The funkcja free() w C służy do zwalniania lub cofania alokacji dynamicznie przydzielonej pamięci i pomaga w zmniejszeniu marnotrawstwa pamięci. The C za darmo() funkcji nie można użyć do zwolnienia pamięci przydzielonej statycznie (np. zmiennych lokalnych) ani pamięci przydzielonej na stosie. Można jej używać wyłącznie do zwalniania pamięci sterty przydzielonej wcześniej za pomocą funkcji malloc(), calloc() i realloc().
Wewnątrz zdefiniowana jest funkcja free(). plik nagłówkowy.
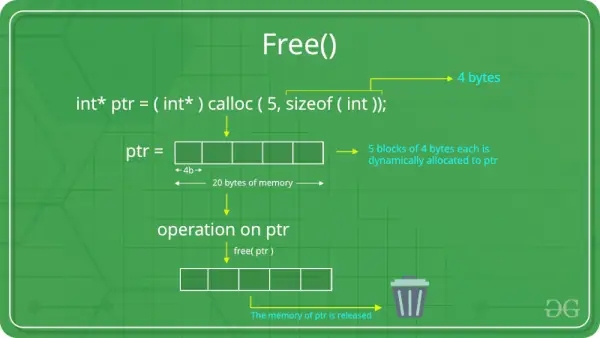
Funkcja C free().
Składnia funkcji free() w C
void free (void * ptr );>
Parametry
- ptr jest wskaźnikiem do bloku pamięci, który należy zwolnić lub cofnąć alokację.
Wartość zwracana
- Funkcja free() nie zwraca żadnej wartości.
Przykłady free()
Przykład 1:
Poniższy program w języku C ilustruje użycie metody kaloc() funkcja dynamicznej alokacji pamięci i bezpłatny() funkcję zwalniającą tę pamięć.
C
Java elseif
// C program to demonstrate use of> // free() function using calloc()> #include> #include> int> main()> {> >// This pointer ptr will hold the> >// base address of the block created> >int>* ptr;> >int> n = 5;> >// Get the number of elements for the array> >printf>(>'Enter number of Elements: %d
'>, n);> >scanf>(>'%d'>, &n);> >// Dynamically allocate memory using calloc()> >ptr = (>int>*)>calloc>(n,>sizeof>(>int>));> >// Check if the memory has been successfully> >// allocated by calloc() or not> >if> (ptr == NULL) {> >printf>(>'Memory not allocated
'>);> >exit>(0);> >}> >// Memory has been Successfully allocated using calloc()> >printf>(>'Successfully allocated the memory using '> >'calloc().
'>);> >// Free the memory> >free>(ptr);> >printf>(>'Calloc Memory Successfully freed.'>);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>Wyjście
Enter number of Elements: 5 Successfully allocated the memory using calloc(). Calloc Memory Successfully freed.>
Przykład 2:
Poniższy program w języku C ilustruje użycie metody malloc() funkcja dynamicznej alokacji pamięci i bezpłatny() funkcję zwalniającą tę pamięć.
C
// C program to demonstrate use of> // free() function using malloc()> #include> #include> int> main()> {> >// This pointer ptr will hold the> >// base address of the block created> >int>* ptr;> >int> n = 5;> >// Get the number of elements for the array> >printf>(>'Enter number of Elements: %d
'>, n);> >scanf>(>'%d'>, &n);> >// Dynamically allocate memory using malloc()> >ptr = (>int>*)>malloc>(n *>sizeof>(>int>));> >// Check if the memory has been successfully> >// allocated by malloc() or not> >if> (ptr == NULL) {> >printf>(>'Memory not allocated
'>);> >exit>(0);> >}> >// Memory has been Successfully allocated using malloc()> >printf>(>'Successfully allocated the memory using '> >'malloc().
'>);> >// Free the memory> >free>(ptr);> >printf>(>'Malloc Memory Successfully freed.'>);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
usuń pierwszy znak w programie ExcelWyjście
Enter number of Elements: 5 Successfully allocated the memory using malloc(). Malloc Memory Successfully freed.>
