Biorąc pod uwagę zbiór miast i odległość między każdą parą miast, problemem jest znalezienie najkrótszej możliwej wycieczki, która odwiedzi każde miasto dokładnie raz i wróci do punktu początkowego.
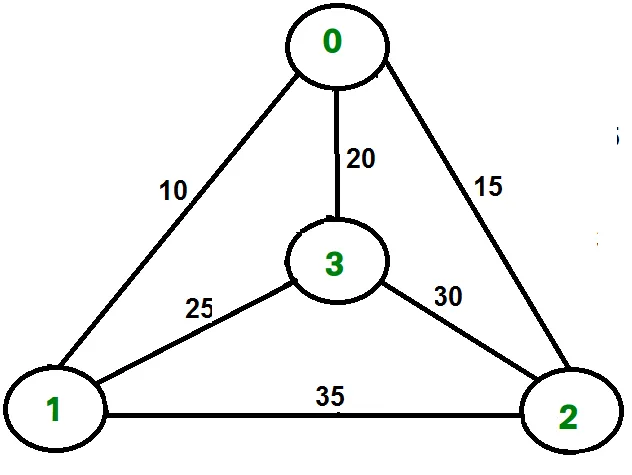
Rozważmy na przykład wykres pokazany na rysunku po prawej stronie. Trasa TSP na wykresie to 0-1-3-2-0. Koszt wycieczki to 10+25+30+15 czyli 80.
Omówiliśmy następujące rozwiązania
1) Programowanie naiwne i dynamiczne
2) Przybliżone rozwiązanie przy użyciu MST
Rozwiązanie rozgałęzione i powiązane
Jak widać w poprzednich artykułach w metodzie Branch and Bound dla bieżącego węzła w drzewie, obliczamy granicę najlepszego możliwego rozwiązania, jakie możemy uzyskać, jeśli opuścimy ten węzeł. Jeśli samo ograniczenie najlepszego możliwego rozwiązania jest gorsze od bieżącego najlepszego (najlepiej obliczonego do tej pory), wówczas ignorujemy poddrzewo zakorzenione w węźle.
Należy pamiętać, że koszt przez węzeł obejmuje dwa koszty.
1) Koszt dotarcia do węzła od korzenia (kiedy dotrzemy do węzła, obliczamy ten koszt)
2) Koszt dotarcia odpowiedzi z bieżącego węzła do liścia (obliczamy granicę tego kosztu, aby zdecydować, czy ignorować poddrzewo z tym węzłem, czy nie).
- W przypadkach A problem maksymalizacji górna granica mówi nam o maksymalnym możliwym rozwiązaniu, jeśli podążamy za danym węzłem. Na przykład w W przypadku plecaka 0/1 zastosowaliśmy podejście Greedy, aby znaleźć górną granicę .
- W przypadkach A problem minimalizacji dolna granica mówi nam o minimalnym możliwym rozwiązaniu, jeśli podążamy za danym węzłem. Na przykład w Problem z przydziałem pracy dolną granicę uzyskujemy, przypisując pracownikowi najtańszą pracę.
W przypadku gałęzi i wiązania wyzwaniem jest znalezienie sposobu obliczenia granicy najlepszego możliwego rozwiązania. Poniżej znajduje się pomysł zastosowany do obliczenia granic dla problemu komiwojażera.
Koszt dowolnej wycieczki można zapisać jak poniżej.
Cost of a tour T = (1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two edges adjacent to u and in the tour T) where u ? V For every vertex u if we consider two edges through it in T and sum their costs. The overall sum for all vertices would be twice of cost of tour T (We have considered every edge twice.) (Sum of two tour edges adjacent to u) >= (sum of minimum weight two edges adjacent to u) Cost of any tour >= 1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two minimum weight edges adjacent to u) where u ? V
Rozważmy na przykład powyższy wykres. Poniżej przedstawiono minimalny koszt dwóch krawędzi sąsiadujących z każdym węzłem.
Node Least cost edges Total cost 0 (0 1) (0 2) 25 1 (0 1) (1 3) 35 2 (0 2) (2 3) 45 3 (0 3) (1 3) 45 Thus a lower bound on the cost of any tour = 1/2(25 + 35 + 45 + 45) = 75 Refer this for one more example.
Teraz mamy pomysł na obliczenie dolnej granicy. Zobaczmy, jak zastosować drzewo przeszukiwania przestrzeni stanów. Zaczynamy wyliczać wszystkie możliwe węzły (najlepiej w porządku leksykograficznym)
1. Węzeł główny: Bez utraty ogólności zakładamy, że zaczynamy od wierzchołka „0”, dla którego powyżej obliczono dolną granicę.
Radzenie sobie z poziomem 2: Następny poziom wylicza wszystkie możliwe wierzchołki, do których możemy dojść (pamiętając, że na każdej ścieżce wierzchołek musi wystąpić tylko raz), które wynoszą 1 2 3... n (Zauważ, że graf jest kompletny). Rozważmy, że obliczamy dla wierzchołka 1. Ponieważ przeszliśmy od 0 do 1, nasza wycieczka uwzględnia teraz krawędź 0-1. Dzięki temu możemy dokonać niezbędnych zmian w dolnej granicy pierwiastka.
Lower Bound for vertex 1 = Old lower bound - ((minimum edge cost of 0 + minimum edge cost of 1) / 2) + (edge cost 0-1)
Jak to działa? Aby uwzględnić krawędź 0-1, dodajemy koszt krawędzi 0-1 i odejmujemy wagę krawędzi w taki sposób, aby dolna granica pozostała jak najściślejsza, co byłoby sumą minimalnych krawędzi 0 i 1 podzieloną przez 2. Oczywiście odjęta krawędź nie może być mniejsza niż ta.
Radzenie sobie z innymi poziomami: Przechodząc do następnego poziomu, ponownie wyliczamy wszystkie możliwe wierzchołki. W powyższym przypadku idąc dalej po 1 sprawdzamy 2 3 4 ...n.
Rozważ dolną granicę dla 2, gdy przechodziliśmy od 1 do 1. Dołączamy krawędź 1-2 do trasy i zmieniamy nową dolną granicę dla tego węzła.
Lower bound(2) = Old lower bound - ((second minimum edge cost of 1 + minimum edge cost of 2)/2) + edge cost 1-2)
Uwaga: Jedyna zmiana we wzorze polega na tym, że tym razem uwzględniliśmy drugi minimalny koszt krawędzi za 1, ponieważ minimalny koszt krawędzi został już odjęty na poprzednim poziomie.
// C++ program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. #include
// Java program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. import java.util.*; class GFG { static int N = 4; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int final_path[] = new int[N + 1]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static boolean visited[] = new boolean[N]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal(int curr_path[]) { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) final_path[i] = curr_path[i]; final_path[N] = curr_path[0]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin(int adj[][] int i) { int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) if (adj[i][k] < min && i != k) min = adj[i][k]; return min; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin(int adj[][] int i) { int first = Integer.MAX_VALUE second = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int j=0; j<N; j++) { if (i == j) continue; if (adj[i][j] <= first) { second = first; first = adj[i][j]; } else if (adj[i][j] <= second && adj[i][j] != first) second = adj[i][j]; } return second; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec(int adj[][] int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int curr_path[]) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if (level == N) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if (adj[curr_path[level - 1]][curr_path[0]] != 0) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj[curr_path[level-1]][curr_path[0]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if (curr_res < final_res) { copyToFinal(curr_path); final_res = curr_res; } } return; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if (adj[curr_path[level-1]][i] != 0 && visited[i] == false) { int temp = curr_bound; curr_weight += adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if (level==1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if (curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res) { curr_path[level] = i; visited[i] = true; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec(adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj[curr_path[level-1]][i]; curr_bound = temp; // Also reset the visited array Arrays.fill(visitedfalse); for (int j = 0; j <= level - 1; j++) visited[curr_path[j]] = true; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP(int adj[][]) { int curr_path[] = new int[N + 1]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0; Arrays.fill(curr_path -1); Arrays.fill(visited false); // Compute initial bound for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) curr_bound += (firstMin(adj i) + secondMin(adj i)); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = (curr_bound==1)? curr_bound/2 + 1 : curr_bound/2; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited[0] = true; curr_path[0] = 0; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec(adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { //Adjacency matrix for the given graph int adj[][] = {{0 10 15 20} {10 0 35 25} {15 35 0 30} {20 25 30 0} }; TSP(adj); System.out.printf('Minimum cost : %dn' final_res); System.out.printf('Path Taken : '); for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) { System.out.printf('%d ' final_path[i]); } } } /* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
# Python3 program to solve # Traveling Salesman Problem using # Branch and Bound. import math maxsize = float('inf') # Function to copy temporary solution # to the final solution def copyToFinal(curr_path): final_path[:N + 1] = curr_path[:] final_path[N] = curr_path[0] # Function to find the minimum edge cost # having an end at the vertex i def firstMin(adj i): min = maxsize for k in range(N): if adj[i][k] < min and i != k: min = adj[i][k] return min # function to find the second minimum edge # cost having an end at the vertex i def secondMin(adj i): first second = maxsize maxsize for j in range(N): if i == j: continue if adj[i][j] <= first: second = first first = adj[i][j] elif(adj[i][j] <= second and adj[i][j] != first): second = adj[i][j] return second # function that takes as arguments: # curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node # curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far # level-> current level while moving # in the search space tree # curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored # which would later be copied to final_path[] def TSPRec(adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path visited): global final_res # base case is when we have reached level N # which means we have covered all the nodes once if level == N: # check if there is an edge from # last vertex in path back to the first vertex if adj[curr_path[level - 1]][curr_path[0]] != 0: # curr_res has the total weight # of the solution we got curr_res = curr_weight + adj[curr_path[level - 1]] [curr_path[0]] if curr_res < final_res: copyToFinal(curr_path) final_res = curr_res return # for any other level iterate for all vertices # to build the search space tree recursively for i in range(N): # Consider next vertex if it is not same # (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and # not visited already) if (adj[curr_path[level-1]][i] != 0 and visited[i] == False): temp = curr_bound curr_weight += adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i] # different computation of curr_bound # for level 2 from the other levels if level == 1: curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i)) / 2) else: curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i)) / 2) # curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound # for the node that we have arrived on. # If current lower bound < final_res # we need to explore the node further if curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res: curr_path[level] = i visited[i] = True # call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec(adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path visited) # Else we have to prune the node by resetting # all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i] curr_bound = temp # Also reset the visited array visited = [False] * len(visited) for j in range(level): if curr_path[j] != -1: visited[curr_path[j]] = True # This function sets up final_path def TSP(adj): # Calculate initial lower bound for the root node # using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + # second min) for all edges. Also initialize the # curr_path and visited array curr_bound = 0 curr_path = [-1] * (N + 1) visited = [False] * N # Compute initial bound for i in range(N): curr_bound += (firstMin(adj i) + secondMin(adj i)) # Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = math.ceil(curr_bound / 2) # We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex # in curr_path[] is 0 visited[0] = True curr_path[0] = 0 # Call to TSPRec for curr_weight # equal to 0 and level 1 TSPRec(adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path visited) # Driver code # Adjacency matrix for the given graph adj = [[0 10 15 20] [10 0 35 25] [15 35 0 30] [20 25 30 0]] N = 4 # final_path[] stores the final solution # i.e. the // path of the salesman. final_path = [None] * (N + 1) # visited[] keeps track of the already # visited nodes in a particular path visited = [False] * N # Stores the final minimum weight # of shortest tour. final_res = maxsize TSP(adj) print('Minimum cost :' final_res) print('Path Taken : ' end = ' ') for i in range(N + 1): print(final_path[i] end = ' ') # This code is contributed by ng24_7
// C# program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. using System; public class GFG { static int N = 4; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int[] final_path = new int[N + 1]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static bool[] visited = new bool[N]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Int32.MaxValue; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal(int[] curr_path) { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) final_path[i] = curr_path[i]; final_path[N] = curr_path[0]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin(int[ ] adj int i) { int min = Int32.MaxValue; for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) if (adj[i k] < min && i != k) min = adj[i k]; return min; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin(int[ ] adj int i) { int first = Int32.MaxValue second = Int32.MaxValue; for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) { if (i == j) continue; if (adj[i j] <= first) { second = first; first = adj[i j]; } else if (adj[i j] <= second && adj[i j] != first) second = adj[i j]; } return second; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored // which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec(int[ ] adj int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int[] curr_path) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if (level == N) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if (adj[curr_path[level - 1] curr_path[0]] != 0) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj[curr_path[level - 1] curr_path[0]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if (curr_res < final_res) { copyToFinal(curr_path); final_res = curr_res; } } return; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same // (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and not // visited already) if (adj[curr_path[level - 1] i] != 0 && visited[i] == false) { int temp = curr_bound; curr_weight += adj[curr_path[level - 1] i]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if (level == 1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i)) / 2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i)) / 2); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual // lower bound for the node that we have // arrived on If current lower bound < // final_res we need to explore the node // further if (curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res) { curr_path[level] = i; visited[i] = true; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec(adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path); } // Else we have to prune the node by // resetting all changes to curr_weight and // curr_bound curr_weight -= adj[curr_path[level - 1] i]; curr_bound = temp; // Also reset the visited array Array.Fill(visited false); for (int j = 0; j <= level - 1; j++) visited[curr_path[j]] = true; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP(int[ ] adj) { int[] curr_path = new int[N + 1]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0; Array.Fill(curr_path -1); Array.Fill(visited false); // Compute initial bound for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) curr_bound += (firstMin(adj i) + secondMin(adj i)); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = (curr_bound == 1) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited[0] = true; curr_path[0] = 0; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec(adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path); } // Driver code static public void Main() { // Adjacency matrix for the given graph int[ ] adj = { { 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP(adj); Console.WriteLine('Minimum cost : ' + final_res); Console.Write('Path Taken : '); for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) { Console.Write(final_path[i] + ' '); } } } // This code is contributed by Rohit Pradhan
const N = 4; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. let final_path = Array (N + 1).fill (-1); // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path let visited = Array (N).fill (false); // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. let final_res = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution function copyToFinal (curr_path){ for (let i = 0; i < N; i++){ final_path[i] = curr_path[i]; } final_path[N] = curr_path[0]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function firstMin (adj i){ let min = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; for (let k = 0; k < N; k++){ if (adj[i][k] < min && i !== k){ min = adj[i][k]; } } return min; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function secondMin (adj i){ let first = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; let second = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; for (let j = 0; j < N; j++){ if (i == j){ continue; } if (adj[i][j] <= first){ second = first; first = adj[i][j]; } else if (adj[i][j] <= second && adj[i][j] !== first){ second = adj[i][j]; } } return second; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] function TSPRec (adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if (level == N) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if (adj[curr_path[level - 1]][curr_path[0]] !== 0) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got let curr_res = curr_weight + adj[curr_path[level - 1]][curr_path[0]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if (curr_res < final_res) { copyToFinal (curr_path); final_res = curr_res; } } return; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for (let i = 0; i < N; i++){ // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if (adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i] !== 0 && !visited[i]){ let temp = curr_bound; curr_weight += adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if (level == 1){ curr_bound -= (firstMin (adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin (adj i)) / 2; } else { curr_bound -= (secondMin (adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin (adj i)) / 2; } // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if (curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res){ curr_path[level] = i; visited[i] = true; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec (adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i]; curr_bound = temp; // Also reset the visited array visited.fill (false) for (var j = 0; j <= level - 1; j++) visited[curr_path[j]] = true; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] function TSP (adj) { let curr_path = Array (N + 1).fill (-1); // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array let curr_bound = 0; visited.fill (false); // compute initial bound for (let i = 0; i < N; i++){ curr_bound += firstMin (adj i) + secondMin (adj i); } // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = curr_bound == 1 ? (curr_bound / 2) + 1 : (curr_bound / 2); // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited[0] = true; curr_path[0] = 0; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec (adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path); } //Adjacency matrix for the given graph let adj =[[0 10 15 20] [10 0 35 25] [15 35 0 30] [20 25 30 0]]; TSP (adj); console.log (`Minimum cost:${final_res}`); console.log (`Path Taken:${final_path.join (' ')}`); // This code is contributed by anskalyan3.
Wyjście :
Minimum cost : 80 Path Taken : 0 1 3 2 0
Zaokrąglanie odbywa się w następującym wierszu kodu:
if (level==1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2);
W algorytmie Branch and Bound TSP obliczamy dolną granicę całkowitego kosztu rozwiązania optymalnego, dodając minimalne koszty krawędzi dla każdego wierzchołka, a następnie dzieląc przez dwa. Jednakże ta dolna granica nie może być liczbą całkowitą. Aby uzyskać dolną granicę liczby całkowitej, możemy zastosować zaokrąglenie.
W powyższym kodzie zmienna curr_bound utrzymuje bieżącą dolną granicę całkowitego kosztu optymalnego rozwiązania. Kiedy odwiedzamy nowy wierzchołek na poziomie poziomu, obliczamy nową dolną granicę new_bound, biorąc sumę minimalnych kosztów krawędzi dla nowego wierzchołka i jego dwóch najbliższych sąsiadów. Następnie aktualizujemy zmienną curr_bound, zaokrąglając new_bound do najbliższej liczby całkowitej.
Jeśli poziom wynosi 1, zaokrąglamy w dół do najbliższej liczby całkowitej. Dzieje się tak dlatego, że do tej pory odwiedziliśmy tylko jeden wierzchołek i chcemy zachować ostrożność w szacunkach całkowitego kosztu optymalnego rozwiązania. Jeśli poziom jest większy niż 1, stosujemy bardziej agresywną strategię zaokrąglania, która uwzględnia fakt, że odwiedziliśmy już pewne wierzchołki i dzięki temu możemy dokładniej oszacować całkowity koszt optymalnego rozwiązania.
Złożoność czasowa: W najgorszym przypadku złożoność Branch and Bound pozostaje taka sama jak w przypadku Brute Force, ponieważ w najgorszym przypadku możemy nigdy nie mieć szansy na przycięcie węzła. Podczas gdy w praktyce działa bardzo dobrze w zależności od innej instancji TSP. Złożoność zależy również od wyboru funkcji ograniczającej, ponieważ to ona decyduje, ile węzłów należy przyciąć.
Referencje:
http://lcm.csa.iisc.ernet.in/dsa/node187.html
