The instrukcja switch w C++ jest potężnym narzędziem struktura kontrolna która umożliwia uruchomienie kilku segmentów kodu w oparciu o wynik wyrażenia. Oferuje wyrafinowany i skuteczny substytut wykorzystania kolejnych instrukcje if-else-if kiedy musisz podjąć decyzję pomiędzy kilkoma możliwościami.
Instrukcja switch języka C++ wykonuje jedną instrukcję na podstawie wielu warunków. Przypomina to instrukcję drabinkową if-else-if w C++.
switch(expression){ case value1: //code to be executed; break; case value2: //code to be executed; break; ...... default: //code to be executed if all cases are not matched; break; } 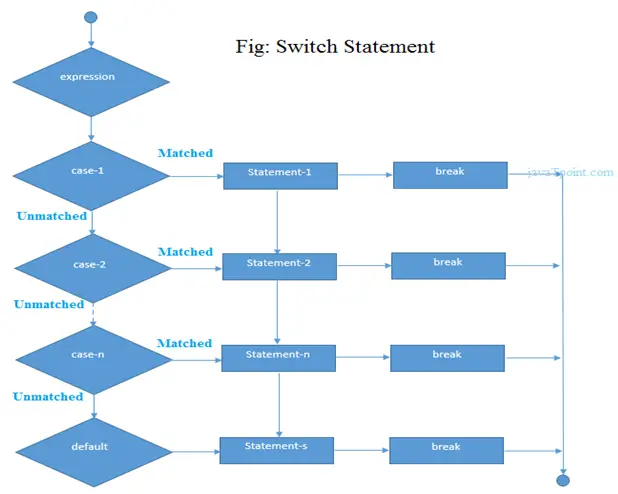
Przykład przełącznika C++
#include using namespace std; int main () { int num; cout<>num; switch (num) { case 10: cout<<'it 20 is 10'; break; case 20: cout<<'it 20'; 30: 30'; default: cout<<'not 10, or } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a number: 10 It is 10 </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a number: 55 Not 10, 20 or 30 </pre> <h2>Features of Switch Statement:</h2> <p>There are several features of the <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> in C++. Some main features of the <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> in C are as follows:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>The <strong> <em>fall-through</em> </strong> behavior of the C++ <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> is one of its key features. The control will <strong> <em>fall through</em> </strong> to the next case if a <strong> <em>break statement</em> </strong> is not used to <strong> <em>stop</em> </strong> a case block. After that, subsequent cases will be processed until a <strong> <em>break</em> </strong> is encountered or the end of the <strong> <em>switch block</em> </strong> is reached. This capability may be purposely used to share common code across several scenarios.</li> <li>The <strong> <em>switch statement's</em> </strong> capacity to simplify code readability and maintenance is one of its fundamental advantages. Comparing a sequence of <strong> <em>nested if-else statements</em> </strong> to a <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> when dealing with many situations can provide clearer, more organized code. Each case label gives the program a unique and unambiguous path to follow, improving the codebase's overall readability. It is very advantageous when working with extensive and complicated programs, where maintaining a <strong> <em>logical flow</em> </strong> is crucial.</li> <li>Another noteworthy benefit of the switch statement is <strong> <em>efficiency</em> </strong> . When done correctly, a <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> may frequently be more effective than a succession of <strong> <em>if-else-if</em> </strong> This effectiveness results from the compiler's ability to optimize the switch statement to produce more effective machine code, which might lead to a quicker execution time. It's crucial to remember that the real speed improvements may differ based on the circumstance and compiler optimizations.</li> </ol> <h2>Limitations of Switch Statement</h2> <p>There are several limitations of the <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> in C++. Some main limitations of the <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> in C are as follows:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>The <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> has several restrictions, so it's important to be aware of those as well as industry standards. For instance, the <strong> <em>switch statement's</em> </strong> expression must be of the <strong> <em>integral</em> </strong> or <strong> <em>enumeration type</em> </strong> . It limits its ability to be used with other data types like <strong> <em>strings</em> </strong> or <strong> <em>floating-point integers</em> </strong> . Additionally, variables or expressions cannot be used as case labels since each case label must reflect a constant value that is known at <strong> <em>compile-time</em> </strong> .</li> <li>It is best practice to add a default case in the <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> to guarantee thorough case coverage. Instances where none of the preceding instances match the value of the phrase are handled by this case. When none of the predetermined situations apply, including a <strong> <em>default case</em> </strong> prevents unexpected behavior and offers a clear path of action.</li> </ol> <h2>Conclusion:</h2> <p>In conclusion, the <strong> <em>C++ switch statement</em> </strong> is a flexible construct that makes it easier for programs to handle a variety of scenarios. Its explicit <strong> <em>case labels</em> </strong> and succinct syntax make code easier to comprehend and maintain, especially in situations when there are many possible outcomes. The <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> improves the organization of program logic by offering a <strong> <em>direct mapping</em> </strong> between <strong> <em>cases</em> </strong> and <strong> <em>actions</em> </strong> . </p> <p>The <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> has advantages over an <strong> <em>if-else-if ladder</em> </strong> in terms of performance since the compiler can optimize it for <strong> <em>quicker execution</em> </strong> . Developers should be aware of its restrictions, such as the need for integral or enumeration expression types and constant case values.</p> <p>It is advised to provide a default case in the <strong> <em>switch statement</em> </strong> to manage mismatched circumstances and use it efficiently and gently. Programmers may take advantage of the switch statement's advantages to create better <strong> <em>organized, effective</em> </strong> , and <strong> <em>understandable</em> </strong> C++ code by following best practices and comprehending its intricacies.</p> <hr></'it> Wyjście:
Enter a number: 55 Not 10, 20 or 30
Funkcje instrukcji Switch:
Istnieje kilka cech instrukcja switch w C++. Niektóre główne cechy instrukcja switch w C są następujące:
- The przepaść zachowanie C++ instrukcja switch jest jedną z jego kluczowych cech. Kontrola będzie nie dojść do skutku do następnego przypadku, jeśli a oświadczenie o złamaniu nie jest do tego przyzwyczajony zatrzymywać się blok spraw. Po tym terminie kolejne sprawy będą rozpatrywane do godz przerwa zostanie napotkany lub koniec blok przełączników został osiągnięty. Ta funkcja może być celowo używana do udostępniania wspólnego kodu w kilku scenariuszach.
- The instrukcja switch Możliwość uproszczenia czytelności kodu i konserwacji jest jedną z jego podstawowych zalet. Porównywanie sekwencji zagnieżdżone instrukcje if-else do instrukcja switch w przypadku wielu sytuacji może zapewnić jaśniejszy, bardziej zorganizowany kod. Każda etykieta przypadku wyznacza programowi unikalną i jednoznaczną ścieżkę do podążania, poprawiając ogólną czytelność bazy kodu. Jest to bardzo korzystne podczas pracy z rozbudowanymi i skomplikowanymi programami, gdzie utrzymanie pliku logiczny przepływ jest kluczowa.
- Kolejną godną uwagi zaletą instrukcji switch jest efektywność . Jeśli zostało to wykonane prawidłowo, a instrukcja switch często może być skuteczniejsze niż seria następujących po sobie jeśli-jeżeli-jeżeli Ta skuteczność wynika ze zdolności kompilatora do optymalizacji instrukcji switch w celu uzyskania bardziej efektywnego kodu maszynowego, co może prowadzić do szybszego czasu wykonania. Należy pamiętać, że rzeczywista poprawa szybkości może się różnić w zależności od okoliczności i optymalizacji kompilatora.
Ograniczenia instrukcji Switch
Istnieje kilka ograniczeń instrukcja switch w C++. Niektóre główne ograniczenia instrukcja switch w C są następujące:
- The instrukcja switch ma kilka ograniczeń, dlatego ważne jest, aby mieć świadomość tych, a także standardów branżowych. Na przykład instrukcja switch wyrażenie musi być typu wyczerpujący Lub typ wyliczeniowy . Ogranicza to możliwość użycia z innymi typami danych, takimi jak smyczki Lub liczby całkowite zmiennoprzecinkowe . Ponadto zmiennych i wyrażeń nie można używać jako etykiet przypadków, ponieważ każda etykieta przypadków musi odzwierciedlać stałą wartość, która jest znana pod adresem czas kompilacji .
- Najlepszą praktyką jest dodanie domyślnej wielkości liter w pliku instrukcja switch aby zagwarantować dokładne pokrycie sprawy. Przypadki, w których żadne z poprzednich wystąpień nie odpowiada wartości frazy, są obsługiwane przez ten przypadek. Jeżeli nie ma zastosowania żadna z wcześniej określonych sytuacji, w tym a domyślny przypadek zapobiega nieoczekiwanym zachowaniom i oferuje jasną ścieżkę działania.
Wniosek:
Podsumowując, Instrukcja przełącznika C++ to elastyczna konstrukcja, która ułatwia programom obsługę różnych scenariuszy. Jest wyraźny etykiety etui i zwięzła składnia sprawiają, że kod jest łatwiejszy do zrozumienia i utrzymania, szczególnie w sytuacjach, gdy istnieje wiele możliwych wyników. The instrukcja switch poprawia organizację logiki programu, oferując a mapowanie bezpośrednie między sprawy I działania .
The instrukcja switch ma przewagę nad drabina „jeśli-jeszcze-jeśli”. pod względem wydajności, ponieważ kompilator może ją zoptymalizować szybsza realizacja . Deweloperzy powinni zdawać sobie sprawę z jego ograniczeń, takich jak potrzeba stosowania typów wyrażeń całkowitych lub wyliczeniowych oraz stałych wartości wielkości liter.
Zaleca się podanie domyślnego przypadku w pliku instrukcja switch zarządzać niedopasowanymi okolicznościami i wykorzystywać je efektywnie i delikatnie. Programiści mogą wykorzystać zalety instrukcji switch, aby tworzyć lepiej zorganizowany, skuteczny , I zrozumiale Koduj C++, postępując zgodnie z najlepszymi praktykami i rozumiejąc jego zawiłości.
