Różnica między dwoma zestawami w Pythonie jest równa różnicy między liczbą elementów w dwóch zestawach. Funkcja różnica() zwraca zbiór będący różnicą pomiędzy dwoma zbiorami. Spróbujmy dowiedzieć się, jaka będzie różnica między dwoma zbiorami A i B. Wtedy (zbiór A – zbiór B) będą elementami obecnymi w zbiorze A, ale nie w B i (zbiór B – zbiór A) będą elementami obecnymi w zestawie B, ale nie w zestawie A.
Przykład:
set A = {10, 20, 30, 40, 80} set B = {100, 30, 80, 40, 60} set A - set B = {10, 20} set B - set A = {100, 60} Explanation: A - B is equal to the elements present in A but not in B B - A is equal to the elements present in B but not in A> Spójrzmy na diagram Venna następującej funkcji zbioru różnicowego. 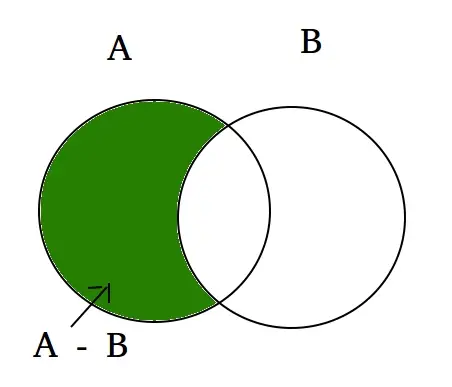 Składnia:
Składnia:
set_A.difference(set_B) for (A - B) set_B.difference(set_A) for (B - A)>
W tym programie spróbujemy znaleźć różnicę między dwoma zbiorami set_A i set_B, w obie strony:
Python3
# Python code to get the difference between two sets> # using difference() between set A and set B> # Driver Code> A>=> {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40>,>80>}> B>=> {>100>,>30>,>80>,>40>,>60>}> print> (A.difference(B))> print> (B.difference(A))> |
mapa drzewa
>
>Wyjście:
{10, 20} {100, 60}> Możemy również użyć operatora –, aby znaleźć różnicę między dwoma zbiorami.
Python3
# Python code to get the difference between two sets> # using difference() between set A and set B> # Driver Code> A>=> {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40>,>80>}> B>=> {>100>,>30>,>80>,>40>,>60>}> print> (A>-> B)> print> (B>-> A)> |
kwartały w roku
>
>Wyjście:
{10, 20} {100, 60}> Jeśli mamy równe zestawy, zwróci zestaw zerowy.
Python3
waga kat timpf
# Python code to get the difference between two sets> # using difference() between set A and set B> # Driver Code> A>=> {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40>,>80>}> B>=> {>10>,>20>,>30>,>40>,>80>,>100>}> print> (A>-> B)> |
>
>Wyjście:
set()>
