Biorąc pod uwagę A podwójnie połączona lista z pismo zadaniem jest sprawdzenie, czy podwójnie połączona lista jest a palindrom lub nie.
Przykłady:
Wejście:
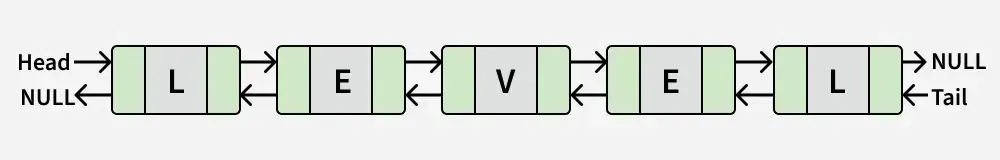
Wyjście: PRAWDA
Wyjaśnienie: Lista odpowiada „LEVEL”, który jest palindromem.
Wejście:
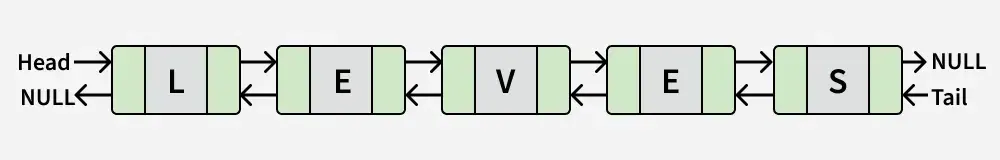
Wyjście: FAŁSZ
Wyjaśnienie: Lista odpowiada „LEVES”, który nie jest palindromem.
Zbliżać się:
Pomysł polega na zainicjowaniu dwóch wskaźników: lewy (początkowo ustawiony na głowę) i Prawidłowy (początkowo ustawiony na ogon). Porównaj wartości dwóch wskaźników while lewy nie jest równe null lub lewy przeniósł się do następnego Prawidłowy. Jeśli wartości dwóch wskaźników wynoszą równy przenosić lewy do następnego wskaźnika i Prawidłowy do poprzedniego wskaźnika. W przeciwnym razie zwróć wartość false.
Poniżej implementacja powyższego podejścia:
C++// C++ program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. #include
// C program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. #include
// Java program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. class Node { char data; Node prev next; Node(char x) { data = x; prev = null; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function that returns true if the // doubly linked list is a palindrome static boolean isPalindrome(Node head) { if (head == null) return true; // Find the tail ptr. Node left = head right = head; while (right.next != null) { right = right.next; } // Check if the doubly linked list is // a palindrome. while (left != right && left.prev != right) { // If char mismatch return // false. if (left.data != right.data) return false; // Move the pointers left = left.next; right = right.prev; } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Doubly Linked list: // L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L Node head = new Node('L'); head.next = new Node('E'); head.next.prev = head; head.next.next = new Node('V'); head.next.next.prev = head.next; head.next.next.next = new Node('E'); head.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next = new Node('L'); head.next.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next.next; if (isPalindrome(head)) System.out.println('True'); else System.out.println('False'); } }
# Python program to check if a doubly # linked list is palindrome. class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.prev = None self.next = None # Function that returns true if the # doubly linked list is a palindrome def isPalindrome(head): if head is None: return True # Find the tail ptr. left = head right = head while right.next is not None: right = right.next # Check if the doubly linked list is # a palindrome. while left != right and left.prev != right: # If char mismatch return # false. if left.data != right.data: return False # Move the pointers left = left.next right = right.prev return True if __name__ == '__main__': # Doubly Linked list: # L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L head = Node('L') head.next = Node('E') head.next.prev = head head.next.next = Node('V') head.next.next.prev = head.next head.next.next.next = Node('E') head.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next head.next.next.next.next = Node('L') head.next.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next.next if isPalindrome(head): print('True') else: print('False')
// C# program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. using System; class Node { public char data; public Node prev next; public Node(char x) { data = x; prev = null; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function that returns true if the // doubly linked list is a palindrome static bool isPalindrome(Node head) { if (head == null) return true; // Find the tail ptr. Node left = head right = head; while (right.next != null) { right = right.next; } // Check if the doubly linked list is // a palindrome. while (left != right && left.prev != right) { // If char mismatch return // false. if (left.data != right.data) return false; // Move the pointers left = left.next; right = right.prev; } return true; } static void Main(string[] args) { // Doubly Linked list: // L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L Node head = new Node('L'); head.next = new Node('E'); head.next.prev = head; head.next.next = new Node('V'); head.next.next.prev = head.next; head.next.next.next = new Node('E'); head.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next = new Node('L'); head.next.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next.next; if (isPalindrome(head)) Console.WriteLine('True'); else Console.WriteLine('False'); } }
// JavaScript program to check if a doubly // linked list is palindrome. class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.prev = null; this.next = null; } } // Function that returns true if the // doubly linked list is a palindrome function isPalindrome(head) { if (head === null) return true; // Find the tail ptr. let left = head right = head; while (right.next !== null) { right = right.next; } // Check if the doubly linked list is // a palindrome. while (left !== right && left.prev !== right) { // If char mismatch return // false. if (left.data !== right.data) return false; // Move the pointers left = left.next; right = right.prev; } return true; } // Doubly Linked list: // L <-> E <-> V <-> E <-> L let head = new Node('L'); head.next = new Node('E'); head.next.prev = head; head.next.next = new Node('V'); head.next.next.prev = head.next; head.next.next.next = new Node('E'); head.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next = new Node('L'); head.next.next.next.next.prev = head.next.next.next; if (isPalindrome(head)) console.log('True'); else console.log('False');
Wyjście
True
Złożoność czasowa: O(n) gdzie n jest liczbą węzłów na podwójnie połączonej liście.
Przestrzeń pomocnicza: O(1)
Powiązane artykuły:
- Funkcja sprawdzająca, czy pojedynczo połączona lista jest palindromem
- Sprawdź, czy połączona lista ciągów tworzy palindrom


