Jaki jest najniższy wspólny przodek w drzewie binarnym?
The najniższy wspólny przodek jest najniższym węzłem w drzewie, który ma zarówno n1, jak i n2 as potomków, gdzie n1 i n2 to węzły, dla których chcemy znaleźć LCA. Zatem LCA drzewa binarnego z węzłami n1 i n2 jest wspólnym przodkiem n1 i n2, który jest położony najdalej od korzenia.
Zastosowanie najniższego wspólnego przodka (LCA):
Aby określić odległość między parami węzłów w drzewie: odległość od n1 do n2 można obliczyć jako odległość od korzenia do n1 plus odległość od korzenia do n2 minus dwukrotność odległości od korzenia do ich najniższej wspólnej przodek.
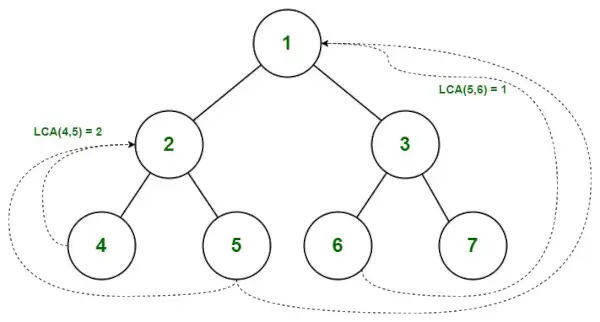
Najniższy wspólny przodek w drzewie binarnym
Zalecana praktyka Najniższy wspólny przodek w drzewie binarnym Spróbuj!
Najniższy wspólny przodek w drzewie binarnym poprzez przechowywanie ścieżek od korzenia do n1 i korzenia do n2:
Ideą tego podejścia jest przechowywanie ścieżki od korzenia do n1 i korzenia do n2 w dwóch oddzielnych strukturach danych. Następnie spójrz jednocześnie na wartości przechowywane w strukturze danych i poszukaj pierwszej niezgodności.
Ilustracja:
Znajdź LCA 5 i 6
Ścieżka od korzenia do 5 = { 1, 2, 5 }
Ścieżka od korzenia do 6 = { 1, 3, 6 }
- Sprawdzanie zaczynamy od indeksu 0. Gdy obie wartości pasują (ścieżkaA[0] = ścieżkaB[0]), przechodzimy do następnego indeksu.
- ścieżkaA[1] nie jest równa ścieżkaB[1], występuje niezgodność, więc bierzemy pod uwagę poprzednią wartość.
- Dlatego LCA (5,6) = 1
Aby rozwiązać problem, wykonaj poniższe czynności:
- Znajdź ścieżkę od korzenia do n1 i zapisz ją w wektorze lub tablicy.
- Znajdź ścieżkę od korzenia do n2 i zapisz ją w innym wektorze lub tablicy.
- Przechodź obie ścieżki, aż wartości w tablicach będą takie same. Zwróć wspólny element tuż przed niezgodnością.
Poniżej znajduje się implementacja powyższego algorytmu:
C++
// C++ Program for Lowest Common Ancestor> // in a Binary Tree> // A O(n) solution to find LCA> // of two given values n1 and n2> #include> using> namespace> std;> // A Binary Tree node> struct> Node {> >int> key;> >struct> Node *left, *right;> };> // Utility function creates a new binary tree node with> // given key> Node* newNode(>int> k)> {> >Node* temp =>new> Node;> >temp->klucz = k;> >temp->lewy = temp->prawy = NULL;> >return> temp;> }> // Finds the path from root node to given root of the tree,> // Stores the path in a vector path[], returns true if path> // exists otherwise false> bool> findPath(Node* root, vector<>int>>& ścieżka,>int> k)> (root->prawo && findPath(root->prawo, ścieżka, k)))> >return> true>;> >// If not present in subtree rooted with root, remove> >// root from path[] and return false> >path.pop_back();> >return> false>;> > // Returns LCA if node n1, n2 are present in the given> // binary tree, otherwise return -1> int> findLCA(Node* root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> > // Driver program to test above functions> int> main()> {> >// Let us create the Binary Tree shown in above diagram.> >Node* root = newNode(1);> >root->lewy = nowyWęzeł(2);> >root->prawo = nowyWęzeł(3);> >root->lewy->lewy = nowyWęzeł(4);> >root->lewy->prawy = nowyWęzeł(5);> >root->prawo->lewo = nowyWęzeł(6);> >root->prawo->prawo = nowyWęzeł(7);> >cout <<>'LCA(4, 5) = '> << findLCA(root, 4, 5);> >cout <<>'
LCA(4, 6) = '> << findLCA(root, 4, 6);> >cout <<>'
LCA(3, 4) = '> << findLCA(root, 3, 4);> >cout <<>'
LCA(2, 4) = '> << findLCA(root, 2, 4);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Jawa
// Java Program for Lowest Common Ancestor> // in a Binary Tree> // A O(n) solution to find LCA of> // two given values n1 and n2> import> java.util.ArrayList;> import> java.util.List;> // A Binary Tree node> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node left, right;> >Node(>int> value)> >{> >data = value;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> public> class> BT_NoParentPtr_Solution1 {> >Node root;> >private> List path1 =>new> ArrayList();> >private> List path2 =>new> ArrayList();> >// Finds the path from root node to given root of the> >// tree.> >int> findLCA(>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >path1.clear();> >path2.clear();> >return> findLCAInternal(root, n1, n2);> >}> >private> int> findLCAInternal(Node root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >if> (!findPath(root, n1, path1)> >|| !findPath(root, n2, path2)) {> >System.out.println((path1.size()>>0>)> >?>'n1 is present'> >:>'n1 is missing'>);> >System.out.println((path2.size()>>0>)> >?>'n2 is present'> >:>'n2 is missing'>);> >return> ->1>;> >}> >int> i;> >for> (i =>0>; i i++) { // System.out.println(path1.get(i) + ' ' + // path2.get(i)); if (!path1.get(i).equals(path2.get(i))) break; } return path1.get(i - 1); } // Finds the path from root node to given root of the // tree, Stores the path in a vector path[], returns // true if path exists otherwise false private boolean findPath(Node root, int n, List path) { // base case if (root == null) { return false; } // Store this node . The node will be removed if // not in path from root to n. path.add(root.data); if (root.data == n || findPath(root.left, n, path) || findPath(root.right, n, path)) { return true; } // If not present in subtree rooted with root, // remove root from path[] and return false path.remove(path.size() - 1); return false; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { BT_NoParentPtr_Solution1 tree = new BT_NoParentPtr_Solution1(); tree.root = new Node(1); tree.root.left = new Node(2); tree.root.right = new Node(3); tree.root.left.left = new Node(4); tree.root.left.right = new Node(5); tree.root.right.left = new Node(6); tree.root.right.right = new Node(7); System.out.println('LCA(4, 5) = ' + tree.findLCA(4, 5)); System.out.println('LCA(4, 6) = ' + tree.findLCA(4, 6)); System.out.println('LCA(3, 4) = ' + tree.findLCA(3, 4)); System.out.println('LCA(2, 4) = ' + tree.findLCA(2, 4)); } } // This code is contributed by Sreenivasulu Rayanki.> |
>
>
Python3
# Python Program for Lowest Common Ancestor in a Binary Tree> # O(n) solution to find LCS of two given values n1 and n2> # A binary tree node> class> Node:> ># Constructor to create a new binary node> >def> __init__(>self>, key):> >self>.key>=> key> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> # Finds the path from root node to given root of the tree.> # Stores the path in a list path[], returns true if path> # exists otherwise false> def> findPath(root, path, k):> ># Baes Case> >if> root>is> None>:> >return> False> ># Store this node is path vector. The node will be> ># removed if not in path from root to k> >path.append(root.key)> ># See if the k is same as root's key> >if> root.key>=>=> k:> >return> True> ># Check if k is found in left or right sub-tree> >if> ((root.left !>=> None> and> findPath(root.left, path, k))>or> >(root.right !>=> None> and> findPath(root.right, path, k))):> >return> True> ># If not present in subtree rooted with root, remove> ># root from path and return False> >path.pop()> >return> False> # Returns LCA if node n1 , n2 are present in the given> # binary tree otherwise return -1> def> findLCA(root, n1, n2):> ># To store paths to n1 and n2 fromthe root> >path1>=> []> >path2>=> []> ># Find paths from root to n1 and root to n2.> ># If either n1 or n2 is not present , return -1> >if> (>not> findPath(root, path1, n1)>or> not> findPath(root, path2, n2)):> >return> ->1> ># Compare the paths to get the first different value> >i>=> 0> >while>(i <>len>(path1)>and> i <>len>(path2)):> >if> path1[i] !>=> path2[i]:> >break> >i>+>=> 1> >return> path1[i>->1>]> # Driver program to test above function> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> > ># Let's create the Binary Tree shown in above diagram> >root>=> Node(>1>)> >root.left>=> Node(>2>)> >root.right>=> Node(>3>)> >root.left.left>=> Node(>4>)> >root.left.right>=> Node(>5>)> >root.right.left>=> Node(>6>)> >root.right.right>=> Node(>7>)> > >print>(>'LCA(4, 5) = %d'> %> (findLCA(root,>4>,>5>,)))> >print>(>'LCA(4, 6) = %d'> %> (findLCA(root,>4>,>6>)))> >print>(>'LCA(3, 4) = %d'> %> (findLCA(root,>3>,>4>)))> >print>(>'LCA(2, 4) = %d'> %> (findLCA(root,>2>,>4>)))> # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> |
>
>
C#
// C# Program for Lowest Common> // Ancestor in a Binary Tree> // A O(n) solution to find LCA> // of two given values n1 and n2> using> System.Collections;> using> System;> // A Binary Tree node> class> Node {> >public> int> data;> >public> Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> value)> >{> >data = value;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> public> class> BT_NoParentPtr_Solution1 {> >Node root;> >private> ArrayList path1 =>new> ArrayList();> >private> ArrayList path2 =>new> ArrayList();> >// Finds the path from root> >// node to given root of the> >// tree.> >int> findLCA(>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >path1.Clear();> >path2.Clear();> >return> findLCAInternal(root, n1, n2);> >}> >private> int> findLCAInternal(Node root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >if> (!findPath(root, n1, path1)> >|| !findPath(root, n2, path2)) {> >Console.Write((path1.Count>0)> >?>'n1 is present'> >:>'n1 is missing'>);> >Console.Write((path2.Count>0)> >?>'n2 is present'> >:>'n2 is missing'>);> >return> -1;> >}> >int> i;> >for> (i = 0; i i++) { // System.out.println(path1.get(i) // + ' ' + path2.get(i)); if ((int)path1[i] != (int)path2[i]) break; } return (int)path1[i - 1]; } // Finds the path from root node // to given root of the tree, // Stores the path in a vector // path[], returns true if path // exists otherwise false private bool findPath(Node root, int n, ArrayList path) { // base case if (root == null) { return false; } // Store this node . The node // will be removed if not in // path from root to n. path.Add(root.data); if (root.data == n) { return true; } if (root.left != null && findPath(root.left, n, path)) { return true; } if (root.right != null && findPath(root.right, n, path)) { return true; } // If not present in subtree // rooted with root, remove root // from path[] and return false path.RemoveAt(path.Count - 1); return false; } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { BT_NoParentPtr_Solution1 tree = new BT_NoParentPtr_Solution1(); tree.root = new Node(1); tree.root.left = new Node(2); tree.root.right = new Node(3); tree.root.left.left = new Node(4); tree.root.left.right = new Node(5); tree.root.right.left = new Node(6); tree.root.right.right = new Node(7); Console.Write('LCA(4, 5) = ' + tree.findLCA(4, 5)); Console.Write('
LCA(4, 6) = ' + tree.findLCA(4, 6)); Console.Write('
LCA(3, 4) = ' + tree.findLCA(3, 4)); Console.Write('
LCA(2, 4) = ' + tree.findLCA(2, 4)); } } // This code is contributed by Rutvik_56> |
>
>
JavaScript
> >// JavaScript Program for Lowest Common> >// Ancestor in a Binary Tree> >// A O(n) solution to find LCA of> >// two given values n1 and n2> > >class Node> >{> >constructor(value) {> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >this>.data = value;> >}> >}> > >let root;> >let path1 = [];> >let path2 = [];> > >// Finds the path from root node to given root of the tree.> >function> findLCA(n1, n2) {> >path1 = [];> >path2 = [];> >return> findLCAInternal(root, n1, n2);> >}> > >function> findLCAInternal(root, n1, n2) {> > >if> (!findPath(root, n1, path1) || !findPath(root, n2, path2))> >{> >document.write((path1.length>0)?> >'n1 is present'> :>'n1 is missing'>);> >document.write((path2.length>0)?> >'n2 is present'> :>'n2 is missing'>);> >return> -1;> >}> > >let i;> >for> (i = 0; i // System.out.println(path1.get(i) + ' ' + path2.get(i)); if (path1[i] != path2[i]) break; } return path1[i-1]; } // Finds the path from root node to // given root of the tree, Stores the // path in a vector path[], returns true // if path exists otherwise false function findPath(root, n, path) { // base case if (root == null) { return false; } // Store this node . The node will be removed if // not in path from root to n. path.push(root.data); if (root.data == n) { return true; } if (root.left != null && findPath(root.left, n, path)) { return true; } if (root.right != null && findPath(root.right, n, path)) { return true; } // If not present in subtree rooted with root, // remove root from // path[] and return false path.pop(); return false; } root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(6); root.right.right = new Node(7); document.write('LCA(4, 5) = ' + findLCA(4,5) + ''); document.write('LCA(4, 6) = ' + findLCA(4,6) + ''); document.write('LCA(3, 4) = ' + findLCA(3,4) + ''); document.write('LCA(2, 4) = ' + findLCA(2,4));> |
>
>Wyjście
LCA(4, 5) = 2 LCA(4, 6) = 1 LCA(3, 4) = 1 LCA(2, 4) = 2>
Złożoność czasowa: NA). Drzewo jest przeglądane dwukrotnie, a następnie porównywane są tablice ścieżek.
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: NA). Dodatkowe miejsce na ścieżkę 1 i ścieżkę 2.
Najniższy wspólny przodek w drzewie binarnym według pojedynczego przejścia:
Pomysł jest taki, aby przejść przez drzewo zaczynając od korzenia. Jeśli którykolwiek z podanych kluczy (n1 i n2) pasuje do korzenia, wówczas korzeniem jest LCA (zakładając, że oba klucze są obecne). Jeśli korzeń nie pasuje do żadnego z kluczy, powtarzamy dla lewego i prawego poddrzewa.
- Węzeł, który ma jeden klucz w lewym poddrzewie, a drugi w prawym poddrzewie, to LCA.
- Jeśli oba klucze leżą w lewym poddrzewie, to lewe poddrzewo również ma LCA,
- W przeciwnym razie LCA leży w prawym poddrzewie.
Ilustracja:
Znajdź LCA 5 i 6
Źródło wskazuje na węzeł o wartości 1, ponieważ jego wartość nie pasuje do { 5, 6 }. Klucza szukamy w lewym i prawym poddrzewie.
- Lewe poddrzewo:
- Nowy pierwiastek = { 2 } ≠ 5 lub 6, dlatego będziemy kontynuować naszą rekurencję
- New Root = { 4 } , jego lewe i prawe poddrzewo ma wartość null, dla tego wywołania zwrócimy NULL
- New Root = { 5 } , wartość odpowiada 5, więc zwróci węzeł o wartości 5
- Wywołanie funkcji root o wartości 2 zwróci wartość 5
- Prawe poddrzewo:
- Pierwiastek = { 3 } ≠ 5 lub 6, dlatego kontynuujemy naszą rekurencję
- Root = { 6 } = 5 lub 6 , zwrócimy ten węzeł z wartością 6
- Root = { 7 } ≠ 5 lub 6, zwrócimy NULL
- Zatem wywołanie funkcji root o wartości 3 zwróci węzeł o wartości 6
- Ponieważ zarówno lewe, jak i prawe poddrzewo węzła o wartości 1 nie ma wartości NULL, zatem 1 to LCA
Aby rozwiązać problem, wykonaj poniższe czynności:
- Przekazujemy pierwiastek do funkcji pomocniczej i sprawdzamy, czy wartość pierwiastka pasuje do którejkolwiek z wartości n1 i n2.
- Jeśli TAK, zwróć root
- w przeciwnym razie wywołanie rekurencyjne w lewym i prawym poddrzewie
- Zasadniczo wykonujemy przechodzenie w przedsprzedaży, najpierw sprawdzamy, czy pierwiastek->wartość pasuje do n1 lub n2. Następnie przejdź przez lewe i prawe poddrzewo.
- Jeśli istnieje jakiś pierwiastek, który zwraca jedną wartość NULL i inną wartość NON-NULL, zwrócimy odpowiednią wartość NON-NULL dla tego węzła.
- Węzeł, który zwraca obie wartości NON-NULL zarówno dla lewego, jak i prawego poddrzewa, jest naszym najniższym wspólnym przodkiem.
Poniżej implementacja powyższego podejścia.
C++
/* C++ Program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one traversal> >* of Binary Tree */> #include> using> namespace> std;> // A Binary Tree Node> struct> Node {> >struct> Node *left, *right;> >int> key;> };> // Utility function to create a new tree Node> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >Node* temp =>new> Node;> >temp->klucz = klucz;> >temp->lewy = temp->prawy = NULL;> >return> temp;> }> // This function returns pointer to LCA of two given values> // n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and n2 are> // present in Binary Tree> struct> Node* findLCA(>struct> Node* root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> > >// Base case> >if> (root == NULL)> >return> NULL;> >// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key, report> >// the presence by returning root (Note that if a key is> >// ancestor of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA> >if> (root->klucz == n1> // Driver program to test above functions> int> main()> {> >// Let us create binary tree given in the above example> >Node* root = newNode(1);> >root->lewy = nowyWęzeł(2);> >root->prawo = nowyWęzeł(3);> >root->lewy->lewy = nowyWęzeł(4);> >root->lewy->prawy = nowyWęzeł(5);> >root->prawo->lewo = nowyWęzeł(6);> >root->prawo->prawo = nowyWęzeł(7);> >cout <<>'LCA(4, 5) = '> cout << '
LCA(4, 6) = ' cout << '
LCA(3, 4) = ' cout << '
LCA(2, 4) = ' return 0; } // This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)> |
>
>
C
// C Program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one traversalof> // Binary Tree> #include> #include> // A Binary Tree Node> typedef> struct> Node {> >struct> Node *left, *right;> >int> key;> } Node;> // Utility function to create a new tree Node> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >Node* temp = (Node*)>malloc>(>sizeof>(Node));> >temp->klucz = klucz;> >temp->lewy = temp->prawy = NULL;> >return> temp;> }> // This function returns pointer to LCA of two given values> // n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and n2 are> // present in Binary Tree> Node* findLCA(Node* root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> > >// Base case> >if> (root == NULL)> >return> NULL;> >// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key, report> >// the presence by returning root (Note that if a key is> >// ancestor of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA> >if> (root->klucz == n1> // Driver program to test above functions> int> main()> {> >// Let us create binary tree given in the above example> >Node* root = newNode(1);> >root->lewy = nowyWęzeł(2);> >root->prawo = nowyWęzeł(3);> >root->lewy->lewy = nowyWęzeł(4);> >root->lewy->prawy = nowyWęzeł(5);> >root->prawo->lewo = nowyWęzeł(6);> >root->prawo->prawo = nowyWęzeł(7);> >printf>(>'LCA(4, 5) = %d'>, findLCA(root, 4, 5)->klucz);> >printf>(>'
LCA(4, 6) = %d'>, findLCA(root, 4, 6)->klucz);> >printf>(>'
LCA(3, 4) = %d'>, findLCA(root, 3, 4)->klucz);> >printf>(>'
LCA(2, 4) = %d'>, findLCA(root, 2, 4)->klucz);> >return> 0;> }> // This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)> |
>
>
Jawa
// Java implementation to find lowest common ancestor of> // n1 and n2 using one traversal of binary tree> /* Class containing left and right child of current> >node and key value*/> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item)> >{> >data = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> >// Root of the Binary Tree> >Node root;> >Node findLCA(>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >return> findLCA(root, n1, n2);> >}> >// This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> >// values n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and> >// n2 are present in Binary Tree> >Node findLCA(Node node,>int> n1,>int> n2)> >> >// Base case> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> null>;> >// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key,> >// report the presence by returning root (Note that> >// if a key is ancestor of other, then the ancestor> >// key becomes LCA> >if> (node.data == n1> >/* Driver program to test above functions */> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >BinaryTree tree =>new> BinaryTree();> >tree.root =>new> Node(>1>);> >tree.root.left =>new> Node(>2>);> >tree.root.right =>new> Node(>3>);> >tree.root.left.left =>new> Node(>4>);> >tree.root.left.right =>new> Node(>5>);> >tree.root.right.left =>new> Node(>6>);> >tree.root.right.right =>new> Node(>7>);> >System.out.println(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(>4>,>5>).data);> >System.out.println(>'LCA(4, 6) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(>4>,>6>).data);> >System.out.println(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(>3>,>4>).data);> >System.out.println(>'LCA(2, 4) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(>2>,>4>).data);> >}> }> |
>
>
Python3
# Python program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one> # traversal of Binary tree> # A binary tree node> class> Node:> ># Constructor to create a new tree node> >def> __init__(>self>, key):> >self>.key>=> key> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> # This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> # values n1 and n2> # This function assumes that n1 and n2 are present in> # Binary Tree> def> findLCA(root, n1, n2):> ># Base Case> >if> root>is> None>:> >return> None> ># If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key, report> ># the presence by returning root (Note that if a key is> ># ancestor of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA> >if> root.key>=>=> n1>or> root.key>=>=> n2:> >return> root> ># Look for keys in left and right subtrees> >left_lca>=> findLCA(root.left, n1, n2)> >right_lca>=> findLCA(root.right, n1, n2)> ># If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then one key> ># is present in once subtree and other is present in other,> ># So this node is the LCA> >if> left_lca>and> right_lca:> >return> root> ># Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree is LCA> >return> left_lca>if> left_lca>is> not> None> else> right_lca> # Driver code> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> > ># Let us create a binary tree given in the above example> >root>=> Node(>1>)> >root.left>=> Node(>2>)> >root.right>=> Node(>3>)> >root.left.left>=> Node(>4>)> >root.left.right>=> Node(>5>)> >root.right.left>=> Node(>6>)> >root.right.right>=> Node(>7>)> >print>(>'LCA(4, 5) = '>, findLCA(root,>4>,>5>).key)> >print>(>'LCA(4, 6) = '>, findLCA(root,>4>,>6>).key)> >print>(>'LCA(3, 4) = '>, findLCA(root,>3>,>4>).key)> >print>(>'LCA(2, 4) = '>, findLCA(root,>2>,>4>).key)> # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> |
>
>
C#
// C# implementation to find lowest common> // ancestor of n1 and n2 using one traversal> // of binary tree> using> System;> // Class containing left and right> // child of current node and key value> public> class> Node {> >public> int> data;> >public> Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item)> >{> >data = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> class> BinaryTree {> >// Root of the Binary Tree> >Node root;> >Node findLCA(>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >return> findLCA(root, n1, n2);> >}> >// This function returns pointer to LCA> >// of two given values n1 and n2. This> >// function assumes that n1 and n2 are> >// present in Binary Tree> >Node findLCA(Node node,>int> n1,>int> n2)> > node.data == n2)> >return> node;> >// Look for keys in left and right subtrees> >Node left_lca = findLCA(node.left, n1, n2);> >Node right_lca = findLCA(node.right, n1, n2);> >// If both of the above calls return Non-NULL,> >// then one key is present in once subtree> >// and other is present in other, So this> >// node is the LCA> >if> (left_lca !=>null> && right_lca !=>null>)> >return> node;> >// Otherwise check if left subtree or> >// right subtree is LCA> >return> (left_lca !=>null>) ? left_lca : right_lca;> >> >// Driver code> >public> static> void> Main(>string>[] args)> >{> >BinaryTree tree =>new> BinaryTree();> >tree.root =>new> Node(1);> >tree.root.left =>new> Node(2);> >tree.root.right =>new> Node(3);> >tree.root.left.left =>new> Node(4);> >tree.root.left.right =>new> Node(5);> >tree.root.right.left =>new> Node(6);> >tree.root.right.right =>new> Node(7);> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(4, 5).data);> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(4, 6) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(4, 6).data);> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(3, 4).data);> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(2, 4) = '> >+ tree.findLCA(2, 4).data);> >}> }> // This code is contributed by pratham76> |
>
>
JavaScript
> >// JavaScript implementation to find> >// lowest common ancestor of> >// n1 and n2 using one traversal of binary tree> > >class Node> >{> >constructor(item) {> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >this>.data = item;> >}> >}> > >//Root of the Binary Tree> >let root;> > >function> findlCA(n1, n2)> >{> >return> findLCA(root, n1, n2);> >}> > >// This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> >// values n1 and n2. This function assumes that n1 and> >// n2 are present in Binary Tree> >function> findLCA(node, n1, n2)> >> > >root =>new> Node(1);> >root.left =>new> Node(2);> >root.right =>new> Node(3);> >root.left.left =>new> Node(4);> >root.left.right =>new> Node(5);> >root.right.left =>new> Node(6);> >root.right.right =>new> Node(7);> >document.write(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> +> >findlCA(4, 5).data +>''>);> >document.write(>'LCA(4, 6) = '> +> >findlCA(4, 6).data +>''>);> >document.write(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> +> >findlCA(3, 4).data +>''>);> >document.write(>'LCA(2, 4) = '> +> >findlCA(2, 4).data +>''>);> > > |
>
>Wyjście
LCA(4, 5) = 2 LCA(4, 6) = 1 LCA(3, 4) = 1 LCA(2, 4) = 2>
Złożoność czasu : O(N), ponieważ metoda wykonuje proste przechodzenie przez drzewo w sposób oddolny.
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(H), gdzie H jest wysokością drzewa.
Notatka: Powyższa metoda zakłada, że klucze są obecne w drzewie binarnym . Jeśli jeden klucz jest obecny, a drugiego nie ma, zwraca bieżący klucz jako LCA (w idealnym przypadku powinien zwrócić NULL). Możemy rozszerzyć tę metodę, aby obsłużyła wszystkie przypadki, sprawdzając najpierw, czy w drzewie obecne są n1 i n2, a następnie znajdując LCA n1 i n2. Aby sprawdzić, czy węzeł jest obecny w drzewie binarnym, czy nie, należy przejść przez drzewo osobno dla obu węzłów n1 i n2.
C++
/* C++ program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one traversal> >of Binary Tree. It handles all cases even when n1 or n2> >is not there in Binary Tree */> #include> using> namespace> std;> // A Binary Tree Node> struct> Node {> >struct> Node *left, *right;> >int> key;> };> // Utility function to create a new tree Node> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >Node* temp =>new> Node;> >temp->klucz = klucz;> >temp->lewy = temp->prawy = NULL;> >return> temp;> }> // This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> // valuesn1 and n2.> struct> Node* findLCAUtil(>struct> Node* root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> > // Returns true if key k is present in tree rooted with root> bool> find(Node* root,>int> k)> find(root->prawda, k))> >return> true>;> >// Else return false> >return> false>;> > // This function returns LCA of n1 and n2 only if both n1> // and n2 are present in tree, otherwise returns NULL;> Node* findLCA(Node* root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> {> >// Return LCA only if both n1 and n2 are present in tree> >if> (find(root, n1) and find(root, n2))> >return> findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2);> >// Else return NULL> >return> NULL;> }> // Driver program to test above functions> int> main()> {> >// Let us create a binary tree given in the above> >// example> >Node* root = newNode(1);> >root->lewy = nowyWęzeł(2);> >root->prawo = nowyWęzeł(3);> >root->lewy->lewy = nowyWęzeł(4);> >root->lewy->prawy = nowyWęzeł(5);> >root->prawo->lewo = nowyWęzeł(6);> >root->prawo->prawo = newNode(7);> >Node* lca = findLCA(root, 4, 5);> >if> (lca != NULL)> >cout <<>'LCA(4, 5) = '> else cout << 'Keys are not present '; lca = findLCA(root, 4, 10); if (lca != NULL) cout << '
LCA(4, 10) = ' else cout << '
Keys are not present '; return 0; } // This code is contributed by Kshitij Dwivedi // (kshitijdwivedi28)> |
>
>
Jawa
// Java implementation to find lowest common ancestor of> // n1 and n2 using one traversal of binary tree> // It also handles cases even when n1 and n2 are not there> // in Tree> /* Class containing left and right child of current node and> >* key */> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item)> >{> >data = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> >// Root of the Binary Tree> >Node root;> >static> boolean> v1 =>false>, v2 =>false>;> >// This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> >// values n1 and n2.> >// v1 is set as true by this function if n1 is found> >// v2 is set as true by this function if n2 is found> >Node findLCAUtil(Node node,>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >// Base case> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> null>;> >// Store result in temp, in case of key match so> >// that we can search for other key also.> >Node temp =>null>;> >// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key,> >// report the presence by setting v1 or v2 as true> >// and return root (Note that if a key is ancestor> >// of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA)> >if> (node.data == n1) {> >v1 =>true>;> >temp = node;> >}> >if> (node.data == n2) {> >v2 =>true>;> >temp = node;> >}> >// Look for keys in left and right subtrees> >Node left_lca = findLCAUtil(node.left, n1, n2);> >Node right_lca = findLCAUtil(node.right, n1, n2);> >if> (temp !=>null>)> >return> temp;> >// If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then> >// one key is present in once subtree and other is> >// present in other, So this node is the LCA> >if> (left_lca !=>null> && right_lca !=>null>)> >return> node;> >// Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree> >// is LCA> >return> (left_lca !=>null>) ? left_lca : right_lca;> >}> >// Finds lca of n1 and n2 under the subtree rooted with> >// 'node'> >Node findLCA(>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >// Initialize n1 and n2 as not visited> >v1 =>false>;> >v2 =>false>;> >// Find lca of n1 and n2 using the technique> >// discussed above> >Node lca = findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2);> >// Return LCA only if both n1 and n2 are present in> >// tree> >if> (v1 && v2)> >return> lca;> >// Else return NULL> >return> null>;> >}> >/* Driver program to test above functions */> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >BinaryTree tree =>new> BinaryTree();> >tree.root =>new> Node(>1>);> >tree.root.left =>new> Node(>2>);> >tree.root.right =>new> Node(>3>);> >tree.root.left.left =>new> Node(>4>);> >tree.root.left.right =>new> Node(>5>);> >tree.root.right.left =>new> Node(>6>);> >tree.root.right.right =>new> Node(>7>);> >Node lca = tree.findLCA(>4>,>5>);> >if> (lca !=>null>)> >System.out.println(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> + lca.data);> >else> >System.out.println(>'Keys are not present'>);> >lca = tree.findLCA(>4>,>10>);> >if> (lca !=>null>)> >System.out.println(>'LCA(4, 10) = '> + lca.data);> >else> >System.out.println(>'Keys are not present'>);> >}> }> |
>
>
Python3
''' Program to find LCA of n1 and n2 using one traversal of> >Binary tree> It handles all cases even when n1 or n2 is not there in tree> '''> # A binary tree node> class> Node:> ># Constructor to create a new node> >def> __init__(>self>, key):> >self>.key>=> key> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> # This function return pointer to LCA of two given values> # n1 and n2> # v1 is set as true by this function if n1 is found> # v2 is set as true by this function if n2 is found> def> findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2, v):> ># Base Case> >if> root>is> None>:> >return> None> ># IF either n1 or n2 matches ith root's key, report> ># the presence by setting v1 or v2 as true and return> ># root (Note that if a key is ancestor of other, then> ># the ancestor key becomes LCA)> >if> root.key>=>=> n1:> >v[>0>]>=> True> >return> root> >if> root.key>=>=> n2:> >v[>1>]>=> True> >return> root> ># Look for keys in left and right subtree> >left_lca>=> findLCAUtil(root.left, n1, n2, v)> >right_lca>=> findLCAUtil(root.right, n1, n2, v)> ># If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then one key> ># is present in once subtree and other is present in other,> ># So this node is the LCA> >if> left_lca>and> right_lca:> >return> root> ># Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree is LCA> >return> left_lca>if> left_lca>is> not> None> else> right_lca> def> find(root, k):> ># Base Case> >if> root>is> None>:> >return> False> ># If key is present at root, or if left subtree or right> ># subtree , return true> >if> (root.key>=>=> k>or> find(root.left, k)>or> >find(root.right, k)):> >return> True> ># Else return false> >return> False> # This function returns LCA of n1 and n2 on value if both> # n1 and n2 are present in tree, otherwise returns None> def> findLCA(root, n1, n2):> ># Initialize n1 and n2 as not visited> >v>=> [>False>,>False>]> ># Find lca of n1 and n2 using the technique discussed above> >lca>=> findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2, v)> ># Returns LCA only if both n1 and n2 are present in tree> >if> (v[>0>]>and> v[>1>]>or> v[>0>]>and> find(lca, n2)>or> v[>1>]>and> >find(lca, n1)):> >return> lca> ># Else return None> >return> None> # Driver program to test above function> root>=> Node(>1>)> root.left>=> Node(>2>)> root.right>=> Node(>3>)> root.left.left>=> Node(>4>)> root.left.right>=> Node(>5>)> root.right.left>=> Node(>6>)> root.right.right>=> Node(>7>)> lca>=> findLCA(root,>4>,>5>)> if> lca>is> not> None>:> >print>(>'LCA(4, 5) = '>, lca.key)> else>:> >print>(>'Keys are not present'>)> lca>=> findLCA(root,>4>,>10>)> if> lca>is> not> None>:> >print>(>'LCA(4,10) = '>, lca.key)> else>:> >print>(>'Keys are not present'>)> # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> |
>
>
C#
using> System;> // c# implementation to find lowest common ancestor of> // n1 and n2 using one traversal of binary tree> // It also handles cases even when n1 and n2 are not there> // in Tree> /* Class containing left and right child of current node and> >* key */> public> class> Node {> >public> int> data;> >public> Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item)> >{> >data = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> public> class> BinaryTree {> >// Root of the Binary Tree> >public> Node root;> >public> static> bool> v1 =>false>, v2 =>false>;> >// This function returns pointer to LCA of two given> >// values n1 and n2.> >// v1 is set as true by this function if n1 is found> >// v2 is set as true by this function if n2 is found> >public> virtual> Node findLCAUtil(Node node,>int> n1,> >int> n2)> >{> >// Base case> >if> (node ==>null>) {> >return> null>;> >}> >// Store result in temp, in case of key match so> >// that we can search for other key also.> >Node temp =>null>;> >// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key,> >// report the presence by setting v1 or v2 as true> >// and return root (Note that if a key is ancestor> >// of other, then the ancestor key becomes LCA)> >if> (node.data == n1) {> >v1 =>true>;> >temp = node;> >}> >if> (node.data == n2) {> >v2 =>true>;> >temp = node;> >}> >// Look for keys in left and right subtrees> >Node left_lca = findLCAUtil(node.left, n1, n2);> >Node right_lca = findLCAUtil(node.right, n1, n2);> >if> (temp !=>null>) {> >return> temp;> >}> >// If both of the above calls return Non-NULL, then> >// one key is present in once subtree and other is> >// present in other, So this node is the LCA> >if> (left_lca !=>null> && right_lca !=>null>) {> >return> node;> >}> >// Otherwise check if left subtree or right subtree> >// is LCA> >return> (left_lca !=>null>) ? left_lca : right_lca;> >}> >// Finds lca of n1 and n2 under the subtree rooted with> >// 'node'> >public> virtual> Node findLCA(>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >// Initialize n1 and n2 as not visited> >v1 =>false>;> >v2 =>false>;> >// Find lca of n1 and n2 using the technique> >// discussed above> >Node lca = findLCAUtil(root, n1, n2);> >// Return LCA only if both n1 and n2 are present in> >// tree> >if> (v1 && v2) {> >return> lca;> >}> >// Else return NULL> >return> null>;> >}> >/* Driver program to test above functions */> >public> static> void> Main(>string>[] args)> >{> >BinaryTree tree =>new> BinaryTree();> >tree.root =>new> Node(1);> >tree.root.left =>new> Node(2);> >tree.root.right =>new> Node(3);> >tree.root.left.left =>new> Node(4);> >tree.root.left.right =>new> Node(5);> >tree.root.right.left =>new> Node(6);> >tree.root.right.right =>new> Node(7);> >Node lca = tree.findLCA(4, 5);> >if> (lca !=>null>) {> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> + lca.data);> >}> >else> {> >Console.WriteLine(>'Keys are not present'>);> >}> >lca = tree.findLCA(4, 10);> >if> (lca !=>null>) {> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(4, 10) = '> + lca.data);> >}> >else> {> >Console.WriteLine(>'Keys are not present'>);> >}> >}> }> // This code is contributed by Shrikant13> |
>
>
JavaScript
> // JavaScript implementation to find lowest> // common ancestor of n1 and n2 using one> // traversal of binary tree. It also handles> // cases even when n1 and n2 are not there in Tree> // Class containing left and right child> // of current node and key> class Node> {> >constructor(item)> >{> >this>.data = item;> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >}> }> class BinaryTree{> > // Root of the Binary Tree> constructor()> {> >this>.root =>null>;> >this>.v1 =>false>;> >this>.v2 =>false>;> }> // This function returns pointer to LCA> // of two given values n1 and n2.> // v1 is set as true by this function> // if n1 is found> // v2 is set as true by this function> // if n2 is found> findLCAUtil(node, n1, n2)> {> > >// Base case> >if> (node ==>null>)> >{> >return> null>;> >}> > >// Store result in temp, in case of> >// key match so that we can search> >// for other key also.> >var> temp =>null>;> > >// If either n1 or n2 matches with root's key,> >// report the presence by setting v1 or v2 as> >// true and return root (Note that if a key> >// is ancestor of other, then the ancestor> >// key becomes LCA)> >if> (node.data == n1)> >{> >this>.v1 =>true>;> >temp = node;> >}> >if> (node.data == n2)> >{> >this>.v2 =>true>;> >temp = node;> >}> > >// Look for keys in left and right subtrees> >var> left_lca =>this>.findLCAUtil(node.left, n1, n2);> >var> right_lca =>this>.findLCAUtil(node.right, n1, n2);> > >if> (temp !=>null>)> >{> >return> temp;> >}> > >// If both of the above calls return Non-NULL,> >// then one key is present in once subtree and> >// other is present in other, So this node is the LCA> >if> (left_lca !=>null> && right_lca !=>null>)> >{> >return> node;> >}> > >// Otherwise check if left subtree or> >// right subtree is LCA> >return> left_lca !=>null> ? left_lca : right_lca;> }> // Finds lca of n1 and n2 under the> // subtree rooted with 'node'> findLCA(n1, n2)> {> > >// Initialize n1 and n2 as not visited> >this>.v1 =>false>;> >this>.v2 =>false>;> > >// Find lca of n1 and n2 using the> >// technique discussed above> >var> lca =>this>.findLCAUtil(>this>.root, n1, n2);> > >// Return LCA only if both n1 and n2> >// are present in tree> >if> (>this>.v1 &&>this>.v2)> >{> >return> lca;> >}> > >// Else return NULL> >return> null>;> }> }> // Driver code> var> tree =>new> BinaryTree();> tree.root =>new> Node(1);> tree.root.left =>new> Node(2);> tree.root.right =>new> Node(3);> tree.root.left.left =>new> Node(4);> tree.root.left.right =>new> Node(5);> tree.root.right.left =>new> Node(6);> tree.root.right.right =>new> Node(7);> var> lca = tree.findLCA(4, 5);> if> (lca !=>null>)> {> >document.write(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> +> >lca.data +>' '>);> }>else> {> >document.write(>'Keys are not present'> +>' '>);> }> lca = tree.findLCA(4, 10);> if> (lca !=>null>)> {> >document.write(>'LCA(4, 10) = '> +> >lca.data +>' '>);> }> else> {> >document.write(>'Keys are not present'> +>' '>);> }> // This code is contributed by rdtank> > |
>
>Wyjście
LCA(4, 5) = 2 Keys are not present>
Złożoność czasu : O(N), ponieważ metoda wykonuje proste przechodzenie przez drzewo w sposób oddolny.
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(H), gdzie h jest wysokością drzewa.
Korzystanie z pomocniczej struktury danych (tablicy skrótów):
The basic idea behind the 'Using an auxiliary data structure' approach for finding the lowest common ancestor of two nodes in a binary tree is to use a hash table or a map to store the parent pointers of each node. Once we have the parent pointers, we can traverse up from the first node and add all its ancestors to a set or a list. Then we can traverse up from the second node and check if each ancestor is already in the set or the list. The first ancestor that is already in the set or the list is the lowest common ancestor.>
Wykonaj następujące kroki, aby wdrożyć powyższe podejście:
- Utwórz tablicę mieszającą lub mapę do przechowywania wskaźników nadrzędnych każdego węzła w drzewie binarnym.
- Przejdź przez drzewo binarne i wypełnij tablicę mieszającą lub mapę wskaźnikami nadrzędnymi dla każdego węzła.
- Zaczynając od pierwszego węzła, przejdź w górę drzewa i dodaj każdego przodka do zbioru lub listy.
- Zaczynając od drugiego węzła, przejdź w górę drzewa i sprawdź, czy każdy przodek znajduje się już w zestawie lub na liście. Pierwszym przodkiem, który znajduje się już w zestawie lub na liście, jest najniższy wspólny przodek.
- Jeśli nie zostanie znaleziony żaden wspólny przodek, zwróć wartość null lub inną wartość wskazującą na brak wspólnego przodka.
Poniżej implementacja powyższego podejścia:
C++
// C++ code to implement above approach> #include> #include> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Definition of a binary tree node> struct> Node {> >int> data;> >Node* left;> >Node* right;> };> // Function to create a new binary tree node> Node* newNode(>int> data)> {> >Node* node =>new> Node;> >node->dane = dane;> >node->po lewej = NULL;> >node->prawo = NULL;> >return> (node);> }> // Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> // pointers for each node in the tree> unordered_map buildParentMap(Node* root)> {> >unordered_map parentMap;> >parentMap[root] = NULL;> >vector queue = { root };> >while> (!queue.empty()) {> >Node* node = queue.front();> >queue.erase(queue.begin());> >if> (node->po lewej) {> >parentMap[node->lewy] = węzeł;> >queue.push_back(node->lewo);> >}> >if> (node->po prawej) {> >parentMap[node->prawo] = węzeł;> >queue.push_back(node->prawda);> >}> >}> >return> parentMap;> }> // Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two nodes> // using an auxiliary data structure> int> findLCA(Node* root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> {> >// Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers for> >// each node in the tree> >unordered_map parentMap> >= buildParentMap(root);> >// Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> >Node* p = NULL;> >Node* q = NULL;> >vector queue = { root };> >while> (!queue.empty()) {> >Node* node = queue.front();> >queue.erase(queue.begin());> >if> (node->dane == n1) {> >p = node;> >}> >if> (node->dane == n2) {> >q = node;> >}> >if> (node->po lewej) {> >queue.push_back(node->lewo);> >}> >if> (node->po prawej) {> >queue.push_back(node->prawda);> >}> >}> >// Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set or a> >// list> >set ancestors;> >while> (p) {> >ancestors.insert(p);> >p = parentMap[p];> >}> >// Traverse up from the second node and check if each> >// ancestor is already in the set or the list> >while> (q) {> >if> (ancestors.find(q) != ancestors.end()) {> >return> q> >->dane;>// The first ancestor that is> >// already in the set or the list is> >// the lowest common ancestor> >}> >q = parentMap[q];> >}> >return> -1;>// No common ancestor found> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >Node* root = newNode(1);> >root->lewy = nowyWęzeł(2);> >root->prawo = nowyWęzeł(3);> >root->lewy->lewy = nowyWęzeł(4);> >root->lewy->prawy = nowyWęzeł(5);> >root->prawo->lewo = nowyWęzeł(6);> >root->prawo->prawo = newNode(7);> >cout <<>'LCA(4, 5) = '> << findLCA(root, 4, 5) << endl;> >cout <<>'LCA(4, 6) = '> << findLCA(root, 4, 6) << endl;> >cout <<>'LCA(3,4) = '> << findLCA(root, 3, 4) << endl;> >cout <<>'LCA(2, 4) = '> << findLCA(root, 2, 4) << endl;> >return> 0;> }> // This code is contributed by Veerendra_Singh_Rajpoot> |
>
>
Jawa
import> java.util.*;> // Definition of a binary tree node> class> Node {> >int> data;> >Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item)> >{> >data = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> class> Main {> >// Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> >// pointers for each node in the tree> >static> Map buildParentMap(Node root)> >{> >Map parentMap =>new> HashMap();> >parentMap.put(root,>null>);> >Queue queue =>new> LinkedList();> >queue.add(root);> >while> (!queue.isEmpty()) {> >Node node = queue.poll();> >if> (node.left !=>null>) {> >parentMap.put(node.left, node);> >queue.add(node.left);> >}> >if> (node.right !=>null>) {> >parentMap.put(node.right, node);> >queue.add(node.right);> >}> >}> >return> parentMap;> >}> >// Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two> >// nodes using an auxiliary data structure> >static> int> findLCA(Node root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >// Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers> >// for each node in the tree> >Map parentMap = buildParentMap(root);> >// Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> >Node p =>null>, q =>null>;> >Queue queue =>new> LinkedList();> >queue.add(root);> >while> (!queue.isEmpty()) {> >Node node = queue.poll();> >if> (node.data == n1) {> >p = node;> >}> >if> (node.data == n2) {> >q = node;> >}> >if> (node.left !=>null>) {> >queue.add(node.left);> >}> >if> (node.right !=>null>) {> >queue.add(node.right);> >}> >}> >// Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set> >// or a list> >Set ancestors =>new> HashSet();> >while> (p !=>null>) {> >ancestors.add(p);> >p = parentMap.get(p);> >}> >// Traverse up from the second node and check if> >// each ancestor is already in the set or the list> >while> (q !=>null>) {> >if> (ancestors.contains(q)) {> >return> q.data;> >}> >q = parentMap.get(q);> >}> >return> ->1>;>// No common ancestor found> >}> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >Node root =>new> Node(>1>);> >root.left =>new> Node(>2>);> >root.right =>new> Node(>3>);> >root.left.left =>new> Node(>4>);> >root.left.right =>new> Node(>5>);> >root.right.left =>new> Node(>6>);> >root.right.right =>new> Node(>7>);> >System.out.println(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> >+ findLCA(root,>4>,>5>));> >System.out.println(>'LCA(4, 6) = '> >+ findLCA(root,>4>,>6>));> >System.out.println(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> >+ findLCA(root,>3>,>4>));> >System.out.println(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> >+ findLCA(root,>2>,>4>));> >}> }> |
>
>
Python3
from> collections>import> deque> # Definition of a binary tree node> class> Node:> >def> __init__(>self>, data):> >self>.data>=> data> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> # Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> # pointers for each node in the tree> def> buildParentMap(root):> >parentMap>=> {}> >parentMap[root]>=> None> >queue>=> deque([root])> >while> queue:> >node>=> queue.popleft()> >if> node.left:> >parentMap[node.left]>=> node> >queue.append(node.left)> >if> node.right:> >parentMap[node.right]>=> node> >queue.append(node.right)> >return> parentMap> # Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two nodes> # using an auxiliary data structure> def> findLCA(root, n1, n2):> ># Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers for> ># each node in the tree> >parentMap>=> buildParentMap(root)> ># Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> >p, q>=> None>,>None> >queue>=> deque([root])> >while> queue:> >node>=> queue.popleft()> >if> node.data>=>=> n1:> >p>=> node> >if> node.data>=>=> n2:> >q>=> node> >if> node.left:> >queue.append(node.left)> >if> node.right:> >queue.append(node.right)> ># Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set or a> ># list> >ancestors>=> set>()> >while> p:> >ancestors.add(p)> >p>=> parentMap[p]> ># Traverse up from the second node and check if each> ># ancestor is already in the set or the list> >while> q:> >if> q>in> ancestors:> >return> q.data> >q>=> parentMap[q]> >return> ->1> # No common ancestor found> # Driver code> if> __name__>=>=> '__main__'>:> >root>=> Node(>1>)> >root.left>=> Node(>2>)> >root.right>=> Node(>3>)> >root.left.left>=> Node(>4>)> >root.left.right>=> Node(>5>)> >root.right.left>=> Node(>6>)> >root.right.right>=> Node(>7>)> >print>(>'LCA(4, 5) = '>, findLCA(root,>4>,>5>))> >print>(>'LCA(4, 6) = '>, findLCA(root,>4>,>6>))> >print>(>'LCA(3, 4) = '>, findLCA(root,>3>,>4>))> >print>(>'LCA(2, 4) = '>, findLCA(root,>2>,>4>))> |
>
>
C#
using> System;> using> System.Collections.Generic;> // Definition of a binary tree node> class> Node> {> >public> int> data;> >public> Node left, right;> >public> Node(>int> item)> >{> >data = item;> >left = right =>null>;> >}> }> class> MainClass> {> >// Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> >// pointers for each node in the tree> >static> Dictionary BuildParentMap(Node root)> >{> >Dictionary parentMap =>new> Dictionary();> >parentMap.Add(root,>null>);> >Queue queue =>new> Queue();> >queue.Enqueue(root);> >while> (queue.Count != 0)> >{> >Node node = queue.Dequeue();> >if> (node.left !=>null>)> >{> >parentMap.Add(node.left, node);> >queue.Enqueue(node.left);> >}> >if> (node.right !=>null>)> >{> >parentMap.Add(node.right, node);> >queue.Enqueue(node.right);> >}> >}> >return> parentMap;> >}> >// Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two> >// nodes using an auxiliary data structure> >static> int> FindLCA(Node root,>int> n1,>int> n2)> >{> >// Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers> >// for each node in the tree> >Dictionary parentMap = BuildParentMap(root);> >// Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> >Node p =>null>, q =>null>;> >Queue queue =>new> Queue();> >queue.Enqueue(root);> >while> (queue.Count != 0)> >{> >Node node = queue.Dequeue();> >if> (node.data == n1)> >{> >p = node;> >}> >if> (node.data == n2)> >{> >q = node;> >}> >if> (node.left !=>null>)> >{> >queue.Enqueue(node.left);> >}> >if> (node.right !=>null>)> >{> >queue.Enqueue(node.right);> >}> >}> >// Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set> >// or a list> >HashSet ancestors =>new> HashSet();> >while> (p !=>null>)> >{> >ancestors.Add(p);> >p = parentMap[p];> >}> >// Traverse up from the second node and check if> >// each ancestor is already in the set or the list> >while> (q !=>null>)> >{> >if> (ancestors.Contains(q))> >{> >return> q.data;> >}> >q = parentMap[q];> >}> >return> -1;>// No common ancestor found> >}> >public> static> void> Main()> >{> >Node root =>new> Node(1);> >root.left =>new> Node(2);> >root.right =>new> Node(3);> >root.left.left =>new> Node(4);> >root.left.right =>new> Node(5);> >root.right.left =>new> Node(6);> >root.right.right =>new> Node(7);> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> + FindLCA(root, 4, 5));> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(4, 6) = '> + FindLCA(root, 4, 6));> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> + FindLCA(root, 3, 4));> >Console.WriteLine(>'LCA(2, 4) = '> + FindLCA(root, 2, 4));> >}> }> // This code is contributed by akashish__> |
>
>
JavaScript
// javascript code addition> // Definition of a binary tree node> class Node {> >constructor(item) {> >this>.data = item;> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >}> }> // Function to build a hash table or a map of parent> // pointers for each node in the tree> function> buildParentMap(root) {> >const parentMap =>new> Map();> >parentMap.set(root,>null>);> >const queue = [];> >queue.push(root);> >while> (queue.length>0) {> >const node = queue.shift();> >if> (node.left !=>null>) {> >parentMap.set(node.left, node);> >queue.push(node.left);> >}> >if> (node.right !=>null>) {> >parentMap.set(node.right, node);> >queue.push(node.right);> >}> >}> >return> parentMap;> }> // Function to find the lowest common ancestor of two> // nodes using an auxiliary data structure> function> findLCA(root, n1, n2) {> >// Build a hash table or a map of parent pointers> >// for each node in the tree> >const parentMap = buildParentMap(root);> >// Find the nodes with values n1 and n2> >let p =>null>, q =>null>;> >const queue = [];> >queue.push(root);> >while> (queue.length>0) {> >const node = queue.shift();> >if> (node.data === n1) {> >p = node;> >}> >if> (node.data === n2) {> >q = node;> >}> >if> (node.left !=>null>) {> >queue.push(node.left);> >}> >if> (node.right !=>null>) {> >queue.push(node.right);> >}> >}> >// Add all the ancestors of the first node to a set> >// or a list> >const ancestors =>new> Set();> >while> (p !=>null>) {> >ancestors.add(p);> >p = parentMap.get(p);> >}> >// Traverse up from the second node and check if> >// each ancestor is already in the set or the list> >while> (q !=>null>) {> >if> (ancestors.has(q)) {> >return> q.data;> >}> >q = parentMap.get(q);> >}> >return> -1;>// No common ancestor found> }> // Test the function> const root =>new> Node(1);> root.left =>new> Node(2);> root.right =>new> Node(3);> root.left.left =>new> Node(4);> root.left.right =>new> Node(5);> root.right.left =>new> Node(6);> root.right.right =>new> Node(7);> console.log(>'LCA(4, 5) = '> + findLCA(root, 4, 5));> console.log(>'LCA(4, 6) = '> + findLCA(root, 4, 6));> console.log(>'LCA(3, 4) = '> + findLCA(root, 3, 4));> console.log(>'LCA(2, 4) = '> + findLCA(root, 2, 4));> // The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.> |
>
>Wyjście
LCA(4, 5) = 2 LCA(4, 6) = 1 LCA(3,4) = 1 LCA(2, 4) = 2>
Złożoność czasowa: O(n),
usuń pierwszy znak Excel
Złożoność czasowa danego kodu wynosi O(n), gdzie n jest liczbą węzłów w drzewie binarnym.
Budowanie mapy nadrzędnej dla każdego węzła w drzewie wymaga jednorazowego odwiedzenia każdego węzła, co zajmuje czas O(n). Znalezienie węzłów o wartościach n1 i n2 wymaga jednokrotnego odwiedzenia każdego węzła, co również zajmuje czas O(n). Przejście od drugiego węzła i sprawdzenie, czy każdy przodek znajduje się już w zbiorze lub na liście, zajmuje czas O(h), gdzie h jest wysokością drzewa binarnego.
W najgorszym przypadku wysokość drzewa binarnego wynosi O(n), jeśli drzewo binarne jest przekrzywione. Zatem całkowita złożoność czasowa danego kodu wynosi O(n) + O(n) + O(n) = O(n).
Złożoność przestrzenna: O(n),
Złożoność przestrzenna danego kodu wynosi w najgorszym przypadku O(n). Dzieje się tak, ponieważ rozmiar mapy nadrzędnej zbudowanej dla każdego węzła w drzewie wynosi O(n). Dodatkowo zbiór przodków może w najgorszym przypadku zawierać wszystkie węzły drzewa binarnego, co również zajmuje przestrzeń O(n). Wreszcie kolejka używana do przechodzenia przez drzewo binarne zajmuje przestrzeń O(n). Dlatego ogólna złożoność przestrzenna danego kodu wynosi O(n) + O(n) + O(n) = O(n).
Omówiliśmy skuteczne rozwiązanie umożliwiające znalezienie LCA w drzewie wyszukiwania binarnego. W drzewie wyszukiwania binarnego, korzystając z właściwości BST, możemy znaleźć LCA w czasie O(h), gdzie h jest wysokością drzewa. Taka implementacja nie jest możliwa w Binary Tree, ponieważ klucze w węzłach Binary Tree nie mają żadnej kolejności.
Być może zainteresują Cię także poniższe artykuły:
LCA przy użyciu wskaźnika nadrzędnego
Najniższy wspólny przodek w drzewie wyszukiwania binarnego.
Znajdź LCA w drzewie binarnym za pomocą RMQ
