W tym samouczku dowiesz się, jak zastosować algorytm wyszukiwania binarnego za pomocą Pythona, aby znaleźć pozycję indeksu elementu na podanej liście.
Wstęp
Wyszukiwanie binarne to algorytm pozwalający znaleźć konkretny element na liście. Załóżmy, że mamy listę tysięcy elementów i musimy uzyskać pozycję indeksu konkretnego elementu. Za pomocą algorytmu wyszukiwania binarnego możemy bardzo szybko znaleźć pozycję indeksu elementu.
Istnieje wiele algorytmów wyszukiwania, ale wśród nich najpopularniejsze jest wyszukiwanie binarne.
wyjątek rzuca java
Aby zastosować algorytm wyszukiwania binarnego, elementy na liście muszą zostać posortowane. Jeśli elementy nie są posortowane, najpierw je posortuj.
Rozumiemy koncepcję wyszukiwania binarnego.
Koncepcja wyszukiwania binarnego
W algorytmie wyszukiwania binarnego położenie elementu możemy znaleźć następującymi metodami.
- Metoda rekurencyjna
- Metoda iteracyjna
Po podejściu „dziel i zwyciężaj” następuje metoda rekurencyjna. W tej metodzie funkcja jest wywoływana wielokrotnie, aż znajdzie element na liście.
Zestaw instrukcji jest powtarzany wielokrotnie w celu znalezienia pozycji indeksu elementu w metodzie iteracyjnej. The chwila pętla służy do wykonania tego zadania.
Wyszukiwanie binarne jest bardziej efektywne niż wyszukiwanie liniowe, ponieważ nie musimy przeszukiwać każdego indeksu listy. Lista musi zostać posortowana, aby uzyskać algorytm wyszukiwania binarnego.
Przeprowadźmy krok po kroku implementację wyszukiwania binarnego.
Mamy posortowaną listę elementów i szukamy pozycji indeksu wynoszącej 45.
[12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54]
Dlatego na naszej liście umieszczamy dwa wskaźniki. Jeden wskaźnik służy do oznaczenia mniejszej wartości, tzw Niski a drugi wskaźnik służy do oznaczenia najwyższej wywoływanej wartości wysoki .
Następnie obliczamy wartość tzw środek element tablicy.
mid = (low+high)/2 Here, the low is 0 and the high is 7. mid = (0+7)/2 mid = 3 (Integer)
Teraz porównamy szukany element ze średnią wartością indeksu. W tym przypadku, 32 nie jest równe Cztery pięć. Musimy więc przeprowadzić dalsze porównania, aby znaleźć element.
Jeśli szukana liczba jest równa połowie. Potem wróć Środek w przeciwnym razie przejdź do dalszego porównania.
Liczba do przeszukania jest większa niż środek numer, porównujemy N ze środkowym elementem elementów po prawej stronie Środek i ustaw niski poziom na niski = średni + 1.
W przeciwnym razie porównaj N z element środkowy elementów po lewej stronie Środek i nastaw wysoki Do wysoki = średni - 1.
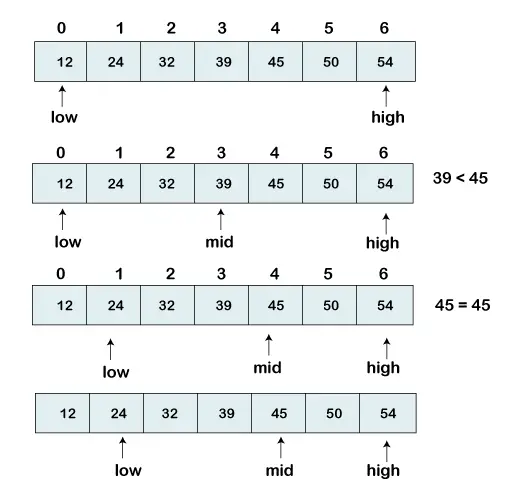
Powtarzaj aż do znalezienia szukanego numeru.
Zaimplementuj wyszukiwanie binarne w Pythonie
Najpierw implementujemy wyszukiwanie binarne metodą iteracyjną. Powtórzymy zestaw instrukcji i wykonamy iterację każdego elementu listy. Znajdziemy wartość środkową aż do zakończenia wyszukiwania.
Rozumiemy następujący program metody iteracyjnej.
polecenie make w Linuksie
Implementacja Pythona
# Iterative Binary Search Function method Python Implementation # It returns index of n in given list1 if present, # else returns -1 def binary_search(list1, n): low = 0 high = len(list1) - 1 mid = 0 while low <= 1 2 high: # for get integer result mid="(high" + low) check if n is present at list1[mid] n: high="mid" - smaller, compared to the left of else: return element was not in list, -1 initial list1 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54] function call n) !="-1:" print('element index', str(result)) list1') < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Element is present at index 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above program -</p> <ul> <li>We have created a function called <strong>binary_search()</strong> function which takes two arguments - a list to sorted and a number to be searched.</li> <li>We have declared two variables to store the lowest and highest values in the list. The low is assigned initial value to 0, <strong>high</strong> to <strong>len(list1)</strong> - 1 and mid as 0.</li> <li>Next, we have declared the <strong>while</strong> loop with the condition that the <strong>lowest</strong> is equal and smaller than the <strong>highest</strong> The while loop will iterate if the number has not been found yet.</li> <li>In the while loop, we find the mid value and compare the index value to the number we are searching for.</li> <li>If the value of the mid-index is smaller than <strong>n</strong> , we increase the mid value by 1 and assign it to The search moves to the left side.</li> <li>Otherwise, decrease the mid value and assign it to the <strong>high</strong> . The search moves to the right side.</li> <li>If the n is equal to the mid value then return <strong>mid</strong> .</li> <li>This will happen until the <strong>low</strong> is equal and smaller than the <strong>high</strong> .</li> <li>If we reach at the end of the function, then the element is not present in the list. We return -1 to the calling function.</li> </ul> <p>Let's understand the recursive method of binary search.</p> <h2>Recursive Binary Search</h2> <p>The recursion method can be used in the binary search. In this, we will define a recursive function that keeps calling itself until it meets the condition.</p> <p>Let's understand the above program using the recursive function.</p> <h3>Python Program</h3> <pre> # Python program for recursive binary search. # Returns index position of n in list1 if present, otherwise -1 def binary_search(list1, low, high, n): # Check base case for the recursive function if low n: return binary_search(list1, low, mid - 1, n) # Else the search moves to the right sublist1 else: return binary_search(list1, mid + 1, high, n) else: # Element is not available in the list1 return -1 # Test list1ay list1 = [12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54] n = 32 # Function call res = binary_search(list1, 0, len(list1)-1, n) if res != -1: print('Element is present at index', str(res)) else: print('Element is not present in list1') </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Element is present at index 2 </pre> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> </p> <p>The above program is similar to the previous program. We declared a recursive function and its base condition. The condition is the lowest value is smaller or equal to the highest value.</p> <ul> <li>We calculate the middle number as in the last program.</li> <li>We have used the <strong>if</strong> statement to proceed with the binary search.</li> <li>If the middle value equal to the number that we are looking for, the middle value is returned.</li> <li>If the middle value is less than the value, we are looking then our recursive function <strong>binary_search()</strong> again and increase the mid value by one and assign to low.</li> <li>If the middle value is greater than the value we are looking then our recursive function <strong>binary_search()</strong> again and decrease the mid value by one and assign it to low.</li> </ul> <p>In the last part, we have written our main program. It is the same as the previous program, but the only difference is that we have passed two parameters in the <strong>binary_search()</strong> function.</p> <p>This is because we can't assign the initial values to the low, high and mid in the recursive function. Every time the recursive is called the value will be reset for those variables. That will give the wrong result.</p> <h2>Complexity</h2> <p>The complexity of the binary search algorithm is <strong>O(1)</strong> for the best case. This happen if the element that element we are looking find in the first comparison. The <strong>O(logn)</strong> is the worst and the average case complexity of the binary search. This depends upon the number of searches are conducted to find the element that we are looking for.</p> <h2>Conclusion</h2> <p>A binary search algorithm is the most efficient and fast way to search an element in the list. It skips the unnecessary comparison. As the name suggests, the search is divided into two parts. It focuses on the side of list, which is close to the number that we are searching.</p> <p>We have discussed both methods to find the index position of the given number.</p> <hr></=> Wyjaśnienie:
W powyższym programie -
- Stworzyliśmy funkcję o nazwie wyszukiwanie_binarne() funkcja pobierająca dwa argumenty - listę do posortowania i liczbę do przeszukania.
- Zadeklarowaliśmy dwie zmienne do przechowywania najniższej i najwyższej wartości na liście. Niskiemu przypisuje się wartość początkową 0, wysoki Do dł.(lista1) - 1 i środek jako 0.
- Następnie zadeklarowaliśmy chwila pętlę z warunkiem, że najniższy jest równy i mniejszy niż najwyższy Pętla while wykona iterację, jeśli liczba nie została jeszcze znaleziona.
- W pętli while znajdujemy wartość środkową i porównujemy wartość indeksu z szukaną liczbą.
- Jeżeli wartość indeksu środkowego jest mniejsza niż N , zwiększamy wartość środkową o 1 i przypisujemy ją do. Wyszukiwanie przesuwa się w lewą stronę.
- W przeciwnym razie zmniejsz wartość środkową i przypisz ją do wysoki . Wyszukiwanie przesuwa się w prawą stronę.
- Jeśli n jest równe wartości środkowej, wróć Środek .
- Stanie się tak do godz Niski jest równy i mniejszy niż wysoki .
- Jeśli dotrzemy do końca funkcji, to elementu nie ma na liście. Zwracamy -1 do funkcji wywołującej.
Rozumiemy rekursywną metodę wyszukiwania binarnego.
Rekurencyjne wyszukiwanie binarne
W wyszukiwaniu binarnym można zastosować metodę rekurencji. W tym miejscu zdefiniujemy funkcję rekurencyjną, która będzie się wywoływać, dopóki nie spełni warunku.
Rozumiemy powyższy program za pomocą funkcji rekurencyjnej.
Program w Pythonie
# Python program for recursive binary search. # Returns index position of n in list1 if present, otherwise -1 def binary_search(list1, low, high, n): # Check base case for the recursive function if low n: return binary_search(list1, low, mid - 1, n) # Else the search moves to the right sublist1 else: return binary_search(list1, mid + 1, high, n) else: # Element is not available in the list1 return -1 # Test list1ay list1 = [12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54] n = 32 # Function call res = binary_search(list1, 0, len(list1)-1, n) if res != -1: print('Element is present at index', str(res)) else: print('Element is not present in list1')
Wyjście:
Element is present at index 2
Wyjaśnienie
Powyższy program jest podobny do poprzedniego programu. Zadeklarowaliśmy funkcję rekurencyjną i jej warunek podstawowy. Warunek jest taki, że najniższa wartość jest mniejsza lub równa najwyższej wartości.
- Liczbę środkową obliczamy jak w ostatnim programie.
- Skorzystaliśmy z Jeśli instrukcja, aby kontynuować wyszukiwanie binarne.
- Jeśli środkowa wartość jest równa szukanej liczbie, zwracana jest wartość środkowa.
- Jeśli środkowa wartość jest mniejsza niż wartość, szukamy wówczas naszej funkcji rekurencyjnej wyszukiwanie_binarne() ponownie i zwiększ wartość średnią o jeden i przypisz do niskiej.
- Jeśli środkowa wartość jest większa niż wartość, której szukamy, to nasza funkcja rekurencyjna wyszukiwanie_binarne() ponownie i zmniejsz wartość średnią o jeden i przypisz ją do niskiej.
W ostatniej części napisaliśmy nasz program główny. Jest taki sam jak poprzedni program, z tą tylko różnicą, że przekazaliśmy w pliku dwa parametry wyszukiwanie_binarne() funkcjonować.
Dzieje się tak, ponieważ w funkcji rekurencyjnej nie możemy przypisać wartości początkowych do niskiej, wysokiej i średniej. Za każdym razem, gdy wywoływana jest metoda rekurencyjna, wartość tych zmiennych zostanie zresetowana. To da błędny wynik.
Złożoność
Złożoność algorytmu wyszukiwania binarnego wynosi O(1) w najlepszym przypadku. Dzieje się tak, jeśli element, którego szukamy, znajdzie się w pierwszym porównaniu. The O(zaloguj się) jest najgorszą i średnią złożonością przypadku wyszukiwania binarnego. Zależy to od liczby wyszukiwań prowadzonych w celu znalezienia szukanego przez nas elementu.
Wniosek
Algorytm wyszukiwania binarnego to najskuteczniejsza i najszybsza metoda wyszukiwania elementu na liście. Pomija niepotrzebne porównania. Jak sama nazwa wskazuje, wyszukiwanie jest podzielone na dwie części. Koncentruje się na tej stronie listy, która jest bliska szukanemu numerowi.
gimp usuń znak wodny
Omówiliśmy obie metody znajdowania pozycji indeksu danej liczby.
