Możemy stworzyć program Java do sortowania elementów tablicy za pomocą sortowania przez wybór. W algorytmie sortowania przez selekcję wyszukujemy najniższy element i ustawiamy go w odpowiednim miejscu. Zamieniamy bieżący element na kolejny najniższy numer.
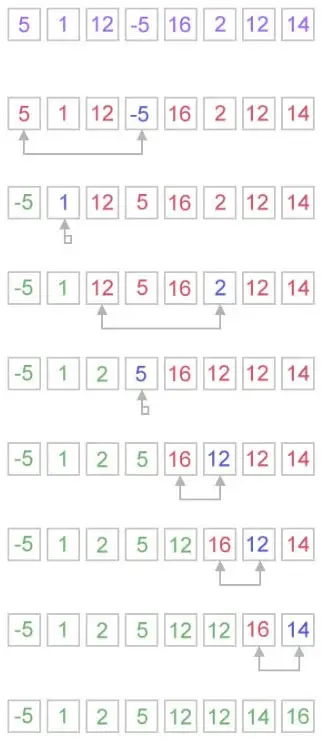
Jak działa sortowanie przez wybór?
Algorytm sortowania przez wybór działa w bardzo prosty sposób. Utrzymuje dwie podtablice dla danej tablicy.
kolejka i kolejka priorytetowa w Javie
- Podtablica jest już posortowana.
- Druga podtablica jest nieposortowana.
Przy każdej iteracji sortowania przez wybór element jest wybierany z nieposortowanej podtablicy i przenoszony do posortowanej podtablicy.
jak pobierać muzykę
arr[] = 25 35 45 12 65 10 // Find the minimum element in arr[0...5] and place it at beginning. 10 25 35 45 12 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[1...5] and place it at beginning of arr[1...5] 10 12 25 35 45 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[2...5] and place it at beginning of arr[2...5] No, you can see that the array is already sorted. 10 12 25 35 45 65
Złożoność czasu
To, co najlepsze: ?(n^2)Przeciętny: ?(n^2)
Najgorszy: O(n^2)
Złożoność przestrzeni
O(1)Przykład sortowania przez wybór w języku Java
public class SelectionSortExample { public static void selectionSort(int[] arr){ for (int i = 0; i <arr.length - 1; i++) { int index="i;" for (int j="i" + < arr.length; j++){ if (arr[j] arr[index]){ lowest } smallernumber="arr[index];" arr[index]="arr[i];" arr[i]="smallerNumber;" public static void main(string a[]){ int[] arr1="{9,14,3,2,43,11,58,22};" system.out.println('before selection sort'); for(int i:arr1){ system.out.print(i+' '); system.out.println(); selectionsort(arr1); sorting array using sort system.out.println('after pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Before Selection Sort 9 14 3 2 43 11 58 22 After Selection Sort 2 3 9 11 14 22 43 58 </pre> <h2>Selection Sort in Java (Another way)</h2> <p>You can also use a method where array is not predefined. Here, user has to put the elements as input.</p> <p>In the following Java program, we ask user to enter the array elements or number, now compare the array's element and start swapping with the variable temp. Put the first element in the temp and the second element in the first, and then temp in the second number and continue for the next match to sort the whole array in ascending order.</p> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print('sorting array using selection sort technique..
'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print('now the after sorting is :
'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ ' '); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;></pre></arr.length> Sortowanie przez wybór w Javie (inny sposób)
Można także użyć metody, w której tablica nie jest predefiniowana. Tutaj użytkownik musi umieścić elementy jako dane wejściowe.
W poniższym programie Java prosimy użytkownika o wprowadzenie elementów tablicy lub liczby, następnie porównaj element tablicy i rozpocznij zamianę ze zmienną temp. Umieść pierwszy element w temp, drugi element w pierwszym, a następnie temp w drugiej liczbie i kontynuuj do następnego dopasowania, aby posortować całą tablicę w kolejności rosnącej.
import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print(\'sorting array using selection sort technique..
\'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print(\'now the after sorting is :
\'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ \' \'); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;>