Język programowania R to język programowania typu open source, który jest szeroko stosowany jako oprogramowanie statystyczne i narzędzie do analizy danych. Ramki danych w języku R to ogólne obiekty danych języka R, które służą do przechowywania danych tabelarycznych.
Ramki danych można również interpretować jako macierze, w których każda kolumna a matryca mogą mieć różne typy danych. R DataFrame składa się z trzech głównych komponentów: danych, wierszy i kolumn.
Struktura ramek danych R
Jak widać na poniższym obrazku, tak zbudowana jest ramka danych.
Dane prezentowane są w formie tabelarycznej, co ułatwia obsługę i zrozumienie.
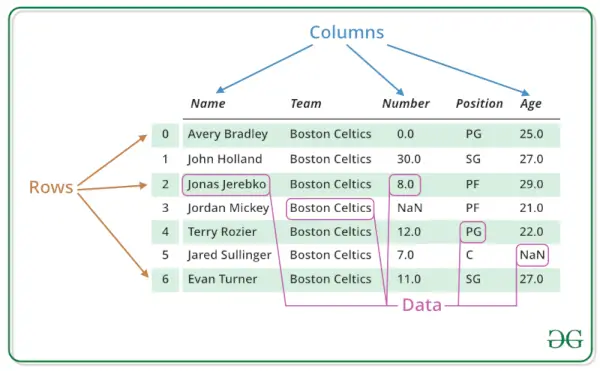
R – Ramki danych
Utwórz ramkę danych w języku programowania R
Aby utworzyć ramkę danych R, użyj ramka danych() funkcję, a następnie przekaż każdy z utworzonych wektorów jako argumenty funkcji.
R
# R program to create dataframe> # creating a data frame> friend.data <->data.frame>(> >friend_id =>c>(1:5),> >friend_name =>c>(>'Sachin'>,>'Sourav'>,> >'Dravid'>,>'Sehwag'>,> >'Dhoni'>),> >stringsAsFactors =>FALSE> )> # print the data frame> print>(friend.data)> |
>
>
Wyjście:
friend_id friend_name 1 1 Sachin 2 2 Sourav 3 3 Dravid 4 4 Sehwag 5 5 Dhoni>
Uzyskaj strukturę ramki danych R
Można uzyskać strukturę ramki danych R za pomocą str() funkcja w R.
Może wyświetlać nawet wewnętrzną strukturę dużych list, które są zagnieżdżone. Zapewnia jednowierszowe wyjście dla podstawowych obiektów R, informując użytkownika o obiekcie i jego składnikach.
R
stałe Java
# R program to get the> # structure of the data frame> # creating a data frame> friend.data <->data.frame>(> >friend_id =>c>(1:5),> >friend_name =>c>(>'Sachin'>,>'Sourav'>,> >'Dravid'>,>'Sehwag'>,> >'Dhoni'>),> >stringsAsFactors =>FALSE> )> # using str()> print>(>str>(friend.data))> |
>
>
Wyjście:
'data.frame': 5 obs. of 2 variables: $ friend_id : int 1 2 3 4 5 $ friend_name: chr 'Sachin' 'Sourav' 'Dravid' 'Sehwag' ... NULL>
Podsumowanie danych w ramce danych R
W ramce danych R podsumowanie statystyczne i charakter danych można uzyskać poprzez zastosowanie streszczenie() funkcjonować.
Jest to funkcja ogólna używana do tworzenia podsumowań wyników różnych funkcji dopasowania modelu. Funkcja wywołuje określone metody, które zależą od klasy pierwszego argumentu.
R
# R program to get the> # summary of the data frame> # creating a data frame> friend.data <->data.frame>(> >friend_id =>c>(1:5),> >friend_name =>c>(>'Sachin'>,>'Sourav'>,> >'Dravid'>,>'Sehwag'>,> >'Dhoni'>),> >stringsAsFactors =>FALSE> )> # using summary()> print>(>summary>(friend.data))> |
>
>
Wyjście:
friend_id friend_name Min. :1 Length:5 1st Qu.:2 Class :character Median :3 Mode :character Mean :3 3rd Qu.:4 Max. :5>
Wyodrębnij dane z ramki danych w R
Wyodrębnianie danych z ramki danych R oznacza dostęp do jej wierszy lub kolumn. Można wyodrębnić określoną kolumnę z ramki danych R, używając jej nazwy kolumny.
R
# R program to extract> # data from the data frame> # creating a data frame> friend.data <->data.frame>(> >friend_id =>c>(1:5),> >friend_name =>c>(>'Sachin'>,>'Sourav'>,> >'Dravid'>,>'Sehwag'>,> >'Dhoni'>),> >stringsAsFactors =>FALSE> )> # Extracting friend_name column> result <->data.frame>(friend.data$friend_name)> print>(result)> |
>
>
Wyjście:
friend.data.friend_name 1 Sachin 2 Sourav 3 Dravid 4 Sehwag 5 Dhoni>
Rozwiń ramkę danych w języku R
Ramkę danych w R można rozszerzyć, dodając nowe kolumny i wiersze do już istniejącej ramki danych R.
R
# R program to expand> # the data frame> # creating a data frame> friend.data <->data.frame>(> >friend_id =>c>(1:5),> >friend_name =>c>(>'Sachin'>,>'Sourav'>,> >'Dravid'>,>'Sehwag'>,> >'Dhoni'>),> >stringsAsFactors =>FALSE> )> # Expanding data frame> friend.data$location <->c>(>'Kolkata'>,>'Delhi'>,> >'Bangalore'>,>'Hyderabad'>,> >'Chennai'>)> resultant <- friend.data> # print the modified data frame> print>(resultant)> |
>
>
Wyjście:
friend_id friend_name location 1 1 Sachin Kolkata 2 2 Sourav Delhi 3 3 Dravid Bangalore 4 4 Sehwag Hyderabad 5 5 Dhoni Chennai>
W R można wykonywać różne rodzaje operacji na ramce danych, np uzyskiwanie dostępu do wierszy i kolumn, wybieranie podzbioru ramki danych, edycja ramek danych, usuwanie wierszy i kolumn w ramce danych itp.
Należy zapoznać się Operacje na ramkach danych w R wiedzieć o wszystkich typach operacji, które można wykonać na ramce danych.
Uzyskaj dostęp do elementów w ramce danych R
Możemy wybrać i uzyskać dostęp do dowolnego elementu z ramki danych za pomocą single$>,nawiasy[ ] or>podwójne nawiasy[[]]>aby uzyskać dostęp do kolumn z ramki danych.
R
# creating a data frame> friend.data <->data.frame>(> >friend_id =>c>(1:5),> >friend_name =>c>(>'Sachin'>,>'Sourav'>,> >'Dravid'>,>'Sehwag'>,> >'Dhoni'>),> >stringsAsFactors =>FALSE> )> # Access Items using []> friend.data[1]> # Access Items using [[]]> friend.data[[>'friend_name'>]]> # Access Items using $> friend.data$friend_id> |
>
>
Wyjście:
friend_id 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 Access Items using [[]] [1] 'Sachin' 'Sourav' 'Dravid' 'Sehwag' 'Dhoni' Access Items using $ [1] 1 2 3 4 5>
Liczba wierszy i kolumn
Możemy dowiedzieć się, ile wierszy i kolumn analizuje nasza ramka danych, używając funkcji dim.
R
nieokreślone nachylenie
# creating a data frame> friend.data <->data.frame>(> >friend_id =>c>(1:5),> >friend_name =>c>(>'Sachin'>,>'Sourav'>,> >'Dravid'>,>'Sehwag'>,> >'Dhoni'>),> >stringsAsFactors =>FALSE> )> # find out the number of rows and clumns> dim>(friend.data)> |
>
>
Wyjście:
[1] 5 2>
Dodaj wiersze i kolumny w ramce danych R
Możesz łatwo dodawać wiersze i kolumny w ramce danych R. Wstawianie pomaga w rozbudowie już istniejącej ramki DataFrame, bez konieczności tworzenia nowej.
Przyjrzyjmy się, jak dodać wiersze i kolumny w ramce DataFrame? z przykładem:
Dodaj wiersze w ramce danych R
Aby dodać wiersze w ramce danych, możesz użyć wbudowanej funkcji rbind().
Poniższy przykład demonstruje działanie rbind() w ramce danych R.
R
# Creating a dataframe representing products in a store> Products <->data.frame>(> >Product_ID =>c>(101, 102, 103),> >Product_Name =>c>(>'T-Shirt'>,>'Jeans'>,>'Shoes'>),> >Price =>c>(15.99, 29.99, 49.99),> >Stock =>c>(50, 30, 25)> )> # Print the existing dataframe> cat>(>'Existing dataframe (Products):
'>)> print>(Products)> # Adding a new row for a new product> New_Product <->c>(104,>'Sunglasses'>, 39.99, 40)> Products <->rbind>(Products, New_Product)> # Print the updated dataframe after adding the new product> cat>(>'
Updated dataframe after adding a new product:
'>)> print>(Products)> |
>
>
Wyjście:
Existing dataframe (Products): Product_ID Product_Name Price Stock 1 101 T-Shirt 15.99 50 2 102 Jeans 29.99 30 3 103 Shoes 49.99 25 Updated dataframe after adding a new product: Product_ID Product_Name Price Stock 1 101 T-Shirt 15.99 50 2 102 Jeans 29.99 30 3 103 Shoes 49.99 25 4 104 Sunglasses 39.99 40>
Dodaj kolumny w ramce danych R
Aby dodać kolumny w ramce danych, możesz skorzystać z wbudowanej funkcji cbind().
Poniższy przykład demonstruje działanie cbind() w ramce danych R .
R
śnieg kontra lód
# Existing dataframe representing products in a store> Products <->data.frame>(> >Product_ID =>c>(101, 102, 103),> >Product_Name =>c>(>'T-Shirt'>,>'Jeans'>,>'Shoes'>),> >Price =>c>(15.99, 29.99, 49.99),> >Stock =>c>(50, 30, 25)> )> # Print the existing dataframe> cat>(>'Existing dataframe (Products):
'>)> print>(Products)> # Adding a new column for 'Discount' to the dataframe> Discount <->c>(5, 10, 8)># New column values for discount> Products <->cbind>(Products, Discount)> # Rename the added column> colnames>(Products)[>ncol>(Products)] <->'Discount'> # Renaming the last column> # Print the updated dataframe after adding the new column> cat>(>'
Updated dataframe after adding a new column 'Discount':
'>)> print>(Products)> |
>
>
Wyjście:
Existing dataframe (Products): Product_ID Product_Name Price Stock 1 101 T-Shirt 15.99 50 2 102 Jeans 29.99 30 3 103 Shoes 49.99 25 Updated dataframe after adding a new column 'Discount': Product_ID Product_Name Price Stock Discount 1 101 T-Shirt 15.99 50 5 2 102 Jeans 29.99 30 10 3 103 Shoes 49.99 25 8>
Usuń wiersze i kolumny
Ramka danych w R usuwa kolumny i wiersze z już istniejącej ramki danych R.
Usuń wiersz w ramce danych R
R
library>(dplyr)> # Create a data frame> data <->data.frame>(> >friend_id =>c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5),> >friend_name =>c>(>'Sachin'>,>'Sourav'>,>'Dravid'>,>'Sehwag'>,>'Dhoni'>),> >location =>c>(>'Kolkata'>,>'Delhi'>,>'Bangalore'>,>'Hyderabad'>,>'Chennai'>)> )> data> # Remove a row with friend_id = 3> data <->subset>(data, friend_id != 3)> data> |
>
>
Wyjście:
friend_id friend_name location 1 1 Sachin Kolkata 2 2 Sourav Delhi 3 3 Dravid Bangalore 4 4 Sehwag Hyderabad 5 5 Dhoni Chennai # Remove a row with friend_id = 3 friend_id friend_name location 1 1 Sachin Kolkata 2 2 Sourav Delhi 4 4 Sehwag Hyderabad 5 5 Dhoni Chennai>
W powyższym kodzie najpierw utworzyliśmy ramkę danych o nazwie dane z trzema kolumnami: identyfikator_znajomego , imię przyjaciela , I Lokalizacja . Aby usunąć wiersz za pomocą identyfikator_znajomego równe 3, użyliśmy podzbiór() funkcję i określił warunek id_znajomego != 3 . Spowodowało to usunięcie wiersza z identyfikator_znajomego równy 3.
Usuń kolumnę w ramce danych R
R
library>(dplyr)> # Create a data frame> data <->data.frame>(> >friend_id =>c>(1, 2, 3, 4, 5),> >friend_name =>c>(>'Sachin'>,>'Sourav'>,>'Dravid'>,>'Sehwag'>,>'Dhoni'>),> >location =>c>(>'Kolkata'>,>'Delhi'>,>'Bangalore'>,>'Hyderabad'>,>'Chennai'>)> )> data> # Remove the 'location' column> data <->select>(data, -location)> data> |
>
>
Wyjście:
friend_id friend_name location 1 1 Sachin Kolkata 2 2 Sourav Delhi 3 3 Dravid Bangalore 4 4 Sehwag Hyderabad 5 5 Dhoni Chennai>Usuń kolumnę 'lokalizacja' id_znajomego nazwa_znajomego 1 1 Sachin 2 2 Sourav 3 3 Dravid 4 4 Sehwag 5 5 Dhoni>
Aby usunąć Lokalizacja kolumnę, użyliśmy wybierać() funkcja i określone -Lokalizacja . The – znak wskazuje, że chcemy usunąć Lokalizacja kolumna. Wynikowa ramka danych dane będzie miał tylko dwie kolumny: identyfikator_znajomego I imię przyjaciela .
Łączenie ramek danych w R
Istnieją 2 sposoby łączenia ramek danych w R. Można je łączyć w pionie lub w poziomie.
Spójrzmy na oba przypadki na przykładzie:
Połącz ramkę danych R w pionie
Jeśli chcesz połączyć 2 ramki danych w pionie, możesz użyć funkcja rbind(). Ta funkcja działa w przypadku kombinacji dwóch lub więcej ramek danych.
R
# Creating two sample dataframes> df1 <->data.frame>(> >Name =>c>(>'Alice'>,>'Bob'>),> >Age =>c>(25, 30),> >Score =>c>(80, 75)> )> df2 <->data.frame>(> >Name =>c>(>'Charlie'>,>'David'>),> >Age =>c>(28, 35),> >Score =>c>(90, 85)> )> # Print the existing dataframes> cat>(>'Dataframe 1:
'>)> print>(df1)> cat>(>'
Dataframe 2:
'>)> print>(df2)> # Combining the dataframes using rbind()> combined_df <->rbind>(df1, df2)> # Print the combined dataframe> cat>(>'
Combined Dataframe:
'>)> print>(combined_df)> |
>
>
Wyjście:
Dataframe 1: Name Age Score 1 Alice 25 80 2 Bob 30 75 Dataframe 2: Name Age Score 1 Charlie 28 90 2 David 35 85 Combined Dataframe: Name Age Score 1 Alice 25 80 2 Bob 30 75 3 Charlie 28 90 4 David 35 85>
Połącz ramkę danych R poziomo:
Jeśli chcesz połączyć 2 ramki danych w poziomie, możesz użyć funkcja cbind(). Ta funkcja działa w przypadku kombinacji dwóch lub więcej ramek danych.
R
wydrukuj tablicę w Javie
# Creating two sample dataframes> df1 <->data.frame>(> >Name =>c>(>'Alice'>,>'Bob'>),> >Age =>c>(25, 30),> >Score =>c>(80, 75)> )> df2 <->data.frame>(> >Height =>c>(160, 175),> >Weight =>c>(55, 70)> )> # Print the existing dataframes> cat>(>'Dataframe 1:
'>)> print>(df1)> cat>(>'
Dataframe 2:
'>)> print>(df2)> # Combining the dataframes using cbind()> combined_df <->cbind>(df1, df2)> # Print the combined dataframe> cat>(>'
Combined Dataframe:
'>)> print>(combined_df)> |
>
>
Wyjście:
Dataframe 1: Name Age Score 1 Alice 25 80 2 Bob 30 75 Dataframe 2: Height Weight 1 160 55 2 175 70 Combined Dataframe: Name Age Score Height Weight 1 Alice 25 80 160 55 2 Bob 30 75 175 70>
Przeczytaj także:
- R – Przedmioty
- Struktury danych w programowaniu w języku R
W tym artykule omówiliśmy Ramki danych R, oraz wszystkie podstawowe operacje, takie jak tworzenie, dostęp, podsumowanie, dodawanie i usuwanie. Celem tego artykułu jest zapoznanie Cię z ramkami danych w R, abyś mógł używać ich w swoich projektach.
Mam nadzieję, że pomoże Ci to w zrozumieniu koncepcji ramek danych w R i będziesz mógł łatwo zaimplementować ramki danych R w swoich projektach.
