurencji - O(n) czasu i O(n) przestrzeni
- [Podejście alternatywne] Korzystanie ze stosu - O(n) czasu i O(n) przestrzeni
[Podejście oczekiwane] Korzystanie z rekurencji - O(n) czasu i O(n) przestrzeni
C++Podejście jest takie rekurencyjnie spłaszczyć A połączone wielopoziomowo list, przechodząc przez każdy węzeł i jego węzły podrzędne. Pierwszy spłaszcz listę podrzędną za pomocą rekurencji. Po spłaszczeniu listy podrzędnej przejdź do następny węzeł w sekwencji. Podczas przemierzania utrzymuj a odniesienie do poprzednio odwiedzany węzeł i połącz go z bieżącym węzłem. Proces ten gwarantuje, że wszystkie węzły z różnych poziomów zostaną połączone w jedną całość pojedyncza lista liniowa zachowując jednocześnie porządek w głębi.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise #include
// A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { int data; Node next down; Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void flattenList(Node curr Node[] prev) { if (curr == null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev[0] != null) prev[0].next = curr; prev[0] = curr; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList(curr.down prev); // Recursively add the next list flattenList(next prev); } static void printList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { System.out.print(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); Node[] prev = new Node[1]; flattenList(head prev); printList(head); } }
# A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.down = None def flatten_list(curr prev): if curr is None: return # Add the current element to the list. if prev[0] is not None: prev[0].next = curr prev[0] = curr # Store the next pointer next_node = curr.next # Recursively add the bottom list flatten_list(curr.down prev) # Recursively add the next list flatten_list(next_node prev) def print_list(head): curr = head while curr is not None: print(curr.data end=' ') curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node(5) head.down = Node(7) head.down.down = Node(8) head.down.down.down = Node(30) head.next = Node(10) head.next.next = Node(19) head.next.next.down = Node(22) head.next.next.down.down = Node(50) head.next.next.next = Node(28) prev = [None] flatten_list(head prev) print_list(head)
// A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next down; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList(Node curr ref Node prev) { if (curr == null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list FlattenList(curr.down ref prev); // Recursively add the next list FlattenList(next ref prev); } static void PrintList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Console.Write(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); Node prev = null; FlattenList(head ref prev); PrintList(head); } }
// A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; this.down = null; } } function flattenList(curr prev) { if (curr === null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev[0] !== null) prev[0].next = curr; prev[0] = curr; // Store the next pointer let next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList(curr.down prev); // Recursively add the next list flattenList(next prev); } function printList(head) { let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { console.log(curr.data); curr = curr.next; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); let prev = [null]; flattenList(head prev); printList(head);
Wyjście
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28
[Podejście alternatywne] Korzystanie ze stosu - O(n) czasu i O(n) przestrzeni
C++Podejście polega na przechodzeniu przez wielopoziomowa lista połączona za pomocą stos . Zacznij od popychanie the węzeł główny na stos. Następnie podczas stos nie jest pusty muzyka pop górny węzeł i przetwarzaj go. Dla każdego węzła naciskać jego wskaźniki Dalej i W dół (jeśli istnieją) na stos. Podczas tego procesu połącz bieżący węzeł z poprzednim węzłem utrzymywanie listy w spłaszczonej formie. Przejście zapewnia, że węzły ze wszystkich poziomów są połączone w a jednopoziomowa lista połączona zachowując porządek w głębi.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack #include
// A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack import java.util.Stack; class Node { int data; Node next down; Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void flattenList(Node head) { if (head == null) return; Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(head); Node prev = null; while (!stack.isEmpty()) { Node curr = stack.pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next != null) stack.push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down != null) stack.push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } static void printList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { System.out.print(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); flattenList(head); printList(head); } }
# A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise using stack class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.down = None def flatten_list(head): if head is None: return stack = [head] prev = None while stack: curr = stack.pop() # Push the next node first if curr.next: stack.append(curr.next) # Push the bottom node into stack if curr.down: stack.append(curr.down) # Add the current element to the list if prev: prev.next = curr prev = curr def print_list(head): curr = head while curr: print(curr.data end=' ') curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node(5) head.down = Node(7) head.down.down = Node(8) head.down.down.down = Node(30) head.next = Node(10) head.next.next = Node(19) head.next.next.down = Node(22) head.next.next.down.down = Node(50) head.next.next.next = Node(28) flatten_list(head) print_list(head)
// A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node next down; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList(Node head) { if (head == null) return; Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); stack.Push(head); Node prev = null; while (stack.Count > 0) { Node curr = stack.Pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next != null) stack.Push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down != null) stack.Push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } static void PrintList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Console.Write(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); FlattenList(head); PrintList(head); } }
// A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; this.down = null; } } function flattenList(head) { if (head === null) return; let stack = [head]; let prev = null; while (stack.length > 0) { let curr = stack.pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next !== null) stack.push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down !== null) stack.push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev !== null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } function printList(head) { let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { console.log(curr.data); curr = curr.next; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); flattenList(head); printList(head);
Wyjście
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28