Biorąc pod uwagę pierwiastek a Drzewo wyszukiwania binarnego i liczbę całkowitą k . Zadanie polega na odnalezieniu największa liczba czyli w drzewie wyszukiwania binarnego mniej niż Lub równy do k, jeśli taki element nie istnieje, wydrukuj -1.
Przykłady:
Wejście:
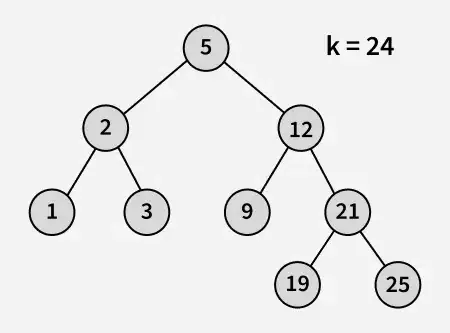
Wyjście : 21
Wyjaśnienie : 19 i 25 to dwie liczby najbliższe 21, a 19 to największa liczba o wartości mniejszej lub równej 21.
Wejście: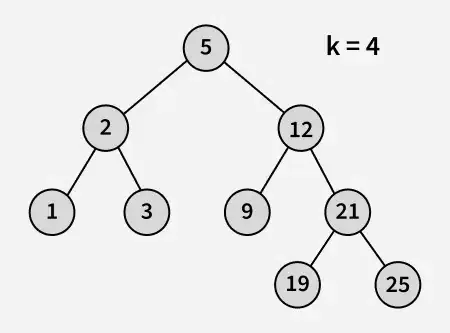
Wyjście : 3
Wyjaśnienie : 3 i 5 to dwie liczby najbliższe 4, a 3 to największa liczba o wartości mniejszej lub równej 4.
Spis treści
- [Podejście naiwne] Korzystanie z rekurencji - czas O(h) i przestrzeń O(h).
- [Podejście oczekiwane] Przy użyciu iteracji – czas O(h) i przestrzeń O(1).
[Podejście naiwne] Korzystanie z rekurencji - czas O(h) i przestrzeń O(h).
C++Pomysł jest taki, żeby zacząć od źródło i porównaj jego wartość z k. Jeśli wartość węzła jest większa niż k, przejdź do lewego poddrzewa. W przeciwnym razie znajdź wartość największej liczby mniejszą niż równa k w prawe poddrzewo . Jeśli prawe poddrzewo zwróci -1 (co oznacza, że taka wartość nie istnieje), zwróć wartość bieżącego węzła. W przeciwnym razie zwróć wartość zwróconą przez prawe poddrzewo (ponieważ będzie większa niż wartość bieżącego węzła, ale mniejsza niż równa k).
przykłady kodu w języku c#
// C++ code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion #include
// Java code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int findMaxFork(Node root int k) { // Base cases if (root == null) return -1; if (root.data == k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { int x = findMaxFork(root.right k); if (x == -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k); } public static void main(String[] args) { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); System.out.println(findMaxFork(root k)); } }
# Python code to find the largest value # smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node: def __init__(self val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None # function to find max value less than k def findMaxFork(root k): # Base cases if root is None: return -1 if root.data == k: return k # If root's value is smaller # try in right subtree elif root.data < k: x = findMaxFork(root.right k) if x == -1: return root.data else: return x # If root's data is greater # return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k) if __name__ == '__main__': k = 24 # creating following BST # # 5 # / # 2 12 # / / # 1 3 9 21 # / # 19 25 root = Node(5) root.left = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(1) root.left.right = Node(3) root.right = Node(12) root.right.left = Node(9) root.right.right = Node(21) root.right.right.left = Node(19) root.right.right.right = Node(25) print(findMaxFork(root k))
// C# code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int FindMaxFork(Node root int k) { // Base cases if (root == null) return -1; if (root.data == k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { int x = FindMaxFork(root.right k); if (x == -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return FindMaxFork(root.left k); } static void Main() { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); Console.WriteLine(FindMaxFork(root k)); } }
// JavaScript code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to find max value less than k function findMaxFork(root k) { // Base cases if (root === null) return -1; if (root.data === k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { let x = findMaxFork(root.right k); if (x === -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k); } let k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); console.log(findMaxFork(root k));
Wyjście
21
[Podejście oczekiwane] Przy użyciu iteracji – czas O(h) i przestrzeń O(1).
C++Pomysł jest taki, żeby zacząć od źródło i porównaj jego wartość z k . Jeśli wartość węzła wynosi <= k zaktualizuj wartość wyniku do wartości root i przejdź do Prawidłowy poddrzewo w innym przypadku przejdź do lewy poddrzewo. Przez iteracyjnie stosując tę operację we wszystkich węzłach, możemy zminimalizować przestrzeń potrzebną do rekurencja stos.
// C++ code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion #include
// Java code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int findMaxFork(Node root int k) { int result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root != null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); System.out.println(findMaxFork(root k)); } }
# Python code to find the largest value # smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node: def __init__(self val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None # function to find max value less than k def findMaxFork(root k): result = -1 # Start from root and keep looking for larger while root is not None: # If root is smaller go to right side if root.data <= k: result = root.data root = root.right # If root is greater go to left side else: root = root.left return result if __name__ == '__main__': k = 24 # creating following BST # # 5 # / # 2 12 # / / # 1 3 9 21 # / # 19 25 root = Node(5) root.left = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(1) root.left.right = Node(3) root.right = Node(12) root.right.left = Node(9) root.right.right = Node(21) root.right.right.left = Node(19) root.right.right.right = Node(25) print(findMaxFork(root k))
// C# code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int FindMaxFork(Node root int k) { int result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root != null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } static void Main() { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); Console.WriteLine(FindMaxFork(root k)); } }
// JavaScript code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to find max value less than k function findMaxFork(root k) { let result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root !== null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } let k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); console.log(findMaxFork(root k));
Wyjście
21Utwórz quiz


