Biorąc pod uwagę A drzewo binarne zadaniem jest trzepnięcie drzewo binarne w kierunku właściwy kierunek to znaczy zgodnie ze wskazówkami zegara.
Wejście:
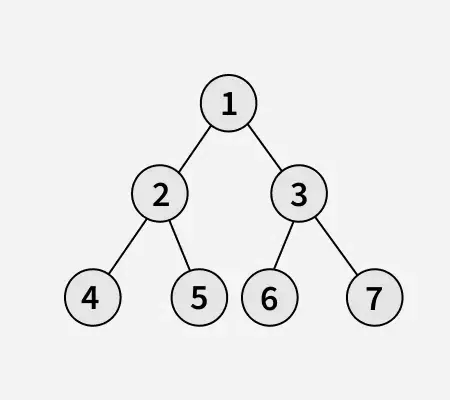
Wyjście:
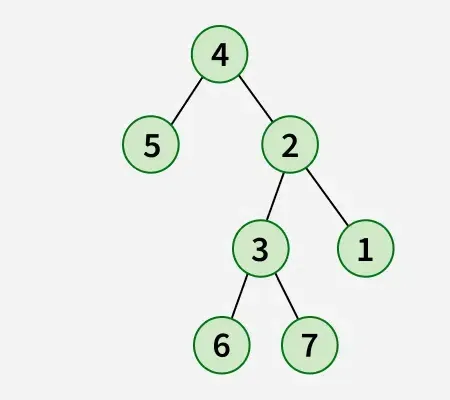
Wyjaśnienie: W operacji odwracania węzeł położony skrajnie na lewo staje się korzeniem odwróconego drzewa, jego rodzic staje się jego prawym dzieckiem, a prawe rodzeństwo staje się jego lewym dzieckiem. To samo należy zrobić rekurencyjnie dla wszystkich węzłów znajdujących się najbardziej na lewo.
Spis treści
- [Oczekiwane podejście - 1] Korzystanie z rekurencji - O(n) czasu i O(n) przestrzeni
- [Podejście oczekiwane - 2] Podejście iteracyjne - O(n) czasu i O(1) przestrzeni
[Oczekiwane podejście - 1] Korzystanie z rekurencji - O(n) czasu i O(n) przestrzeni
Pomysł jest taki rekurencyjnie odwróć drzewo binarne, zamieniając lewy I Prawidłowy poddrzewa każdego węzła. Po odwróceniu struktura drzewa zostanie odwrócona i nowy korzeń drzewa przewrócone drzewo będzie pierwotnym węzłem liścia położonym skrajnie po lewej stronie.
Poniżej znajduje się główne kod rotacji poddrzewa:
- root->lewy->lewy = korzeń->prawy
- root->lewy->prawy = korzeń
- root->lewy = NULL
- root->right = NULL
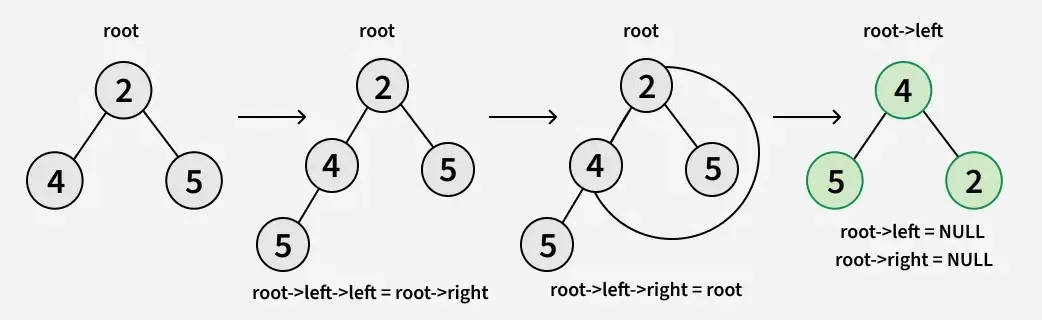
Poniżej implementacja powyższego podejścia:
C++// C++ program to flip a binary tree // using recursion #include
// Java program to flip a binary tree // using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root) { // Base cases if (root == null) return root; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root; // Recursively call the same method Node flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root.left.left = root.right; root.left.right = root; root.left = root.right = null; return flippedRoot; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void printLevelOrder(Node root) { // Base Case if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal java.util.Queue<Node> q = new java.util.LinkedList<>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.add(root); while (!q.isEmpty()) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.size(); // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.poll(); System.out.print(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.add(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.add(node.right); nodeCount--; } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(root); } }
# Python program to flip a binary # tree using recursion class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None def flipBinaryTree(root): # Base cases if root is None: return root if root.left is None and root.right is None: return root # Recursively call the same method flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left) # Rearranging main root Node after returning # from recursive call root.left.left = root.right root.left.right = root root.left = root.right = None return flippedRoot # Iterative method to do level order # traversal line by line def printLevelOrder(root): # Base Case if root is None: return # Create an empty queue for # level order traversal queue = [] queue.append(root) while queue: nodeCount = len(queue) while nodeCount > 0: node = queue.pop(0) print(node.data end=' ') if node.left is not None: queue.append(node.left) if node.right is not None: queue.append(node.right) nodeCount -= 1 print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Make a binary tree # # 1 # / # 2 3 # / # 4 5 root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.right.left = Node(4) root.right.right = Node(5) root = flipBinaryTree(root) printLevelOrder(root)
// C# program to flip a binary tree // using recursion using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node FlipBinaryTree(Node root) { if (root == null) return root; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return root; // Recursively call the same method Node flippedRoot = FlipBinaryTree(root.left); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root.left.left = root.right; root.left.right = root; root.left = root.right = null; return flippedRoot; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void PrintLevelOrder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.Enqueue(root); while (q.Count > 0) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.Count; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.Dequeue(); Console.Write(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.Enqueue(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.Enqueue(node.right); nodeCount--; } Console.WriteLine(); } } static void Main(string[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = FlipBinaryTree(root); PrintLevelOrder(root); } }
// JavaScript program to flip a binary // tree using recursion class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Method to flip the binary tree function flipBinaryTree(root) { if (root === null) return root; if (root.left === null && root.right === null) return root; // Recursively call the same method const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root.left); // Rearranging main root Node after returning // from recursive call root.left.left = root.right; root.left.right = root; root.left = root.right = null; return flippedRoot; } // Iterative method to do level order traversal // line by line function printLevelOrder(root) { if (root === null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal const queue = [root]; while (queue.length > 0) { let nodeCount = queue.length; while (nodeCount > 0) { const node = queue.shift(); console.log(node.data + ' '); if (node.left !== null) queue.push(node.left); if (node.right !== null) queue.push(node.right); nodeCount--; } console.log(); } } // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(flippedRoot);
Wyjście
2 3 1 4 5
[Oczekiwane podejście – 2] Podejście iteracyjne - O(n) czasu i O(n) przestrzeni
The rozwiązanie iteracyjne stosuje to samo podejście, co rekurencyjne jedyną rzeczą, na którą musimy zwrócić uwagę, jest oszczędność informacje o węźle, które będą nadpisany .
Poniżej implementacja powyższego podejścia:
C++// C++ program to flip a binary tree using // iterative approach #include
// Java program to flip a binary tree // using iterative approach class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node flipBinaryTree(Node root) { // Initializing the pointers to do the // swapping and storing states Node curr = root; Node next = null; Node prev = null; Node ptr = null; while (curr != null) { // Pointing the next pointer to // the current next of left next = curr.left; // Making the right child of // prev as curr left child curr.left = ptr; // Storing the right child // of curr in ptr ptr = curr.right; curr.right = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void printLevelOrder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for level // order traversal java.util.Queue<Node> q = new java.util.LinkedList<>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize // height q.add(root); while (!q.isEmpty()) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.size(); // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.poll(); System.out.print(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.add(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.add(node.right); nodeCount--; } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(root); } }
# Python program to flip a binary tree # using iterative approach class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Method to flip the binary tree # iteratively def flip_binary_tree(root): # Initializing the pointers to do # the swapping and storing states curr = root next = None prev = None ptr = None while curr is not None: # Pointing the next pointer to the # current next of left next = curr.left # Making the right child of prev # as curr left child curr.left = ptr # Storing the right child of # curr in ptr ptr = curr.right curr.right = prev prev = curr curr = next return prev # Iterative method to do level order # traversal line by line def printLevelOrder(root): if root is None: return # Create an empty queue for # level order traversal queue = [] queue.append(root) while queue: nodeCount = len(queue) while nodeCount > 0: node = queue.pop(0) print(node.data end=' ') if node.left is not None: queue.append(node.left) if node.right is not None: queue.append(node.right) nodeCount -= 1 print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Make a binary tree # # 1 # / # 2 3 # / # 4 5 root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.right.left = Node(4) root.right.right = Node(5) root = flip_binary_tree(root) printLevelOrder(root)
// C# program to flip a binary tree // using iterative approach using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Method to flip the binary tree static Node FlipBinaryTree(Node root) { // Initializing the pointers to // do the swapping and storing states Node curr = root; Node next = null; Node prev = null; Node ptr = null; while (curr != null) { // Pointing the next pointer to // the current next of left next = curr.left; // Making the right child of prev // as curr left child curr.left = ptr; // Storing the right child // of curr in ptr ptr = curr.right; curr.right = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line static void PrintLevelOrder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty queue for // level order traversal Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.Enqueue(root); while (q.Count > 0) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level int nodeCount = q.Count; // Dequeue all nodes of current level // and Enqueue all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node node = q.Dequeue(); Console.Write(node.data + ' '); if (node.left != null) q.Enqueue(node.left); if (node.right != null) q.Enqueue(node.right); nodeCount--; } Console.WriteLine(); } } static void Main(string[] args) { // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); root = FlipBinaryTree(root); PrintLevelOrder(root); } }
// JavaScript program to flip a binary // tree using iterative approach class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function flipBinaryTree(root) { // Initializing the pointers to do the // swapping and storing states let curr = root; let next = null; let prev = null; let ptr = null; while (curr !== null) { // Pointing the next pointer to the // current next of left next = curr.left; // Making the right child of prev // as curr left child curr.left = ptr; // Storing the right child of // curr in ptr ptr = curr.right; curr.right = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } // Iterative method to do level order // traversal line by line function printLevelOrder(root) { if (root === null) return; // Create an empty queue for // level order traversal const queue = [root]; while (queue.length > 0) { let nodeCount = queue.length; while (nodeCount > 0) { const node = queue.shift(); console.log(node.data + ' '); if (node.left !== null) queue.push(node.left); if (node.right !== null) queue.push(node.right); nodeCount--; } console.log(); } } // Make a binary tree // // 1 // / // 2 3 // / // 4 5 const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.right.left = new Node(4); root.right.right = new Node(5); const flippedRoot = flipBinaryTree(root); printLevelOrder(flippedRoot);
Wyjście
2 3 1 4 5



