 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }Mając zbiór punktów as i linię as ax+by+c = 0. Musimy znaleźć punkt na danej prostej, dla którego suma odległości od danego zbioru punktów jest minimalna.
Przykład:
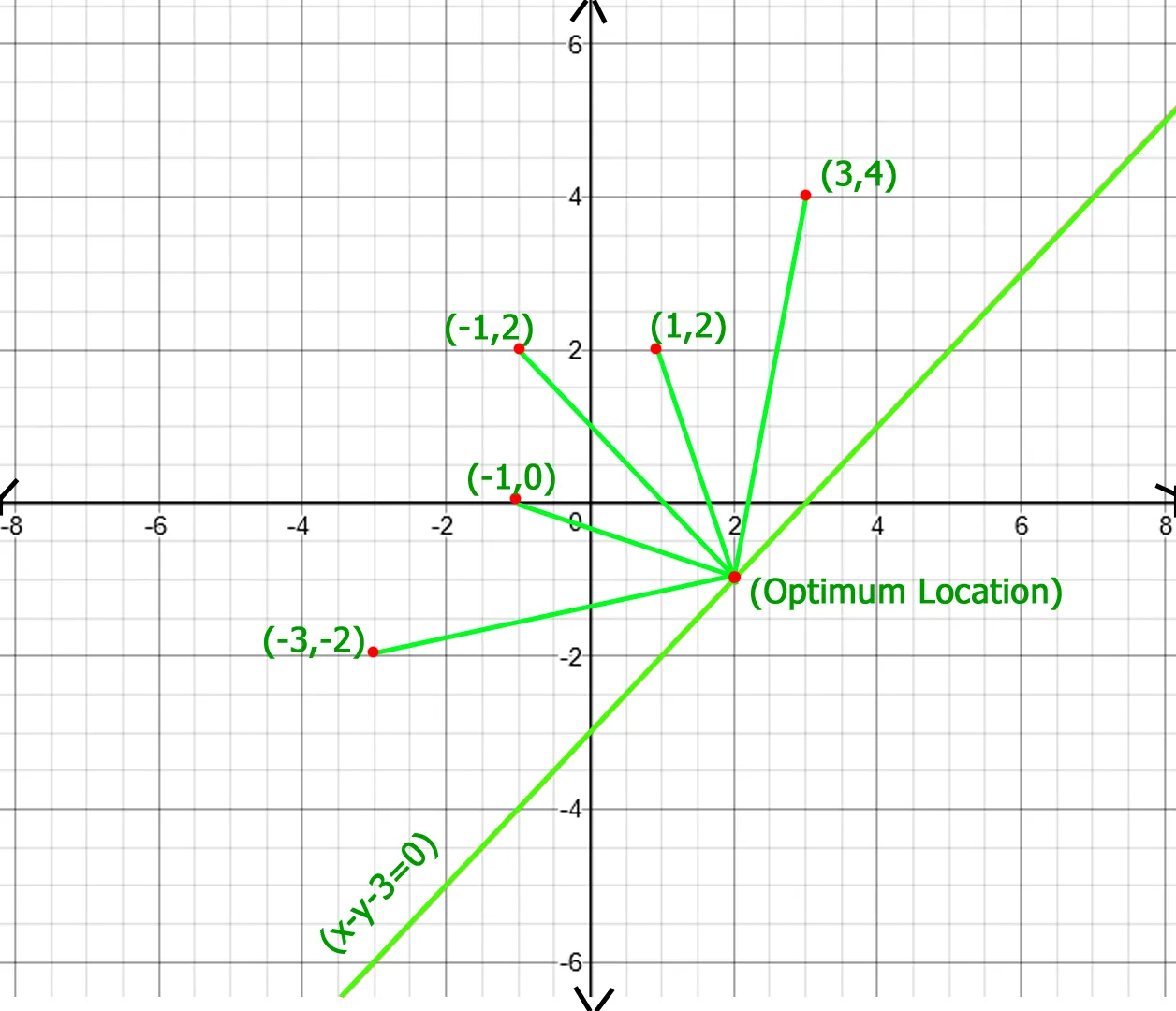
In above figure optimum location of point of x - y - 3 = 0 line is (2 -1) whose total distance with other points is 20.77 which is minimum obtainable total distance.Recommended Practice Optymalna lokalizacja punktu w celu zminimalizowania całkowitej odległości Spróbuj!
Jeśli weźmiemy jeden punkt na danej linii w nieskończonej odległości, wówczas całkowity koszt odległości będzie nieskończony, teraz, gdy przesuniemy ten punkt na linii w kierunku danych punktów, całkowity koszt odległości zacznie maleć, a po pewnym czasie ponownie zacznie rosnąć, aż do nieskończoności na drugim nieskończonym końcu linii, więc krzywa kosztu odległości wygląda jak krzywa U i musimy znaleźć dolną wartość tej krzywej U.
Ponieważ krzywa U nie rośnie ani nie ma monotonicznie, nie możemy użyć wyszukiwania binarnego do znalezienia najniższego punktu, użyjemy wyszukiwania trójskładnikowego do znalezienia najniższego punktu. Przeszukiwanie trójskładnikowe pomija jedną trzecią przestrzeni poszukiwań w każdej iteracji. Możesz przeczytać więcej o wyszukiwaniu trójskładnikowym Tutaj .
Zatem rozwiązanie przebiega w następujący sposób. Zaczynamy od wartości low i high inicjowanych odpowiednio jako najmniejsze i największe wartości, następnie rozpoczynamy iterację w każdej iteracji, obliczamy dwie środkowe mid1 i mid2, które reprezentują 1/3 i 2/3 pozycję w przestrzeni poszukiwań. Obliczamy całkowitą odległość wszystkich punktów z mid1 i mid2 i aktualizujemy niski lub wysoki, porównując te koszty odległości. Ta iteracja jest kontynuowana, aż niski i wysoki staną się w przybliżeniu równe.
C++// C/C++ program to find optimum location and total cost #include
// A Java program to find optimum location // and total cost class GFG { static double sq(double x) { return ((x) * (x)); } static int EPS = (int)(1e-6) + 1; static int N = 5; // structure defining a point static class point { int x y; point() {} public point(int x int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } }; // structure defining a line of ax + by + c = 0 form static class line { int a b c; public line(int a int b int c) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; } }; // method to get distance of point (x y) from point p static double dist(double x double y point p) { return Math.sqrt(sq(x - p.x) + sq(y - p.y)); } /* Utility method to compute total distance all points when choose point on given line has x-coordinate value as X */ static double compute(point p[] int n line l double X) { double res = 0; // calculating Y of chosen point by line equation double Y = -1 * (l.c + l.a * X) / l.b; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) res += dist(X Y p[i]); return res; } // Utility method to find minimum total distance static double findOptimumCostUtil(point p[] int n line l) { double low = -1e6; double high = 1e6; // loop until difference between low and high // become less than EPS while ((high - low) > EPS) { // mid1 and mid2 are representative x // co-ordiantes of search space double mid1 = low + (high - low) / 3; double mid2 = high - (high - low) / 3; double dist1 = compute(p n l mid1); double dist2 = compute(p n l mid2); // if mid2 point gives more total distance // skip third part if (dist1 < dist2) high = mid2; // if mid1 point gives more total distance // skip first part else low = mid1; } // compute optimum distance cost by sending average // of low and high as X return compute(p n l (low + high) / 2); } // method to find optimum cost static double findOptimumCost(int points[][] line l) { point[] p = new point[N]; // converting 2D array input to point array for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) p[i] = new point(points[i][0] points[i][1]); return findOptimumCostUtil(p N l); } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { line l = new line(1 -1 -3); int points[][] = { { -3 -2 } { -1 0 } { -1 2 } { 1 2 } { 3 4 } }; System.out.println(findOptimumCost(points l)); } } // This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
# A Python3 program to find optimum location # and total cost import math class Optimum_distance: # Class defining a point class Point: def __init__(self x y): self.x = x self.y = y # Class defining a line of ax + by + c = 0 form class Line: def __init__(self a b c): self.a = a self.b = b self.c = c # Method to get distance of point # (x y) from point p def dist(self x y p): return math.sqrt((x - p.x) ** 2 + (y - p.y) ** 2) # Utility method to compute total distance # all points when choose point on given # line has x-coordinate value as X def compute(self p n l x): res = 0 y = -1 * (l.a*x + l.c) / l.b # Calculating Y of chosen point # by line equation for i in range(n): res += self.dist(x y p[i]) return res # Utility method to find minimum total distance def find_Optimum_cost_untill(self p n l): low = -1e6 high = 1e6 eps = 1e-6 + 1 # Loop until difference between low # and high become less than EPS while((high - low) > eps): # mid1 and mid2 are representative x # co-ordiantes of search space mid1 = low + (high - low) / 3 mid2 = high - (high - low) / 3 dist1 = self.compute(p n l mid1) dist2 = self.compute(p n l mid2) # If mid2 point gives more total # distance skip third part if (dist1 < dist2): high = mid2 # If mid1 point gives more total # distance skip first part else: low = mid1 # Compute optimum distance cost by # sending average of low and high as X return self.compute(p n l (low + high) / 2) # Method to find optimum cost def find_Optimum_cost(self p l): n = len(p) p_arr = [None] * n # Converting 2D array input to point array for i in range(n): p_obj = self.Point(p[i][0] p[i][1]) p_arr[i] = p_obj return self.find_Optimum_cost_untill(p_arr n l) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': obj = Optimum_distance() l = obj.Line(1 -1 -3) p = [ [ -3 -2 ] [ -1 0 ] [ -1 2 ] [ 1 2 ] [ 3 4 ] ] print(obj.find_Optimum_cost(p l)) # This code is contributed by Sulu_mufi
// C# program to find optimum location // and total cost using System; class GFG { static double sq(double x) { return ((x) * (x)); } static int EPS = (int)(1e-6) + 1; static int N = 5; // structure defining a point public class point { public int x y; public point() {} public point(int x int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } }; // structure defining a line // of ax + by + c = 0 form public class line { public int a b c; public line(int a int b int c) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; } }; // method to get distance of // point (x y) from point p static double dist(double x double y point p) { return Math.Sqrt(sq(x - p.x) + sq(y - p.y)); } /* Utility method to compute total distance of all points when choose point on given line has x-coordinate value as X */ static double compute(point[] p int n line l double X) { double res = 0; // calculating Y of chosen point // by line equation double Y = -1 * (l.c + l.a * X) / l.b; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) res += dist(X Y p[i]); return res; } // Utility method to find minimum total distance static double findOptimumCostUtil(point[] p int n line l) { double low = -1e6; double high = 1e6; // loop until difference between // low and high become less than EPS while ((high - low) > EPS) { // mid1 and mid2 are representative // x co-ordiantes of search space double mid1 = low + (high - low) / 3; double mid2 = high - (high - low) / 3; double dist1 = compute(p n l mid1); double dist2 = compute(p n l mid2); // if mid2 point gives more total distance // skip third part if (dist1 < dist2) high = mid2; // if mid1 point gives more total distance // skip first part else low = mid1; } // compute optimum distance cost by // sending average of low and high as X return compute(p n l (low + high) / 2); } // method to find optimum cost static double findOptimumCost(int[ ] points line l) { point[] p = new point[N]; // converting 2D array input to point array for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) p[i] = new point(points[i 0] points[i 1]); return findOptimumCostUtil(p N l); } // Driver Code public static void Main(String[] args) { line l = new line(1 -1 -3); int[ ] points = { { -3 -2 } { -1 0 } { -1 2 } { 1 2 } { 3 4 } }; Console.WriteLine(findOptimumCost(points l)); } } // This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
<script> // A JavaScript program to find optimum location // and total cost function sq(x) { return x*x; } let EPS = (1e-6) + 1; let N = 5; // structure defining a point class point { constructor(xy) { this.x=x; this.y=y; } } // structure defining a line of ax + by + c = 0 form class line { constructor(abc) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; } } // method to get distance of point (x y) from point p function dist(xyp) { return Math.sqrt(sq(x - p.x) + sq(y - p.y)); } /* Utility method to compute total distance all points when choose point on given line has x-coordinate value as X */ function compute(pnlX) { let res = 0; // calculating Y of chosen point by line equation let Y = -1 * (l.c + l.a * X) / l.b; for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) res += dist(X Y p[i]); return res; } // Utility method to find minimum total distance function findOptimumCostUtil(pnl) { let low = -1e6; let high = 1e6; // loop until difference between low and high // become less than EPS while ((high - low) > EPS) { // mid1 and mid2 are representative x // co-ordiantes of search space let mid1 = low + (high - low) / 3; let mid2 = high - (high - low) / 3; let dist1 = compute(p n l mid1); let dist2 = compute(p n l mid2); // if mid2 point gives more total distance // skip third part if (dist1 < dist2) high = mid2; // if mid1 point gives more total distance // skip first part else low = mid1; } // compute optimum distance cost by sending average // of low and high as X return compute(p n l (low + high) / 2); } // method to find optimum cost function findOptimumCost(pointsl) { let p = new Array(N); // converting 2D array input to point array for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) p[i] = new point(points[i][0] points[i][1]); return findOptimumCostUtil(p N l); } // Driver Code let l = new line(1 -1 -3); let points= [[ -3 -2 ] [ -1 0 ] [ -1 2 ] [ 1 2 ] [ 3 4 ]]; document.write(findOptimumCost(points l)); // This code is contributed by rag2127 </script>
Wyjście
20.7652
Złożoność czasowa: NA2)
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: NA)
