 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }Mając dane drzewo binarne, znajdź długość najdłuższej ścieżki składającej się z węzłów z kolejnymi wartościami w kolejności rosnącej. Każdy węzeł jest uważany za ścieżkę o długości 1.
Przykłady:
In below diagram binary tree with longest consecutive path(LCP) are shown :
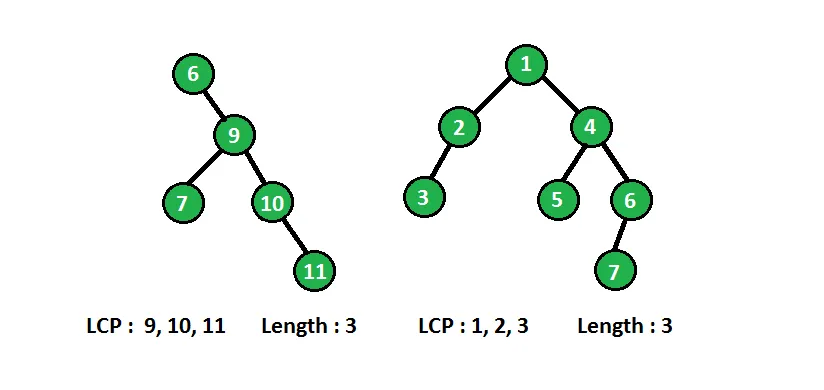
Powyższy problem możemy rozwiązać rekurencyjnie. W każdym węźle potrzebujemy informacji o jego węźle nadrzędnym, jeśli bieżący węzeł ma wartość o jeden większą niż jego węzeł nadrzędny, wówczas tworzy kolejną ścieżkę w każdym węźle. Porównamy wartość węzła z jego wartością nadrzędną i odpowiednio zaktualizujemy najdłuższą kolejną ścieżkę.
Aby uzyskać wartość węzła nadrzędnego, przekażemy (wartość_węzła + 1) jako argument do metody rekurencyjnej i porównamy wartość węzła z tą wartością argumentu, jeśli jest ona zgodna, zaktualizuj bieżącą długość kolejnej ścieżki, w przeciwnym razie ponownie zainicjuj bieżącą długość ścieżki o 1.
Aby lepiej zrozumieć, zobacz poniższy kod:
C++// C/C++ program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree #include
// Java program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class Result { int res = 0; } class BinaryTree { Node root; // method returns length of longest consecutive // sequence rooted at node root int longestConsecutive(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; Result res = new Result(); // call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res); return res.res; } // Utility method to return length of longest // consecutive sequence of tree private void longestConsecutiveUtil(Node root int curlength int expected Result res) { if (root == null) return; // if root data has one more than its parent // then increase current length if (root.data == expected) curlength++; else curlength = 1; // update the maximum by current length res.res = Math.max(res.res curlength); // recursively call left and right subtree with // expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curlength root.data + 1 res); longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curlength root.data + 1 res); } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); tree.root = new Node(6); tree.root.right = new Node(9); tree.root.right.left = new Node(7); tree.root.right.right = new Node(10); tree.root.right.right.right = new Node(11); System.out.println(tree.longestConsecutive(tree.root)); } } // This code is contributed by shubham96301
# Python3 program to find longest consecutive # sequence in binary tree # A utility class to create a node class newNode: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.left = self.right = None # Utility method to return length of # longest consecutive sequence of tree def longestConsecutiveUtil(root curLength expected res): if (root == None): return # if root data has one more than its # parent then increase current length if (root.data == expected): curLength += 1 else: curLength = 1 # update the maximum by current length res[0] = max(res[0] curLength) # recursively call left and right subtree # with expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curLength root.data + 1 res) longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curLength root.data + 1 res) # method returns length of longest consecutive # sequence rooted at node root def longestConsecutive(root): if (root == None): return 0 res = [0] # call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res) return res[0] # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': root = newNode(6) root.right = newNode(9) root.right.left = newNode(7) root.right.right = newNode(10) root.right.right.right = newNode(11) print(longestConsecutive(root)) # This code is contributed by PranchalK
// C# program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class Result { public int res = 0; } class GFG { Node root; // method returns length of longest consecutive // sequence rooted at node root int longestConsecutive(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; Result res = new Result(); // call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res); return res.res; } // Utility method to return length of longest // consecutive sequence of tree private void longestConsecutiveUtil(Node root int curlength int expected Result res) { if (root == null) return; // if root data has one more than its parent // then increase current length if (root.data == expected) curlength++; else curlength = 1; // update the maximum by current length res.res = Math.Max(res.res curlength); // recursively call left and right subtree with // expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curlength root.data + 1 res); longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curlength root.data + 1 res); } // Driver code public static void Main(String []args) { GFG tree = new GFG(); tree.root = new Node(6); tree.root.right = new Node(9); tree.root.right.left = new Node(7); tree.root.right.right = new Node(10); tree.root.right.right.right = new Node(11); Console.WriteLine(tree.longestConsecutive(tree.root)); } } // This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
<script> // JavaScript program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree class Node { constructor(item) { this.data=item; this.left = this.right = null; } } let res = 0; let root; function longestConsecutive(root) { if (root == null) return 0; res=[0]; // call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res); return res[0]; } // Utility method to return length of longest // consecutive sequence of tree function longestConsecutiveUtil(rootcurlength expectedres) { if (root == null) return; // if root data has one more than its parent // then increase current length if (root.data == expected) curlength++; else curlength = 1; // update the maximum by current length res[0] = Math.max(res[0] curlength); // recursively call left and right subtree with // expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curlength root.data + 1 res); longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curlength root.data + 1 res); } // Driver code root = new Node(6); root.right = new Node(9); root.right.left = new Node(7); root.right.right = new Node(10); root.right.right.right = new Node(11); document.write(longestConsecutive(root)); // This code is contributed by rag2127 </script>
Wyjście
3
Złożoność czasowa: O(N), gdzie N jest liczbą węzłów w danym drzewie binarnym.
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(log(N))
Omówiono również pod poniższym linkiem:
Maksymalna rosnąca długość ścieżki w drzewie binarnym
