Funkcja Totient Eulera Φ(n) dla wejścia n to liczba liczb w {1, 2, 3, …, n-1}, które są względnie pierwsze do n, tj. liczb, których GCD (największy wspólny dzielnik) z n jest 1.
Przykłady:
Φ(1) = 1
gcd(1, 1) wynosi 1
Φ(2) = 1
gcd(1, 2) wynosi 1, ale gcd(2, 2) wynosi 2.
Φ(3) = 2
gcd(1, 3) wynosi 1, a gcd(2, 3) wynosi 1
Φ(4) = 2
gcd(1, 4) wynosi 1, a gcd(3, 4) wynosi 1
Φ(5) = 4
gcd(1, 5) wynosi 1, gcd(2, 5) wynosi 1,
gcd(3, 5) wynosi 1, a gcd(4, 5) wynosi 1
Φ(6) = 2
gcd(1, 6) wynosi 1 i gcd(5, 6) wynosi 1,
Zalecana praktyka Funkcja Eulera Totienta Wypróbuj!
Jak obliczyć Φ(n) dla wejścia n?
A proste rozwiązanie polega na iteracji po wszystkich liczbach od 1 do n-1 i zliczeniu liczb za pomocą gcd z n jako 1. Poniżej znajduje się implementacja prostej metody obliczenia funkcji Totient Eulera dla wejściowej liczby całkowitej n.
// A simple C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Jawa // A simple java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sunnusingh>Python3 # A simple Python3 program # to calculate Euler's # Totient Function # Function to return # gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if (a == 0): return b return gcd(b % a, a) # A simple method to evaluate # Euler Totient Function def phi(n): result = 1 for i in range(2, n): if (gcd(i, n) == 1): result+=1 return result # Driver Code for n in range(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') = ', phi(n), sep = '') # This code is contributed # by Smitha>C# // A simple C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for (int n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal>JavaScript >PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi($n) { $result = 1; for ($i = 2; $i <$n; $i++) if (gcd($i, $n) == 1) $result++; return $result; } // Driver Code for ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>C++ // A simple C++ program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function #include using namespace std; // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) cout << 'phi('< Wyjście
fi(1) = 1 fi(2) = 1 fi(3) = 2 fi(4) = 2 fi(5) = 4 fi(6) = 2 fi(7) = 6 fi(8) = 4 fi( 9) = 6 fi(10) = 4
Powyższy kod wywołuje funkcję gcd O(n) razy. Złożoność czasowa funkcji gcd wynosi O(h), gdzie h jest liczbą cyfr mniejszej liczby danych dwóch liczb. Dlatego górna granica na złożoność czasu powyższego rozwiązania to O(N^2 log N) [Jak Φ może być co najwyżej Log10n cyfr we wszystkich liczbach od 1 do n]
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(log N)
Poniżej znajduje się Lepsze rozwiązanie . Pomysł opiera się na wzorze na iloczyn Eulera, który stwierdza, że wartość funkcji tocjalnych jest niższa od ogólnych czynników pierwszych iloczynu p z n.
Wzór zasadniczo mówi, że wartość Φ(n) jest równa n pomnożonemu produktowi ubocznemu (1 – 1/p) dla wszystkich czynników pierwszych p z n. Na przykład wartość Φ(6) = 6 * (1-1/2) * (1 – 1/3) = 2.
Możemy znaleźć wszystkie czynniki pierwsze, korzystając z idei użytej w Ten post.
1) Zainicjuj: wynik = n
2) Uruchom pętlę od „p” = 2 do sqrt(n), wykonaj następujące czynności dla każdego „p”.
a) Jeśli p dzieli n, to
Ustaw: wynik = wynik * (1,0 - (1,0 / (float) p));
Podziel wszystkie wystąpienia p w n.
3) Zwróć wynik
Poniżej znajduje się implementacja formuły iloczynu Eulera.
// C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function using Euler's // product formula #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and for every prime factor p, // multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) wynik -= wynik / n; //Ponieważ w zbiorze {1,2,....,n-1} wszystkie liczby są względnie pierwsze z n //jeśli n jest liczbą pierwszą, return (int)result; } // Kod sterownika int main() { int n; dla(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) <C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula #include int phi(int n) { float result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) wynik -= wynik / n; //Ponieważ w zbiorze {1,2,....,n-1} wszystkie liczby są względnie pierwsze z n //jeśli n jest liczbą pierwszą, return (int)result; } // Program sterownika do testowania powyższej funkcji int main() { int n; dla (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Jawa // Java program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n and for // every prime factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) wynik -= wynik / n; //Ponieważ w zbiorze {1,2,....,n-1} wszystkie liczby są względnie pierwsze z n //jeśli n jest liczbą pierwszą, return (int)result; } // Program sterownika do testowania powyższej funkcji public static void main(String args[]) { int n; dla (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.>Python3 # Python 3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function # using Euler's product formula def phi(n) : result = n # Initialize result as n # Consider all prime factors # of n and for every prime # factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1 / p) p = 2 while p * p<= n : # Check if p is a prime factor. if n % p == 0 : # If yes, then update n and result while n % p == 0 : n = n // p result = result * (1.0 - (1.0 / float(p))) p = p + 1 # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most one # such prime factor) if n>1 : wynik -= wynik // n #Ponieważ w zbiorze {1,2,....,n-1} wszystkie liczby są względnie pierwsze z n #if n jest liczbą pierwszą return int(result) # Sterownik program do testowania powyższej funkcji dla n w zakresie(1, 11): print('phi(', n, ') = ', phi(n)) # Ten kod został napisany # przez Nikitę Tiwari.>C# // C# program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1 / p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (float)(1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) wynik -= wynik / n; //Ponieważ w zbiorze {1,2,....,n-1} wszystkie liczby są względnie pierwsze z n //jeśli n jest liczbą pierwszą, return (int)result; } // Kod sterownika public static void Main() { int n; dla (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.>JavaScript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi(n) { // Initialize result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) wynik -= wynik / n; //Ponieważ w zbiorze {1,2,....,n-1} wszystkie liczby są względnie pierwsze z n //jeśli n jest liczbą pierwszą return parseInt(result); } // Kod kierowcy dla (niech n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi($n) { // Initialize result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n /= $p; $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $wynik -= $wynik / $n; //Ponieważ w zbiorze {1,2,....,n-1} wszystkie liczby są względnie pierwsze z n //jeśli n jest liczbą pierwszą return intertval($result); } // Kod sterownika dla ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>> Wyjście
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Fi(10) = 4
Złożoność czasowa: O(Φ n log n)
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(1)
W powyższej metodzie możemy uniknąć obliczeń zmiennoprzecinkowych. Pomysł polega na tym, aby policzyć wszystkie czynniki pierwsze i ich wielokrotności, a następnie odjąć tę liczbę od n, aby otrzymać wartość funkcji totient (czynniki pierwsze i wielokrotności czynników pierwszych nie będą miały gcd równego 1)
1) Zainicjuj wynik jako n
2) Rozważmy każdą liczbę „p” (gdzie „p” zmienia się od 2 do Φ(n)).
Jeśli p dzieli n, wykonaj następujące czynności
a) Odejmij wszystkie wielokrotności p od 1 do n [wszystkie wielokrotności p
będzie miał gcd więcej niż 1 (co najmniej p) z n]
b) Zaktualizuj n, wielokrotnie dzieląc je przez p.
3) Jeśli zredukowane n jest większe niż 1, usuń wszystkie wielokrotności
z n z wyniku.
Poniżej znajduje się implementacja powyższego algorytmu.
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and subtract their multiples // from result for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) wynik -= wynik / n; zwróć wynik; } // Kod sterownika int main() { int n; dla(n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) << endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu>C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include int phi(int n) { int result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) wynik -= wynik / n; zwróć wynik; } // Program sterownika do testowania powyższej funkcji int main() { int n; dla (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Jawa // Java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) wynik -= wynik / n; zwróć wynik; } // Kod sterownika public static void main (String[] args) { int n; dla (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by ajit>Python3 # Python3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function def phi(n): # Initialize result as n result = n; # Consider all prime factors # of n and subtract their # multiples from result p = 2; while(p * p <= n): # Check if p is a # prime factor. if (n % p == 0): # If yes, then # update n and result while (n % p == 0): n = int(n / p); result -= int(result / p); p += 1; # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most # one such prime factor) if (n>1): wynik -= int(wynik / n); zwróć wynik; # Kod sterownika dla n w zakresie (1, 11): print('phi(',n,') =', phi(n)); # Ten kod został napisany # przez mits>C# // C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and // subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) wynik -= wynik / n; zwróć wynik; } // Kod sterownika static public void Main () { int n; dla (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by akt_mit>JavaScript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi(n) { // Initialize // result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while (n % p == 0) n = parseInt(n / p); result -= parseInt(result / p); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) wynik -= parseInt(wynik / n); zwróć wynik; } // Kod kierowcy dla (niech n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed // by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi($n) { // Initialize // result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n = (int)$n / $p; $result -= (int)$result / $p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $wynik -= (int)$wynik / $n; zwróć $wynik; } // Kod sterownika dla ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(', $n,') =', phi($n), '
'; // This code is contributed // by ajit Φ>> Wyjście
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Fi(10) = 4
Złożoność czasowa: O(Φ n log n)
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(1)
Aby zrozumieć powyższy algorytm, weźmy przykład.
n = 10.
Zainicjuj: wynik = 10
2 jest czynnikiem pierwszym, więc n = n/i = 5, wynik = 5
3 nie jest czynnikiem głównym.
Pętla for zatrzymuje się po 3, ponieważ 4*4 nie jest mniejsze lub równe
do 10.
Po pętli for wynik = 5, n = 5
Ponieważ n> 1, wynik = wynik - wynik/n = 4
Niektóre interesujące właściwości funkcji Totient Eulera
1) Dla liczba pierwsza str ,
Dowód :
indeks_podciągu w sql
Przykłady:
2) Dla dwie liczby pierwsze a i b
Dowód :
Przykłady:
3) Dla liczba pierwsza str ,
Dowód :
Przykłady:
4) Dla dwie cyfry a i b
Przypadek specjalny: gcd(a, b) = 1
metody listy Java
Przykłady:
Szczególny przypadek :
5) Suma wartości funkcji totientnych wszystkich dzielników n jest równa n.
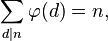
Przykłady:
n = 6
czynniki = {1, 2, 3, 6}
n =
6) Najbardziej znana i najważniejsza cecha wyraża się w Twierdzenie Eulera :
Twierdzenie stwierdza, że jeśli n i a są względnie pierwsze
(lub względnie pierwsze) dodatnie liczby całkowite
AΦ(n)Φ 1 (mod n)
The Kryptosystem RSA opiera się na tym twierdzeniu:
W szczególnym przypadku, gdy m jest liczbą pierwszą, powiedzmy p, twierdzenie Eulera zamienia się w tzw Małe twierdzenie Fermata :
Ap-1Φ 1 (wobec p)
7) Liczba generatorów skończonej grupy cyklicznej pod modulo n wynosi Φ(n) .
Powiązany artykuł:
Funkcja Totient Eulera dla wszystkich liczb mniejszych lub równych n
Zoptymalizowana funkcja Eulera Totient dla wielokrotnych ocen
Bibliografia:
http://e-maxx.ru/algo/euler_function
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
https://cp-algorithms.com/algebra/phi-function.html
http://mathcenter.oxford.memory.edu/site/math125/chineseRemainderTheorem/
