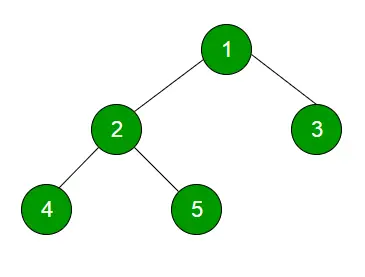
Przechodzenie przez poziom zamówienia technika jest definiowana jako metoda przechodzenia przez drzewo w taki sposób, że wszystkie węzły obecne na tym samym poziomie są całkowicie przemierzane przed przejściem na następny poziom.
Przykład:
Zalecana praktyka Przechodzenie przez kolejne poziomy Wypróbuj!Wejście:
Wyjście:
1
23
Cztery pięć
Jak działa przechodzenie przez poziomy?
Główną ideą przejścia rzędu poziomów jest przejście przez wszystkie węzły niższego poziomu przed przejściem do któregokolwiek z węzłów wyższego poziomu. Można to zrobić na jeden z następujących sposobów:
- naiwny (znalezienie wysokości drzewa i przejście każdego poziomu i wydrukowanie węzłów tego poziomu)
- efektywnie korzystając z kolejki.
Przechodzenie przez kolejność poziomów (podejście naiwne):
Znajdować wysokość drzewa. Następnie dla każdego poziomu uruchom funkcję rekurencyjną, utrzymując bieżącą wysokość. Ilekroć poziom węzła jest zgodny, wydrukuj ten węzeł.
Poniżej implementacja powyższego podejścia:
C++ // Recursive CPP program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include using namespace std; // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child class node { public: int data; node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level); int height(node* node); node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) cout << root->dane<< ' '; else if (level>1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, poziom - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->prawy, poziom - 1); } } // Oblicz 'wysokość' drzewa -- liczbę // węzłów na najdłuższej ścieżce od węzła głównego // do najdalszego węzła liścia. int wysokość(węzeł* węzeł) { if (węzeł == NULL) return 0; else { // Oblicz wysokość każdego poddrzewa int lheight = wysokość(węzeł->left); int rheight = wysokość (węzeł->prawo); // Użyj większego if (lheight> rheight) { return (lheight + 1); } else { return (prawo + 1); } } } // Funkcja pomocnicza, która // przydziela nowy węzeł z podanymi danymi i // NULL lewym i prawym wskaźnikiem. węzeł* nowyWęzeł(int dane) { węzeł* Węzeł = nowy węzeł(); Węzeł->dane = dane; Węzeł->lewy = NULL; Węzeł->prawy = NULL; powrót (węzeł); } // Kod sterownika int main() { węzeł* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->lewy->lewy = newNode(4); root->lewy->prawy = newNode(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra> C // Recursive C program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include #include // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level); int height(struct node* node); struct node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) printf('%d ', root->dane); else if (poziom> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, poziom - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->prawy, poziom - 1); } } // Oblicz 'wysokość' drzewa -- liczbę // węzłów na najdłuższej ścieżce od węzła głównego // w dół do najdalszego węzła liścia int height(struct node* node) { if (node == NULL) zwróć 0; else { // Oblicz wysokość każdego poddrzewa int lheight = wysokość(węzeł->left); int rheight = wysokość (węzeł->prawo); // Użyj większego if (lheight> rheight) return (lheight + 1); w przeciwnym razie zwróć (prawo + 1); } } // Funkcja pomocnicza, która przydziela nowy węzeł z // podanymi danymi i wskaźnikami lewego i prawego NULL. węzeł struktury* newNode(int dane) { węzeł struktury* węzeł = (węzeł struktury*)malloc(rozmiar(węzeł struktury)); węzeł->dane = dane; węzeł->lewy = NULL; węzeł->prawy = NULL; powrót (węzeł); } // Program sterownika do testowania powyższych funkcji int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->lewy->lewy = newNode(4); root->lewy->prawy = newNode(5); printf('Przechodzenie przez porządek poziomów w drzewie binarnym to
'); printLevelOrder(root); zwróć 0; }> Jawa // Recursive Java program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class BinaryTree { // Root of the Binary Tree Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order traversal of tree void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number of // nodes along the longest path from the root node // down to the farthest leaf node. int height(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>rheight) return (lheight + 1); w przeciwnym razie zwróć (prawo + 1); } } // Drukuj węzły na bieżącym poziomie void printCurrentLevel(Korzeń węzła, poziom int) { if (root == null) return; if (poziom == 1) System.out.print(root.data + ' '); else if (poziom> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, poziom - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, poziom - 1); } } // Program sterownika do testowania powyższych funkcji public static void main(String args[]) { Drzewo BinaryTree = nowe Drzewo BinaryTree(); drzewo.root = nowy węzeł(1); drzewo.root.left = nowy węzeł(2); drzewo.root.right = nowy węzeł(3); drzewo.root.left.left = nowy węzeł(4); drzewo.root.left.right = nowy węzeł(5); System.out.println('Przechodzenie przez porządek poziomów' + 'drzewo binarne to '); drzewo.printLevelOrder(); } }> Pyton # Recursive Python program for level # order traversal of Binary Tree # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Function to print level order traversal of tree def printLevelOrder(root): h = height(root) for i in range(1, h+1): printCurrentLevel(root, i) # Print nodes at a current level def printCurrentLevel(root, level): if root is None: return if level == 1: print(root.data, end=' ') elif level>1: printCurrentLevel(root.left, poziom-1) printCurrentLevel(root.right, poziom-1) # Oblicz wysokość drzewa — liczbę węzłów # na najdłuższej ścieżce od węzła głównego do # najdalszego liścia node def wysokość(węzeł): jeśli węzeł to Brak: return 0 else: # Oblicz wysokość każdego poddrzewa lheight = wysokość (węzeł.lewy) rheight = wysokość(węzeł.prawy) # Użyj większego, jeśli lheight> rheight: return lheight+1 else: return rheight+1 # Program sterownika do testowania powyższej funkcji if __name__ == '__main__': root = Węzeł(1) root.left = Węzeł(2) root.right = Węzeł(3) root. left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) print('Przechodzenie według kolejności poziomów w drzewie binarnym to -') printLevelOrder(root) # Ten kod jest autorstwa Nikhila Kumara Singha(nickzuck_007)> C# // Recursive c# program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree using System; // Class containing left and right // child of current node and key value public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class GFG { // Root of the Binary Tree public Node root; public void BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order // traversal of tree public virtual void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) { printCurrentLevel(root, i); } } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- // the number of nodes along the longest // path from the root node down to the // farthest leaf node. public virtual int height(Node root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>rheight) { return (lheight + 1); } else { return (prawo + 1); } } } // Drukuj węzły na bieżącym poziomie public virtual void printCurrentLevel(Korzeń węzła, poziom int) { if (root == null) { return; } if (poziom == 1) { Console.Write(root.data + ' '); } else if (poziom> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, poziom - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, poziom - 1); } } // Kod sterownika public static void Main(string[] args) { Drzewo GFG = nowy GFG(); drzewo.root = nowy węzeł(1); drzewo.root.left = nowy węzeł(2); drzewo.root.right = nowy węzeł(3); drzewo.root.left.left = nowy węzeł(4); drzewo.root.left.right = nowy węzeł(5); Console.WriteLine('Przechodzenie przez porządek poziomów ' + 'drzewa binarnego to '); drzewo.printLevelOrder(); } } // Ten kod pochodzi od Shrikant13> JavaScript // Recursive javascript program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Root of the Binary Tree var root= null; // Function to print level order traversal of tree function printLevelOrder() { var h = height(root); var i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number // of nodes along the longest path // from the root node down to the farthest leaf node. function height(root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree var lheight = height(root.left); var rheight = height(root.right); // Use the larger one if (lheight>rheight) return (lheight + 1); w przeciwnym razie zwróć (prawo + 1); } } // Drukuj węzły na bieżącym poziomie funkcja printCurrentLevel(root , poziom) { if (root == null) return; if (poziom == 1) console.log(root.data + ' '); else if (poziom> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, poziom - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, poziom - 1); } } // Program sterownika do testowania powyższych funkcji root = new Node(1); root.left = nowy węzeł(2); root.right = nowy węzeł(3); root.left.left = nowy węzeł(4); root.left.right = nowy węzeł(5); console.log('Przechodzenie według kolejności poziomów drzewa binarnego to '); printLevelOrder(); // Ten kod został napisany przez umadevi9616> Wyjście
Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
Złożoność czasowa: O(N), gdzie N jest liczbą węzłów w skośnym drzewie.
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(1) Jeśli rozważany jest stos rekurencji, używana przestrzeń to O(N).
utwórz wątek Java
Kolejność poziomów przy użyciu Kolejka
Musimy odwiedzić węzły na niższym poziomie przed jakimkolwiek węzłem na wyższym poziomie. Pomysł ten jest bardzo podobny do kolejki. Wsuń węzły niższego poziomu do kolejki. Kiedy odwiedzany jest dowolny węzeł, usuń ten węzeł z kolejki i wypchnij dziecko tego węzła do kolejki.
Zapewnia to, że węzeł niższego poziomu zostanie odwiedzony przed jakimkolwiek węzłem wyższego poziomu.
Poniżej znajduje się implementacja powyższego podejścia:
C++ // C++ program to print level order traversal #include using namespace std; // A Binary Tree Node struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; }; // Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree void printLevelOrder(Node* root) { // Base Case if (root == NULL) return; // Create an empty queue for level order traversal queueQ; // Umieść w kolejce katalog główny i zainicjuj wysokość q.push(root); while (q.empty() == false) { // Wydrukuj początek kolejki i usuń go z kolejki Węzeł* węzeł = q.front(); cout<< node->dane<< ' '; q.pop(); // Enqueue left child if (node->lewo != NULL) q.push(węzeł->lewo); // Umieść w kolejce prawe dziecko if (node->right != NULL) q.push(node->right); } } // Funkcja narzędziowa do tworzenia nowego węzła drzewa Node* newNode(int data) { Node* temp = new Node; temp->dane = dane; temp->lewo = temp->prawo = NULL; temperatura powrotu; } // Program sterownika do testowania powyższych funkcji int main() { // Stwórzmy drzewo binarne pokazane na powyższym schemacie Węzeł* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->lewy->lewy = newNode(4); root->lewy->prawy = newNode(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; }> C // Iterative Queue based C program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree #include #include #define MAX_Q_SIZE 500 // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node* left; struct node* right; }; // Function prototypes struct node** createQueue(int*, int*); void enQueue(struct node**, int*, struct node*); struct node* deQueue(struct node**, int*); // Given a binary tree, print its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int rear, front; struct node** queue = createQueue(&front, &rear); struct node* temp_node = root; while (temp_node) { printf('%d ', temp_node->dane); // Umieść w kolejce lewe dziecko if (temp_node->left) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->left); // Umieść w kolejce prawe dziecko if (temp_node->right) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->right); // Usuń węzeł z kolejki i ustaw go jako temp_node temp_node = deQueue(queue, &front); } } // Funkcje użytkowe struct węzeł** createQueue(int* przód, int* tył) { węzeł struct** kolejka = (węzeł struct**)malloc( sizeof(węzeł struct*) * MAX_Q_SIZE); *przód = *tył = 0; kolejka powrotna; } void enQueue(węzeł struktury** kolejka, int* tył, węzeł struktury* nowy_węzeł) { kolejka[*tył] = nowy_węzeł; (*tył)++; } węzeł struktury* deQueue(węzeł struktury** kolejka, int* przód) { (*front)++; kolejka powrotna[*front - 1]; } // Funkcja pomocnicza, która przydziela nowy węzeł z // podanymi danymi i wskaźnikami lewego i prawego NULL. węzeł struktury* newNode(int dane) { węzeł struktury* węzeł = (węzeł struktury*)malloc(rozmiar(węzeł struktury)); węzeł->dane = dane; węzeł->lewy = NULL; węzeł->prawy = NULL; powrót (węzeł); } // Program sterownika do testowania powyższych funkcji int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->lewy->lewy = newNode(4); root->lewy->prawy = newNode(5); printf('Przechodzenie przez porządek poziomów w drzewie binarnym to
'); printLevelOrder(root); zwróć 0; }> Jawa // Iterative Queue based Java program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; // Class to represent Tree node class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuekolejka = nowa lista połączona(); kolejka.add(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // poll() usuwa bieżący nagłówek. Węzeł tempNode = kolejka.poll(); System.out.print(tempNode.data + ' '); // Umieść w kolejce lewe dziecko if (tempNode.left != null) { kolejka.add(tempNode.left); } // Umieść w kolejce prawe dziecko if (tempNode.right != null) { kolejka.add(tempNode.right); } } } public static void main(String args[]) { // Tworzenie drzewa binarnego i wprowadzanie // węzłów BinaryTree poziom_drzewa = new BinaryTree(); poziom drzewa.root = nowy węzeł(1); poziom drzewa.root.left = nowy węzeł(2); poziom drzewa.root.right = nowy węzeł(3); poziom drzewa.root.left.left = nowy węzeł(4); poziom drzewa.root.left.right = nowy węzeł(5); System.out.println('Przechodzenie według kolejności poziomów drzewa binarnego to - '); poziom_drzewa.printLevelOrder(); } }> Pyton # Python program to print level # order traversal using Queue # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Iterative Method to print the # height of a binary tree def printLevelOrder(root): # Base Case if root is None: return # Create an empty queue # for level order traversal queue = [] # Enqueue Root and initialize height queue.append(root) while(len(queue)>0): # Wydrukuj początek kolejki i # usuń go z kolejki print(queue[0].data, end=' ') node = kolejka.pop(0) # Umieść w kolejce lewe dziecko, jeśli node.left nie jest Brak: kolejka.append(node.left) # Umieść w kolejce prawe dziecko, jeśli node.right nie jest Brak: kolejka.append(node.right) # Program sterownika do testowania powyższej funkcji if __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1 ) root.left = Węzeł(2) root.right = Węzeł(3) root.left.left = Węzeł(4) root.left.right = Węzeł(5) print('Porządek poziomów Przechodzenie drzewa binarnego to - ') printLevelOrder(root) # Ten kod jest autorstwa Nikhila Kumara Singha (nickzuck_007)> C# // Iterative Queue based C# program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Class to represent Tree node public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal public class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order using // array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuekolejka = nowa kolejka(); kolejka.Enqueue(root); while (queue.Count != 0) { Węzeł tempNode = kolejka.Dequeue(); Console.Write(tempNode.data + ' '); // Umieść w kolejce lewe dziecko if (tempNode.left != null) { kolejka.Enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Umieść w kolejce prawe dziecko if (tempNode.right != null) { kolejka.Enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Kod sterownika public static void Main() { // Tworzenie drzewa binarnego i wprowadzanie // węzłów BinaryTree poziom_drzewa = new BinaryTree(); poziom drzewa.root = nowy węzeł(1); poziom drzewa.root.left = nowy węzeł(2); poziom drzewa.root.right = nowy węzeł(3); poziom drzewa.root.left.left = nowy węzeł(4); poziom drzewa.root.left.right = nowy węzeł(5); Console.WriteLine('Przechodzenie przez porządek poziomów ' + 'drzewa binarnego to - '); poziom_drzewa.printLevelOrder(); } } // Ten kod został napisany przez PrinciRaj1992> JavaScript class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Class to represent a deque (double-ended queue) class Deque { constructor() { this.queue = []; } // Method to add an element to the end of the queue enqueue(item) { this.queue.push(item); } // Method to remove and return the first element of the queue dequeue() { return this.queue.shift(); } // Method to check if the queue is empty isEmpty() { return this.queue.length === 0; } } // Function to perform level order traversal of a binary tree function printLevelOrder(root) { // Create a deque to store nodes for traversal const queue = new Deque(); // Add the root node to the queue queue.enqueue(root); // Continue traversal until the queue is empty while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // Remove and get the first node from the queue const tempNode = queue.dequeue(); // Print the data of the current node console.log(tempNode.data + ' '); // Enqueue the left child if it exists if (tempNode.left !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Enqueue the right child if it exists if (tempNode.right !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Create a binary tree and enter the nodes const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); // Print the level order traversal of the binary tree console.log('Level order traversal of binary tree is - '); printLevelOrder(root);> Wyjście
Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
Złożoność czasowa: O(N) gdzie N jest liczbą węzłów w drzewie binarnym.
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(N) gdzie N jest liczbą węzłów w drzewie binarnym.